Chmod Give All Permissions To Directory

Solved 1 Using The Touch Mkdir Chmod Command Create T Chegg Com

Linux Unix Permissions And Attributes Linuxsecrets

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

Command Line Change Folder Permissions And Ownership Ask Ubuntu

Linux Users And Groups Linode
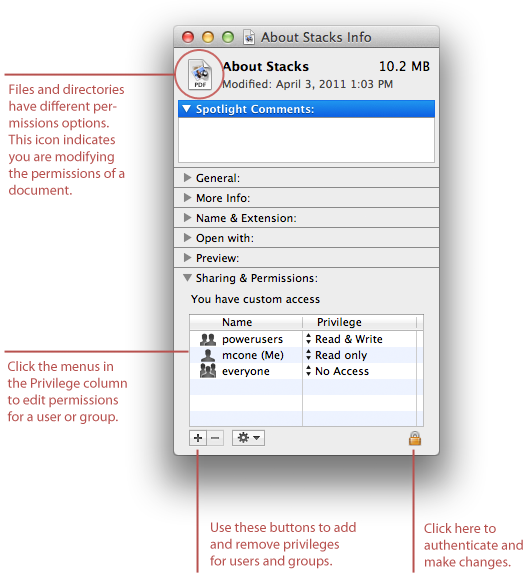
How To Set File Permissions In Mac Os X Macinstruct
This permission give you the authority to open and read a file.

