Chmod Give All Permissions

Linux Permissions An Introduction To Chmod Enable Sysadmin

Introduction To Linux File Permissions Attributes Chmod Globo Tech

Workbook 4 File Ownerships And Permissions Ppt Video Online Download

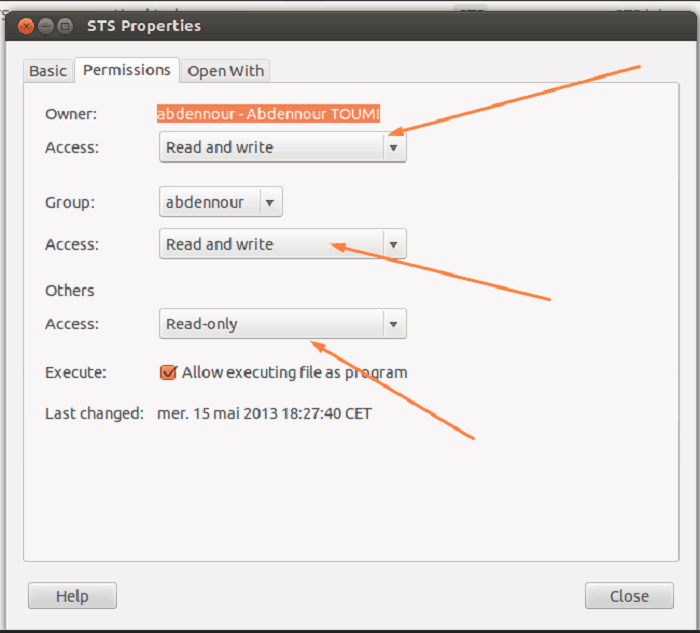
Give Permissions In Ubuntu Itechzo Give Permissions In Ubuntu

Change Ownership And Rights To Files And Folders In Linux Smashing Lab

Linux Chmod Command Tutorial With Examples To Change Permission Of Files And Folders Poftut
Chmod Command in Linux Linux File Permission Introduction to Linux File Permission.