Chmod give all permissions to directory. The chmod command, like other commands, can be executed from the command line or through a script file. How to Change Groups of Files and Directories in Linux. $ chmod -R 0755 directoryNameHere However, if you need to apply conditional file permissions recursively, you need to use combination of the find and chmod command.
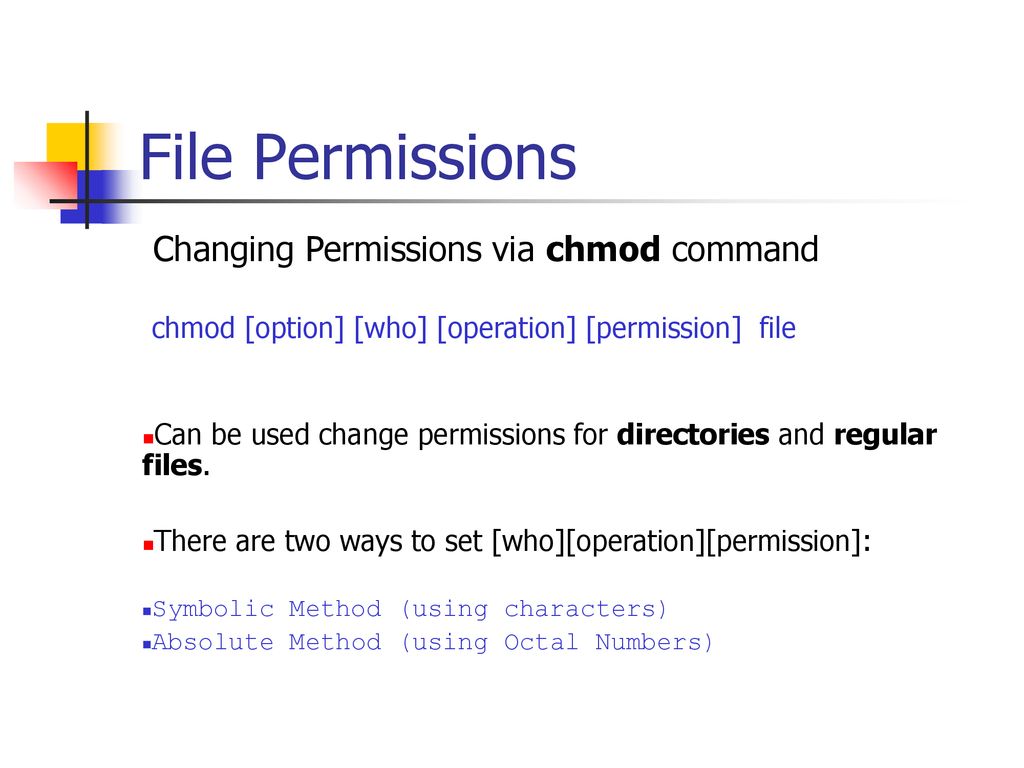
The chmod command allows you to change the permissions of files using symbolic or numeric mode. To change the file or the directory permissions, you use the chmod (change mode) command. If you provide same permissions to directory you can enter into directory but you can’t do anything, directory execute permissions means providing the access to enter into directory.
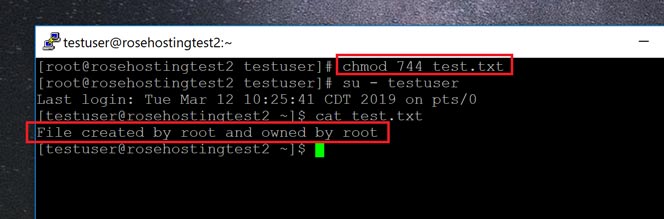
$ chmod 777 file.txt (or) $ chmod ugo+rwx file.txt Give execute privilege to user. How To Change File Permissions In Linux Using ‘chmod’ Command. The chmod command is used to alter file and directory.
However sometimes, you may want to give separate permissions to files and directories. Therefore, Joe can access any file, of which he knows the name, in Fred's home directory. To change directory permissions for everyone, use “u” for users, “g” for group, “o” for others, and “ugo” or “a” (for all).
You can also use the letters r, w, and x to set read, write, and execute permissions and the letters u, g, o, and a to specify user, group, other or all:. + for adding and – for removing. Chmod +x or chmod a+x:.
$ find /home/user/demo -type f -print. Every file and directory in your UNIX/Linux system has following 3 permissions defined for all the 3 owners discussed above. Changing permissions with chmod.
The symbolic method and the absolute form. Once again, we use 'group' and 'other' but we use '+' to allow the execute ('x') permission. Sets read and write permissions for user and Group:.
Save yourself the effort with the – R switch. Do not give full permissions. In this example, you are setting permission to 0755:.
Chmod command is followed by which level user i.e. Let's say the directory chmod_directory was created with the default permissions of 755. You can set all files in a folder or directory to writeable with chmod -R 775 directory.
We can use two ways of calling chmod , symbolic or octal notation. When chmod with –R is used to apply permission in a directory, it assigns the same permission to all the files and subdirectories under it. Neither command is difficult to use.
Therefore, when setting permissions, you are assigning them for yourself, "your group" and "everyone else" in the world. After user level we have provide what needs to be done i.e. If you want to set permissions on all files to a+r, and all directories to a+x, and do that recursively through the complete subdirectory tree, use:.
The highly productive Linux system offers various levels of permission to ensure that the user has enough ways to interact with files and directories. Chmod -R a+rX * click below button to copy the code. File access permissions can be modified via the chmod command.
Chmod 111 techtutorial Execute permissions to all. There are two ways to represent the MODE:. To have combination of permissions, add required numbers.
User can read, write, and execute;. The chmod command changes the access permissions of files and folders. N Description ls binary 0 No permissions at all --- 000 1 Only execute --x 001 2 Only write -w- 010 3 Write and execute -wx 011 4 Only read r-- 100 5 Read and execute r-x 101 6 Read.
Let us understand the Permission system on Linux. However, incorrect permissions often cause hard-to-diagnose issues. In Linux, who can do what to a file or directory is controlled through sets of permissions.
It can be used for individual files or it can be run recursively with the -R option to change permissions for all of the subdirectories and files within a directory. Chmod is command which changes permission of a file or folder for particular user or group as per instructions provided. This command changes the mode of Fred's home directory (represented by the ~), giving permission to all users to get to files in that directory.
Chmod -R u+w,go-w docs:. Use sudo, the find command, and a pipemill to chmod as in the following examples. The owner of a file can also add or subtract permissions for himor herself.
One set for the owner of the file, another set for the members of the file’s group, and a final set for everyone else. Execution for everyone Probably one of the most used case of chmod is to give a file the execution bit. Executing a directory doesn't really make sense, so think of this as a traverse permission.
Chmod permission file_name There are two ways to define permission:. Chmod -R will change all the permissions of each file and folder under a specified directory at once. Group members and other users can read and execute, but cannot write.
Group can read only;. Numeric Method # The syntax of the chmod command when using numeric method has the following format:. Changing File Permissions - Chmod.
For each path name operand that names a directory, chmod will change the file mode bits of the directory and all files in the file hierarchy under it. The permissions control the actions that can be performed on the file or directory. We’ll wrap up with a bit of extra advice related to chmod:.
3 chmod Examples Give read, write and execute to everybody (user, group, and others) read, write and execute = 4 + 2 + 1 = 7. I tested this setting up some dummy directories under my '~' directory and verified it worked. They give you fine-grained control over who can read, write, and execute files.
The command takes the general form:. Others can read only". % chmod u+rw who.out.
Cp original/original file new directory/new file 1. - umask value 644 :. Chmod 777 is considered potentially dangerous because you are giving read, write and execute permission on a file/directory to everyone (who is on your system).
Without them, it would be impossible to safely host multiple users’ websites and data. To remove all existing permissions, set read and write access for the user while allowing read access for all other users, type:. If you need to list a file's permissions, use the ls command.
To modify the permission flags on existing files and directories, use the chmod command ("change mode"). Using symbolic modes (letters to indicate the categories and permission). You would simply substitute the directory name for the file name.
Unlike files, a directory has files in it. Sets read and write permissions for user and Group, and provides read. Chmod -R 755 myfiles.
A user must have execute access to the bin directory in order to execute the ls or the cd command. To set file permissions, you’ll use the chmodcommand at the terminal. Setting permissions for a directory follows exactly the same procedure;.
The chmod command is used to change the various permission bits of a file or directory. Give read, write and execute permission to the file’s owner, read permissions to the file’s group and no permissions to all other users:. If set on the group read permission, it sets the setgid bit.
If you specify the -h flag, the chmod command prevents this mode change. The chown and chgrp commands may also be used with an asterisk (*) to change the permissions or group of all files in a directory. To recursively operate on all files and directories under a given directory, use the chmod command with the -R, (--recursive) option.
The general syntax to recursively change the file’s permissions is as follows:. File permissions are one of your server’s most important security features. At the Unix prompt, Fred should type.
Chmod -R MODE DIRECTORY. When it comes to using the ls and chmod commands, practice makes perfect. You should totally avoid it.
Chmod -R 0777 MinimalDbaseExample/ Following this procedure exactly, grants the folder MinimalDbaseExample/ and all files and subdirectories therein 0777/drwxrwxrwx permissions. Read permission is given the value 4, write permission the value 2 and execute permission 1. Add the file’s owner permissions to the permissions that the members of the file’s group have:.
Mykyta Dolmatov / Getty Images. The basic syntax is:. The name speaks for itself.
There are two ways to use chmod — the. To find all files in /home/user/demo directory, enter:. 111 numerical value will grant execute permissions to user (owner), group and others to specified file.
The name chmod is short for “change mode”. Sudo chmod -R 755 /www/store Each number have meaning in permission. The chmod command specifies which class or classes (user, group, other) have access to the.
Recursively (-R) Change the permissions of the directory myfiles, and all folders and files it contains, to mode 755:. If you want to change all the permissions inside a directory, you can change them for every file by hand — which can take a very long time. The symbolic permissions of the files and folders in your home directory are displayed, as shown below.
This indicates the setuid/setgid permission. Default permission 022 :. There are three sets of permissions.