Chmod give all permissions. Add other options as desired;. Recursively) for owner, and removes write permission for group and others chmod ug=rw groupAgreements.txt:. To give the User group read and write permission, you would add up 4+2 to get 6.
Chmod -R u+w,go-w docs:. Let us understand the Permission system on Linux. Using chmod 777 <file-name> gives everyone rwx permissions, and it is generally not a good practice to give full powers to all the users in a system.
Chmod -R MODE DIRECTORY. Mode can be either a symbolic representation of changes to make, or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new. Chmod is a command to change permission of a file.
We’ll wrap up with a bit of extra advice related to chmod:. This would grant all users and user groups with read and write access to your file, as well as allow all users to execute the file. Chmod -R will change all the permissions of each file and folder under a specified directory at once.
If you need to list a file's permissions, use the ls command. Chmod permission file_name There are two ways to define permission:. The second case, I will leave you guys to figure out.
This permission give you the authority to open and read a file. The numerical equivalent is now:. For example, if you enter:.
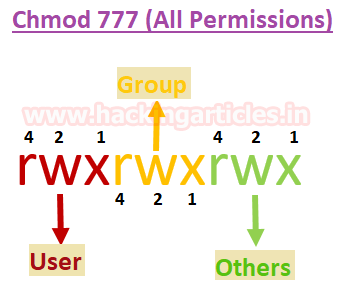
Actually, chmod Command in Linux plays a greater role to keep all the files and directories of the system safe and secure so that no unauthorized person. Mode can be specified with octal numbers or with letters. So if you want to give all permissions (rwx) to a user, we need to add read (4), write (2), and execute (1).
The all (a) mode is the same as ugo, allowing the previous command to be expressed as:. + for adding and – for removing. No such file or directory.
Adds write permission to the directory docs and all its contents (i.e. As you can see, we start by first specifying the group permission group by utilizing the g letter. Chmod is command which changes permission of a file or folder for particular user or group as per instructions provided.
If you want to set permissions on all files to a+r, and all directories to a+x, and do that recursively through the complete subdirectory tree, use:. Correspondingly, users have a username (unique to each user). User, group or all.
Here are the other combinations you can have:. Mykyta Dolmatov / Getty Images. The second way to modify permissions with the chmod command is to use a number to specify each set of permissions for the file.
Each shell script must have the execute permission. The chmod command (change mode) is a shell command in Linux. Therefore, full permissions for everyone on the system would look like:.
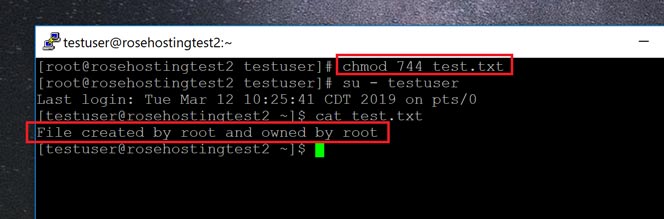
The chmod command, like other commands, can be executed from the command line or through a script file. That’s why we enter 744. To modify the permission flags on existing files and directories, use the chmod command ("change mode").
Avoid using boundary cases, such as chmod 777 <file-name> and chmod 000 <filename>. Chmod a=r foldername to give only read permission for everyone. Chmod 700 filename You can do the same in symbolic mode.
For a directory, whoever has `read'. To give the owner all permissions and world execute you would type chmod 701 filename. Here are some examples of how to use the chmod command in numeric mode:.
Changing permissions with chmod. A = all + = add permissions - = remove permissions r = read w = write x = execute t = sticky bit so to add read permissiones for people in the files group I would do chmod g+r file. Accessing files in the Linux root file system from Linux Any files created, modified, or accessed in the Linux root file system follow standard Linux conventions, such as applying the umask to a newly created file.
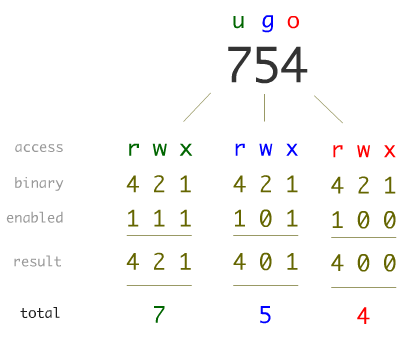
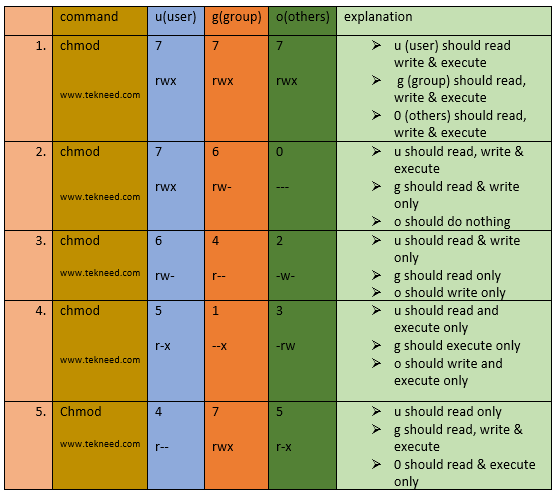
The permissions control the actions that can be performed on the file or directory. The absolute mode functions like the exclusive permission of the symbolic mode in that it exclusively sets the permission specified removing all other. Both the codes give read (code=4) permission to user, write and execute (code=3) for group and read and execute (code=5) for others.
111 numerical value will grant execute permissions to user (owner), group and others to specified file. To give the owner all permissions and world read and execute you would type chmod 705 filename. There are three sets of permissions.
The modes include permissions and special modes. You only want Others to have read permissions, so they get 4. Chmod changes the permissions of each given file according to mode, where mode describes the permissions to modify.
View (u)ser, (g)roup and (o)thers permissions for chmod 644 (chmod a+rwx,u-x,g-wx,o-wx) or use free online chmod calculator to modify permissions easily. So, if you want to give a file 664 permissions, you’d issue the chmod command like this:. I checked permissions and it's in root.
Chmod Modifies File Permissions. It can be used for individual files or it can be run recursively with the -R option to change permissions for all of the subdirectories and files within a directory. Sudo chmod 777 filename = I don't know the file name;.
Sets read and write permissions for user and Group:. Chmod 111 techtutorial Execute permissions to all. To change directory permissions for everyone, use “u” for users, “g” for group, “o” for others, and “ugo” or “a” (for all).
For example, to explicitly make file3 readable and executable to everyone:. If no options are specified, chmod modifies the permissions of the file specified by file name to the permissions specified by permissions. For help, see List the files in a directory in Unix.
The other way is terminal , where you can change the permission via Chmod. It can change file system modes of files and directories. The chmod command specifies which class or classes (user, group, other) have access to the.
Breaking this down, the a means all and rwx means set read, write, and execute. By setting permissions, you are replacing all existing permissions with the ones specified. It stands for change mode.
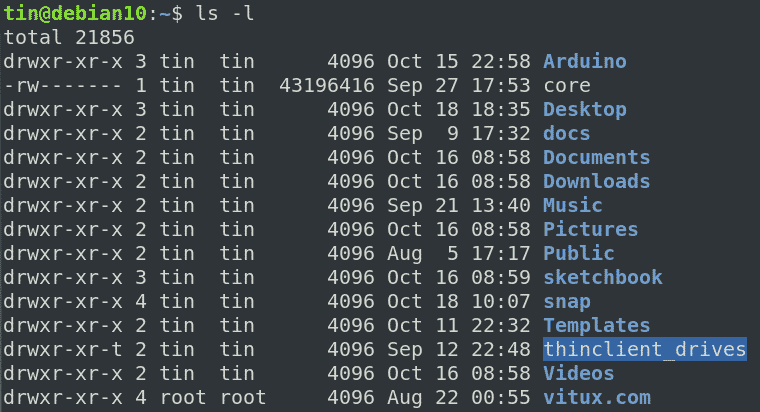
The default umask is 022, or in other words it allows all permissions except write permissions to groups and others. To determine the mode (or permission settings) of a particular file, use the command `ls -lg filename'. User - What the owner of the file can do.