For example, type cd /www to change to the /www directory. # umask 022 # umask 0022 # The umask value is subtracted from the default permissions (666) to give the final permission. Others have read permissions represented by the last bits:.
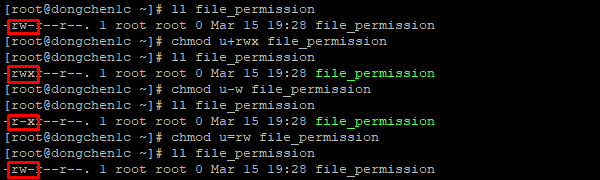
Add a sticky bit to a given directory:. The letter u represents the owner (user), and +rw adds read and write permission. % chmod -v a+x myfile.txt.
$ chmod 777 -R /path/to/Dir To assign reasonably secure permissions to files and folders/directories, it's common to give files a permission of 644 , and directories a 755 permission, using the find command and a pipe we can target just files. The umask command can be used to read or set default file permissions for the current user. The u flag sets the permissions for the file owner, g refers to the user group, while o refers to all other users.
Chmod ugo+rwx foldername to give read, write, and execute to everyone. By - Linux tutorial - team. If you specify both the -h flag and the -R flag, the chmod command descends the specified directories recursively, and when a symbolic link is encountered, the mode of the file or directory pointed to by the link is not changed.
Type chmod 755 foldername, and then press Return. Set the permissions of file.htm to "owner can read and write;. 1) Make your present working directory :.
Examples chmod 644 file.htm. $ chgrp -R www-data / var /www. Chmod a+r file3 This gives all permission to read file “ file3 ”.
Read permission on a directory gives you the ability to lists its content. Chmod a=r foldername to give only read permission for everyone. For example, for read and write permission, it is 4+2 = 6.
There are two basic ways of using chmodto change file permissions:. So after the copy is complete, the first person should modify the file's properties and permissions. Chmod Modifies File Permissions.
Setting Access Permissions Numerically There is a shorthand way of setting permissions by using octal numbers. Recursively) for owner, and removes write permission for group and others chmod ug=rw groupAgreements.txt:. It is important, however, that you understand the only user that can actually modify the permissions or ownership of a file is either the current owner or the root user.
So chmod 744 script.sh would give us the exact same permissions that we just observed on script.sh:. Using Numbers to modify the permissions, and using symbols to modify the permissions. An s can be added to the owner or group 'read' permission.
You can use it to change all the permissions for all the files inside a folder with a single command. Remember that you need read permissions in order to list directories and subdirectories. The owner of a file can change the permissions for user (u), group (g), or others (o) by adding (+) or subtracting (-) the read, write, and execute permissions.
Change the permissions of the file There are two ways to change the permissions of the file, which are:. To change file and directory permissions, use the command chmod(change mode). This command gives the owner read/write permissions for the file called who.out.
Using symbols (alphanumerical characters) using the octal notation method. This changes the permissions of the folder to rwxr-xr-x. As all Linux users, you will at some point need to modify the permission settings of a file/directory.
User, group or all. Chown – change ownership. Owner Group World Therefore, when setting permissions on a file, you will want to assign all three levels of permissions, and not just one user.
The command that executes such tasks is the chmod command. Ideally give 755 permission for security reasons to web folder. A Few Additional chmod Tips.
Adds write permission to the directory docs and all its contents (i.e. You can give yourself permission. Next, change all directories and files in the web root to the same group (www-data) - just in case there are files in there currently:.
Chmod never changes the permissions of symbolic links (or external links), because, on a z/OS system, the permissions on symbolic links (and external links) are never used. Now, let’s see the default permission values for a directory. To give read permission to all for a particular type of file:.
Special permissions can be added which allow you the special ability to automatically change users or group, or to specify a directory as a "temporary" directory. These users are technically know as:. Chmod – change permissions.
$ chmod go+x / var /www.

Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected

Understanding File Permissions

How To Give Read Write Permissions To A Folder In Ubuntu Code Example

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command In Linux

Ownership And Permissions

Changing File Permissions Wordpress Org

Permissions Why Use Chmod Instead Of Chmod U Rw Go R Unix Linux Stack Exchange

An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World
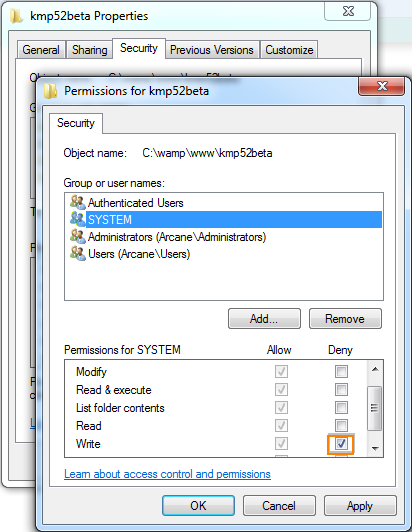
How To Deny File Permissions To Everyone Except Yourself In Linux Linuxhostsupport

Understanding Basic File Permissions And Ownership In Linux The Geek Diary

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission
44 File Permissions Chown Chgrp Chmod Umask Dong A Place To Track My Time Log

Linux Chmod Chown Syntax And Chmod Chown Examples

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight

Granting Write Permissions To A Group To A Folder Unix Linux Stack Exchange

Ownership And Permissions
Q Tbn 3aand9gct I9jvgnhaxowmpzpaajfkfizchmnvqt Bi Nz3ljrxwqpkb8l Usqp Cau

How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux

Add Group Write Permission To Folder In Ubuntu Super User

Change Ownership And Rights To Files And Folders In Linux Smashing Lab

Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials

How To Set Access Rights For Files And Folders With Chmod
Bif703 File Permissions Ppt Download

Linux Terminal File Permissions Chmod Chown And Chgrp Youtube

Setup Correct Files And Folders Access Permissions Efficiently Web Site Scripts Com

Chmod Cheatsheet Linux

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux Basic Linux Permission Linux File Permission Wiz Maverick Benisnous

Linux Chmod Example Linux Hint
Setup Correct Files And Folders Access Permissions Efficiently Web Site Scripts Com

Csc128 Permissions And Links Chmod And Ls

Chmod Umask Stat Fileperms And File Permissions
1
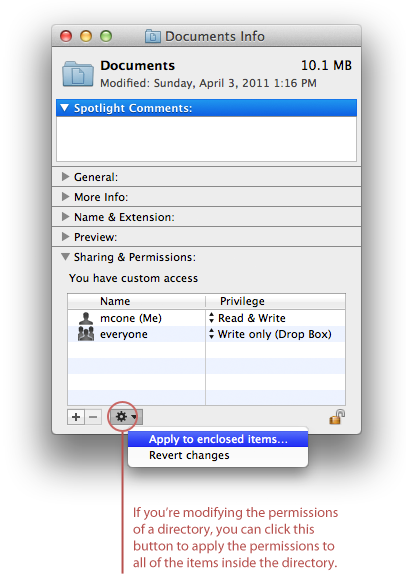
How To Set File Permissions In Mac Os X Macinstruct
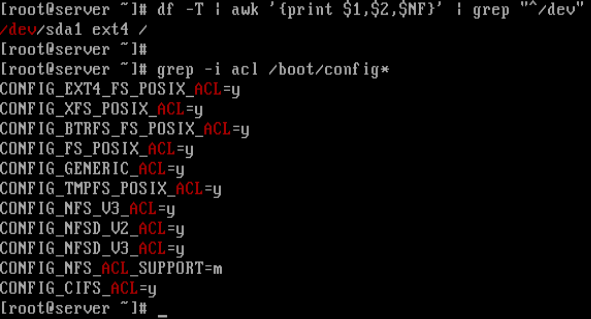
Assign Read Write Access To A User On Specific Directory In Linux

Chmod Command In Linux File Permissions Linuxize
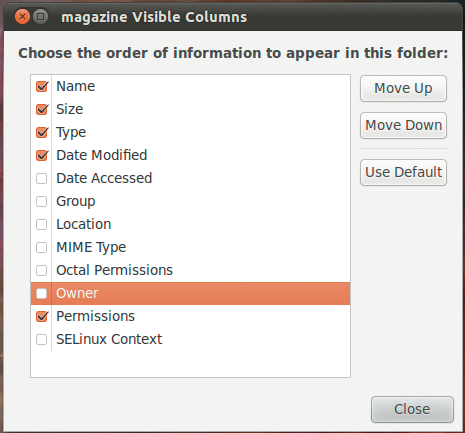
Access Permissions Raspberry Pi Geek

How To Change File Permissions Using The Terminal Chriswrites Com
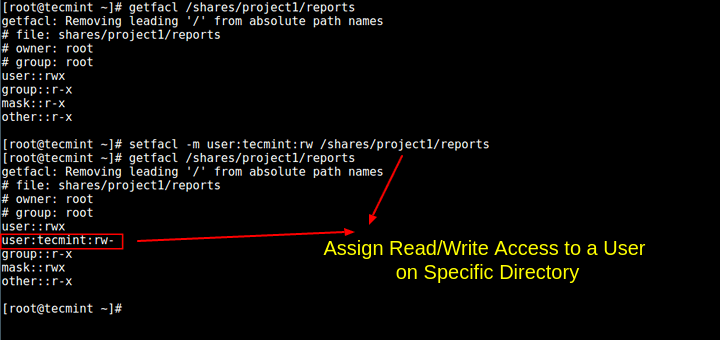
Assign Read Write Access To A User On Specific Directory In Linux
Chmod Chown Wsl Improvements Windows Command Line
Chmod Jessica Peng

How To Fix Folder And File Permissions In Wordpress

Chmod Wikipedia

Using Terminal To Set File Permissions Amsys
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq6mtqrr2tbkvj8mt7j61itbsugnnfl3ltc9cdgqfgdswx0kkor Usqp Cau

Directory How Can I Change Permissions Of A Folder Including Its Enclosed Files And Subdirectories Ask Ubuntu