Using chmod with Absolute Permissions. Recursive chmod using find, pipemill, and sudo To assign reasonably secure permissions to files and folders/directories, it's common to give files a permission of 644, and directories a 755 permission, since chmod -R assigns to both. As all Linux users, you will at some point need to modify the permission settings of a file/directory.
By - Linux tutorial - team. Server$ chmod go-rwx file.txt The file named script.cgi is now executable by the user and group. I'm hoping if I change the permissions to non-root, it will let me add files.
If you provide same permissions to directory you can enter into directory but you can’t do anything, directory execute permissions means providing the access to enter into directory. To remove the write permission for others for file2:. In each group, the first character is for read access ( r ), followed by write access ( w) and the right to execute ( x ).
In the following example, g is group bit, o is the 'other users' bit and the -sign is removing all permissions (rwx):. Therefore, rwx is equal to 7. The general syntax to recursively change the file’s permissions is as follows:.
Chmod 775 /path/to/file chmod command uses & Explanation. The chmod command allows you to change the permissions of files using symbolic or numeric mode. The command that executes such tasks is the chmod command.
Give the file’s owner read and write permissions and only read permissions to group members and all other users:. For our example command, we are going to give the group permission group, read and write privileges on a file called readandwrite. # Permission rwx Binary;.
CHMOD Calculator Chmod 644. The chmod command changes the access permissions of files and folders. Chmod +x filename.sh to make filename.sh executable.
Group - What users of the same group can do. I put in the random numbers/ letters assigned to it, but get error:. For example, to use chmod to set permissions of file "filename" to -rwxrwxrwx you could run:.
Using letters is easier to understand for most people. If chmod a+w filename, chmod +w filename and chmod ugo+w filename are alternative to each other then why not just use +w – Ravi Sevta Mar 10 '18 at 13:04. For example, if you want the owner to have all the permissions and no permissions for the group and public, you need to set the permission 700 in absolute mode:.
View (u)ser, (g)roup and (o)thers permissions for chmod 766 (chmod a+rwx,g-x,o-x) or use free online chmod calculator to modify permissions easily. If you use chmod 777 that means you assigned all the permissions i.e. The = means that permissions are to be set to exactly what we specify.(i.e.
You can combine multiple references and modes to set the desired access all at once. Use u for user, g for group, o for other, and a for all. Sets read and write permissions for user and Group, and provides read.
Chmod -R a+rX * click below button to copy the code. I think that is it, there might be some other options as well, consult the man page. How to Change Groups of Files and Directories in Linux.
We overwrite the current permissions). Chmod ugo+rwx foldername to give read, write, and execute to everyone. A dash means that the permission is turned off.
In Linux, files and directories are treated similarly. For the Group, you need the same permissions, so they get the same number. So chmod 744 script.sh would give us the exact same permissions that we just observed on script.sh:-rwxr–r– Where the user has all permissions ( read, write, execute), and the group and other both only have read permissions.
To give permissions to all users, use chmod a+w testfile.txt. And even this… chmod 775 file_name chmod ug+rwx,o=rx file_name Both the commands give all permissions (code=7) to user and group, read and execute (code=5) for others. Read permission on a directory gives you the ability to lists its content.
To recursively operate on all files and directories under a given directory, use the chmod command with the -R, (--recursive) option. With great power comes great responsibility, and there’s no denying that the chmod command is an extensive and powerful tool to change file permissions on Mac. One set for the owner of the file, another set for the members of the file’s group, and a final set for everyone else.
– Jaken551 Mar 10 '18 at 13:00. Use sudo, the find command, and a pipemill to chmod as in the following examples. After user level we have provide what needs to be done i.e.
Linux File Permission :. A Few Additional chmod Tips. Chmod command is followed by which level user i.e.
Remember, the owner’s permissions always come first, then followed by group and others. Permissions defines the permissions for the owner of the file (the "user"), members of the group who owns the file (the "group"), and anyone else ("others"). The basic syntax is:.
$ chmod 777 -R /path/to/Dir To assign reasonably secure permissions to files and folders/directories, it's common to give files a permission of 644 , and directories a 755 permission, using the find command and a pipe we can target just files. Give the file’s owner read, write and execute permissions, read and execute permissions to group members. In Linux, who can do what to a file or directory is controlled through sets of permissions.
Read, write and execute:. My sd card in my usb card reader will not allow me to add files while in ext4. The permission scheme described above also applies to directories.
Linux file permission is a very important aspects in terms of security issues for the system administrator of Linux Operating System. To view the permissions for all files in a directory, use the lscommand with the -laoptions. To make file readable, writable and executable by everyone.
Meanwhile, since group and others are only allowed to read the file, we give them 4. Each permission is assigned a value, as the following table shows, and the total of each set of permissions provides a number for that set. Remember that you need read permissions in order to list directories and subdirectories.
You can set all files in a folder or directory to writeable with chmod -R 775 directory. Other - What anyone else can do. How to Set File Permissions Using `chmod' Files.