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

How Can I Recursively Change The Permissions Of Files And Directories Ask Ubuntu
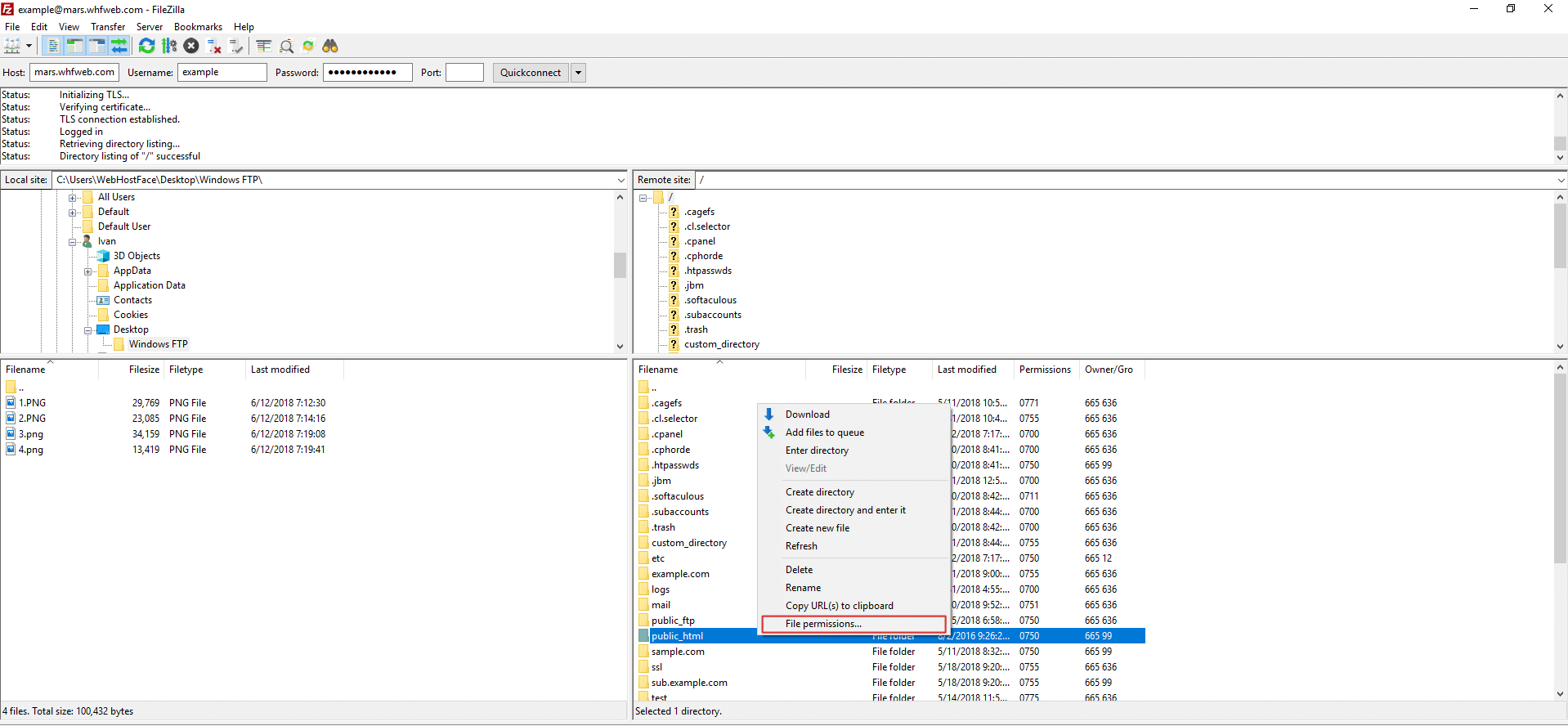
Change Ftp Permissions With Filezilla On Windows Computer

File And Folder Permission Settings For Wordpress Folder On Linux Stack Overflow

Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected

Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu

Linux Chmod Command Tutorial With Examples To Change Permission Of Files And Folders Poftut
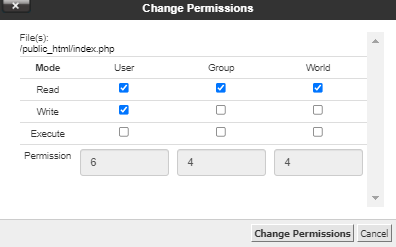
How To Change Permissions Chmod Of A File Hostgator Support

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission

Linux Commands 5 File Permission Chmod Youtube

How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight

8 Linux Chmod Command Examples To Understand It The Linux Juggernaut

Chmod Command In Unix Unix File Permissions Chmod With Examples Chwn Command Chgrp Command Unmask

Setting File And Directory Permissions Computational And Information Systems Laboratory

Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support
Permissions Red Hat Enterprise Rhcsa Rhcse Preparation 0 0 1 Documentation
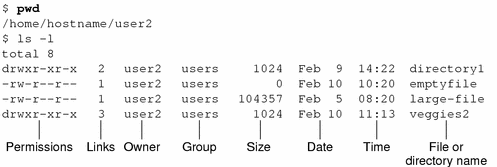
File And Directory Security Solaris Advanced User S Guide

Workbook 4 File Ownerships And Permissions Ppt Video Online Download
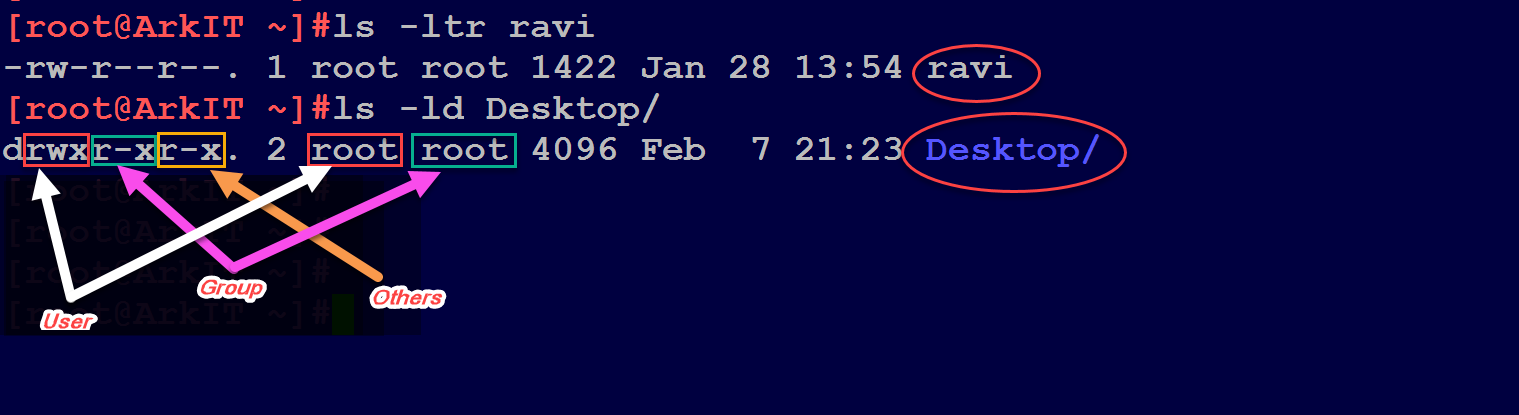
Chmod Command Understanding How To Grant File Permissions

Execute Vs Read Bit How Do Directory Permissions In Linux Work Unix Linux Stack Exchange

Xampp Htdocs Permission Issue And Fix In Ubuntu

Linux File Permissions And Directory Configuration Programmer Sought

Unix Linux Os X File Permissions

Change File And Folder Permission On Ubuntu Chmod Chown Command In Linux Youtube
How To Change Permissions Chmod Of A File Hostgator Support

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight
.png)
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example

File Permissions Rhel 7 Tutorial

How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux

Chmod Why It Matters User Permissions In Os X Droppedframe Com

How To Change File Permissions Using The Terminal Chriswrites Com

Introduction To Linux File Permissions Attributes Chmod Globo Tech

Linux Chmod Command Tutorial With Examples To Change Permission Of Files And Folders Poftut

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

How To Change Permissions And Owners Via Linux Command Line

Chmod How To Set File And Directory Permission In Linux Using Chmod Youtube

Linux Chmod Command Help And Examples
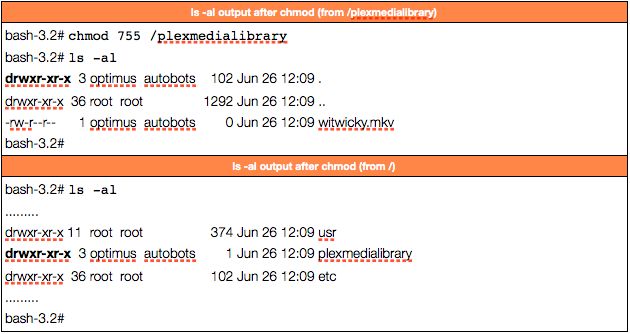
Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

How Do Linux File Permissions Work

How To Set File Permissions In Mac Os X Macinstruct
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/i7guGwCYcn-34e068e148ae4e918b29c86cd2d5740e.png)
Configuring Unix Linux File And Directory Access Rights
Q Tbn 3aand9gcr9rnnth31jdnr94db Zmbdt5bh907clokeeor9me5yqbuufaiw Usqp Cau

Linux Permissions An Introduction To Chmod Enable Sysadmin

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage