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders

Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command Nixcraft

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

Chmod Umask Stat Fileperms And File Permissions

Chmod Ftp File Permissions Stadtaus Com

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command In Linux

Csc128 Permissions And Links Chmod And Ls

Linux Chmod Example Linux Hint

How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials

Directory How Can I Change Permissions Of A Folder Including Its Enclosed Files And Subdirectories Ask Ubuntu

Explained How To Use Chmod Command Complete Guide Youtube

Use Of Chmod Command In Linux Devopsdex
Linux Privilege Escalation Using Suid Binaries
How To Deny File Permissions To Everyone Except Yourself In Linux Linuxhostsupport

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight
.png)
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example

Chmod Wikipedia

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight

How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux
Linux Chmod Tips

Ownership And Permissions

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier
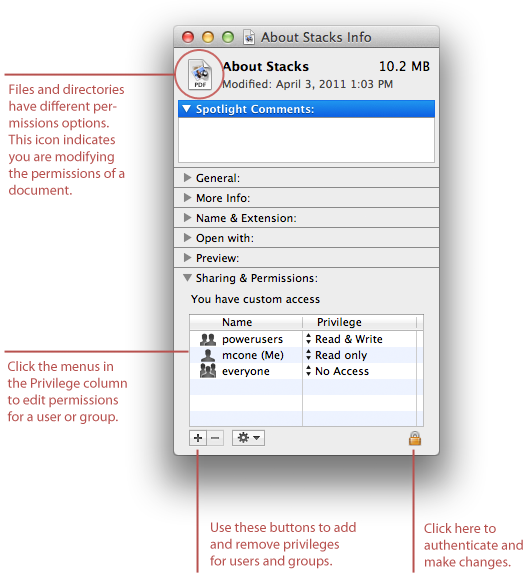
How To Set File Permissions In Mac Os X Macinstruct

What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux Tech Ninja Pro
Chmod Chown Wsl Improvements Windows Command Line

How To Change Permissions And Owners Via Linux Command Line

Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

Linux Chmod Chown Syntax And Chmod Chown Examples

Change File And Folder Permission On Ubuntu Chmod Chown Command In Linux Youtube

Linux File Permissions Tutorial For Beginners

How To Give Read Write Permissions To A Folder In Ubuntu Code Example

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier

Chmod Ftp File Permissions Stadtaus Com

Setting File And Directory Permissions Computational And Information Systems Laboratory

Changing File Permissions In Linux The Chmod Command By Saswat Subhajyoti Mallick Medium
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq1nsq3kxri7ryrifobs2rfobawbv4hezfw9 Ldf4feblahyn09 Usqp Cau

Understand Linux File Permissions Using Chmod And Chown Commands Programming Tips For Versatile Coders

Unix File Permissions Computer Science

8 Linux Chmod Command Examples To Understand It The Linux Juggernaut

Linux Permissions Pluralsight

How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux

Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions

How To Set File Permissions In Mac Os X Macinstruct

An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

Linux Commands 5 File Permission Chmod Youtube
Chmod Command In Unix Unix File Permissions Chmod With Examples Chwn Command Chgrp Command Unmask

Software Carpentry

Changing File Permissions Wordpress Org

Understanding Linux File Permissions With Chmod Umask Chown And Chgrp Liquidon Net
What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux Tech Ninja Pro

Linux Chmod Chown Syntax And Chmod Chown Examples

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected

Linux Chmod Command Tutorial With Examples To Change Permission Of Files And Folders Poftut
/i7guGwCYcn-34e068e148ae4e918b29c86cd2d5740e.png)
Configuring Unix Linux File And Directory Access Rights

Linux Users And Groups Linode

Chmod Cheatsheet Linux

Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

Give Write Access Chmod 775
Change File Permissions Recursively Linux Linux Hint

Linux File Permission Javatpoint

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

Permissions Assignment Owner Can Change Others Can Only Read Automated Hands On Cloudxlab

Give Write Access Chmod Unix
How To Set And Manage File Permission In Linux Part 1
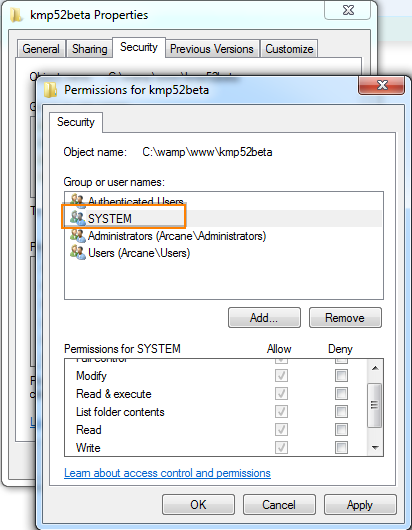
Setup Correct Files And Folders Access Permissions Efficiently Web Site Scripts Com

Chmod Why It Matters User Permissions In Os X Droppedframe Com

Setup Correct Files And Folders Access Permissions Efficiently Web Site Scripts Com

Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod
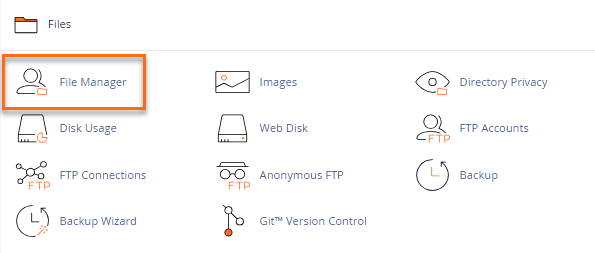
How To Change Permissions Chmod Of A File Hostgator Support

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission
Q Tbn 3aand9gcqylo Axq4l Wudkigbim4eyyuri1sgeprxwkotr9pe74bpl6ic Usqp Cau

Understanding File Permissions

Chmod Command In Linux File Permissions Linuxize

How Do Linux File Permissions Work

Solved Chmod Can Be Used To Change The Mode Of The File Chegg Com

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

Use Of Chmod Command In Linux Devopsdex

Chmod Wiki Ask Ubuntu

How To Modify The File S And Directories Permission In Linux Vasanth Blog

How To Change File Permissions Using The Terminal Chriswrites Com

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux
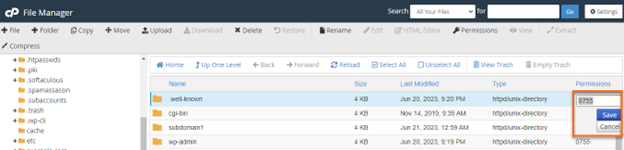
How To Change Permissions Chmod Of A File Hostgator Support
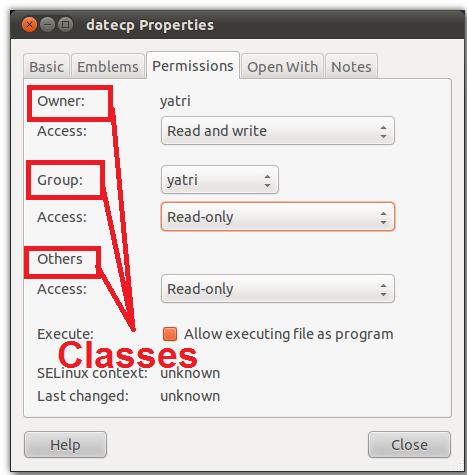
What Is Chmod 777

Linux Unix Permissions And Attributes Linuxsecrets

Linux Terminal File Permissions Chmod Chown And Chgrp Youtube



