Chmod File Permissions Linux

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials

08 Unix Linux Shell File Directories Permission Chmod Command Youtube

Unix Permissions

Linux Chmod Example Linux Hint
What Is Chmod 777

Chmod Command In Linux File Permissions Linuxize
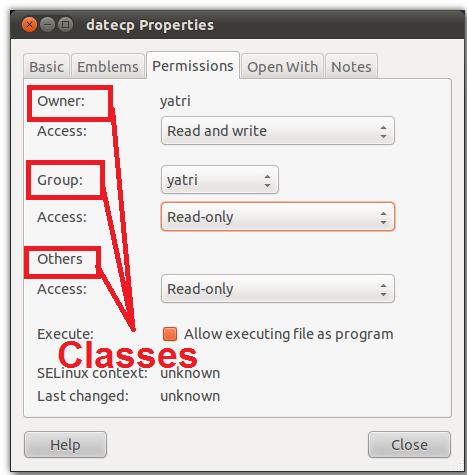
So I already own those files and folders, without having to change anything.

Chmod file permissions linux. The command chmod changes the file mode bits of each given file according to mode, which can be either a symbolic representation of changes to make, or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new mode bits. Sysadmins can enforce a security policy based upon file permissions. Chmod is used to make changes:.
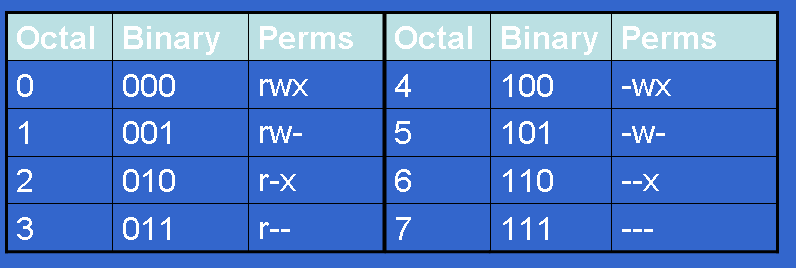
Chmod -R 777 ./ If you need more info about chmod command see:. The three digits of the chmod code set permissions for these groups in this order:. Each class can have read, write and execute permissions.
In Linux, you can easily change the file permissions by right-clicking the file or folder and select “Properties”. X Permission to execute the file, or, in the case of a directory, search it. To recursively operate on all files and directories under a given directory, use the chmod command with the -R, (--recursive) option.
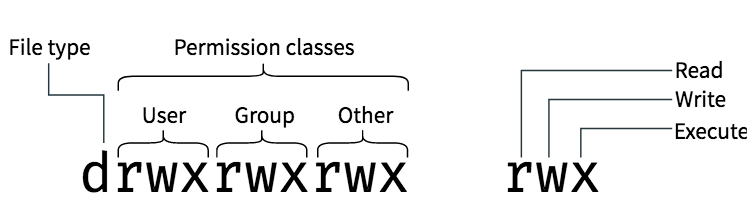
The second represents the Group permissions;. Any files created, modified, or accessed in the Linux root file system follow standard Linux conventions, such as applying the umask to a newly created file. The chmod command, like other commands, can be executed from the command line or through a script file.
Neither command is difficult to use. Permissions used to be called mode of access and hence chmod was the short form of change the mode of access. The chmod command stands for “change mode”, and allows changing permissions of files and folders, also known as “modes” in UNIX.
You can use chmod command for changing the permissions on a file in Linux. Linux File Permissions, chmod, & umask. After changing a directory's mode to 664 the folder's mode will be.
Chmod is a command in Linux and other Unix-like operating systems that allows to change the permissions (or access mode) of a file or directory. Checking through the graphical interface or using the command. After changing a file's mode to 664 the file's mode will be displayed in Unix style file lsting as:.
The tool will provide you with an octal code that corresponds to these permissions which can then be applied to relevant directories and files with chmod. For a directory, whoever has `read'. $ chmod u+x hello_script.sh Step 5:.
To change the permissions — or access mode — of a file, use the chmod command in a terminal. There are 2 ways to use the command -. The chmod command allows you to change the permissions of files using symbolic or numeric mode.
The chmod command in Linux is used to change file and directory permissions using either text (symbolic) or numeric (octal) notation. To meet our goal, we will run:. Just select the appropriate permissions and it will tell you the permissions in both absolute and symbolic mode.
$ chmod a+r sample.txt Make a file readable and writable by the group and others. And the last number represents the permissions for all other. How to Use chmod Command.
On Unix-like operating systems, a set of flags associated with each file determines who can access that file, and how they can access it. Recursive chmod using find, pipemill, and sudo. The -R (or --recursive) options make it recursive.
Use the chmod command to set file permissions. Understanding file permissions for chmod and chown command. Let’s say we want to change Linux file permissions from -rwxrw-rw-to -rwx-r–r–.
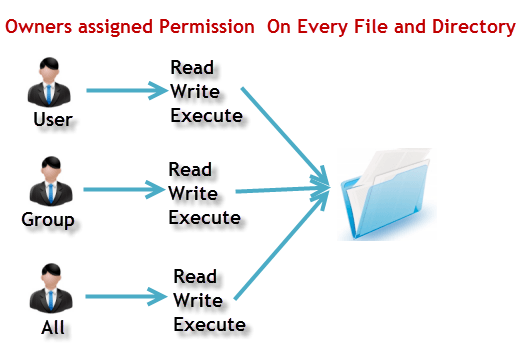
It is important, however, that you understand the only user that can actually modify the permissions or ownership of a file is either the current owner or the root user. In Linux, who can do what to a file or directory is controlled through sets of. In Linux, files and directories are treated similarly.
Each of the three digits in our chmod statement — 7, 7, 0 — corresponds to Owner, Group, and Others rights. A sample permission string would be chmod 640 file1, which means that the owner has read and write permissions, the group has read permissions, and all other user have no rights to the file. Using the command, we can set permissions (read, write, execute) on a file/directory for the owner, group and the world.
To change directory permissions in Linux, use the following:. Accessing files in the Linux root file system from Linux. Change permission on all the files in a directory recursively.
$ chmod a-x sample.txt Allow read permission to everyone. To make a script executable use +x or u+x, for example :. After you have assigned the executable permissions to the script, you can run the script without bash command as shown.
To start with file permissions, you have to find the current Linux permission settings. There's no way to set the permissions for files automatically in only this directory that are created after you set the permissions, but you could change your system-wide default file permissions with by setting umask 022. Chmod 755 -R /opt/lampp/htdocs will recursively set the permissions.
Linux file permission is a very important aspects in terms of security issues for the system administrator of Linux Operating System. Myfile.txt – the name of the file/folder. As explained in the article Permissions in Linux, Linux uses a combination of bits to store the permissions of a file.We can change the permissions using the chmod command, which essentially changes the ‘r’, ‘w’ and ‘x’ characters associated with the file.
Chmod +rwx filename to add permissions. How To Change File Permissions In Linux Using ‘chmod’ Command. The chown command stands for “change owner”, and allows changing the owner of a given file or folder, which can be a user and a group.
Linux File Permission :. The general syntax to recursively change the file’s permissions is as follows:. This is a shortcut, but can save some time.
There are two ways to use the chmod command:. To change file and directory permissions, use the command chmod (change mode). To assign reasonably secure permissions to files and folders/directories, it's common to give files a permission of 644, and directories a 755 permission, since chmod -R assigns to both.
View (u)ser, (g)roup and (o)thers permissions for chmod 664 (chmod a+rwx,u-x,g-x,o-wx) or use free online chmod calculator to modify permissions easily. There are several ways to apply a chmod to files recursively on Linux. There will be a Permission tab where you can change the file permissions.
In Unix and Unix-like operating systems, chmod is the command and system call which is used to change the access permissions of file system objects (files and directories). Rwxrwx--- How does 770 correspond to rwxrwx---?. Change file permissions in Linux.
Further, the ownership of files also depends on the uid (user ID) and the gid (group ID) of the creator, as discussed in this. With the concepts mentioned in this article, you are equipped with sufficient knowledge to handle permissions in Linux-based distros. Again as Rob has said, in 13,.
The name is an abbreviation of change mode. Deny execute permission to everyone. Transferring Ownership with chown.
Chmod +x filename to allow executable permissions. Change into the directory with cd, before you run the find command. A command line / terminal window ( Ctrl + Alt + T or Ctrl + Alt+F2) A user account with sudo privileges (optional) A Linux system.
Chmod changes the permissions of each given file according to mode, where mode describes the permissions to modify. $ chmod go+rw sample.txt Make a shell script executable by the user/owner. Users can simply modify file permissions using the chmod (change mode) command.
There are two options to choose from, depending on your personal preference:. You can configure your file permissions inside of your Windows drives using the mount options in wsl. Use sudo, the find command, and a pipemill to chmod as in the following examples.
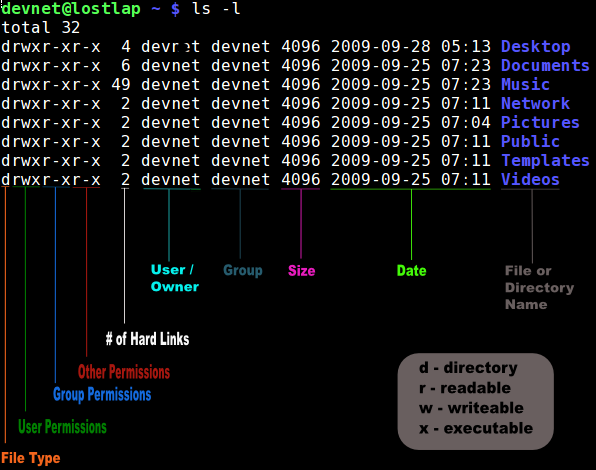
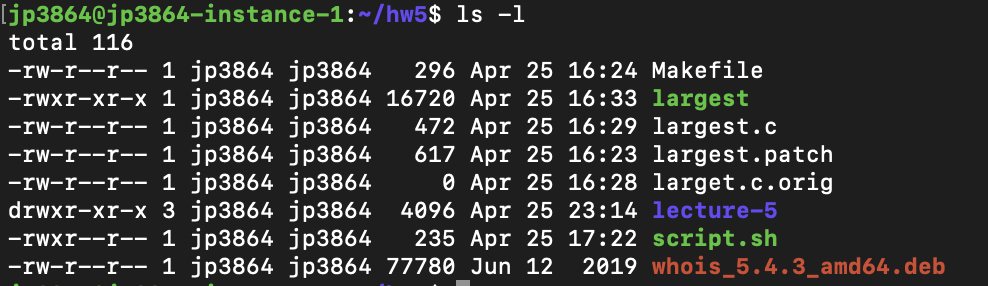
We can use the -l (long format) option to have ls list the file permissions. $ chmod OPTIONS MODE filename Only the root user or a regular user with sudo privileges can change file or directory permissions. In short, “chmod 777” means making.
It takes the following syntax:. Chmod 744 file name By executing this command, the owner can read, write, and execute the file (rwx). Using chmod with Absolute Permissions.
Cd /var/www/mydirectory find. Understand how Ubuntu / Linux file permissions and special mode bits work. However, group and others are only allowed to read (r–).
Select the permissions you require below. Below is the command's general structure:. These flags are called file permissions or modes, as in "mode of access." The command name chmod stands for "change mode." It restricts the way a file can be accessed.
Check Permissions using GUI Finding the file (directory) permission via the graphical user interface is simple. -type f -exec chmod 750 {} +. How to Change File Permissions and Ownership.
Types of permissions which we will be changing using chmod command :. Mykyta Dolmatov / Getty Images. Running chmod 770 on project-a gives us the permission set we want:.
The permission scheme described above also applies to directories. Chmod +x filename.sh to make filename.sh executable. Find out how default permissions for new files are configured via a user's umask value.
The second way to modify permissions with the chmod command is to use a number to specify each set of permissions for the file. All files have three types:. Chmod (this Tutorial's subject) and chown are designed to be able to change the defaults of user access as part of a secure plan by the Administrator, as well as, in the case of chown, modifying downloaded files to make them executable.
Owner – Person or process who created the file. Each permission is assigned a value, as the following table shows, and the total of each set of permissions provides a number for that set. Actually, chmod Command in Linux plays a greater role to keep all the files and directories of the system safe and secure so that no unauthorized person.
Simply enter this line:. File permissions in Linux file system are managed in three distinct user classes:. To determine the mode (or permission settings) of a particular file, use the command `ls -lg filename'.
The request is filtered by the umask. One can use file permissions to control access to their files. You can also add permissions without specifying a full permission string.
The owner of a file can change the permissions for user (u), group (g), or others (o) by adding (+) or subtracting (-) the read, write, and execute permissions. Mode can be specified with octal numbers or with letters. One of the easiest ways is to use the find command to select the files and then run the chmod command with the -exec switch.
We can use the ' chmod' command which stands for 'change mode'. Chmod -R MODE DIRECTORY. Chmod Command in Linux Linux File Permission Introduction to Linux File Permission.
Chmod is a great Linux command for manipulating file and directory permissions. The chmod command changes the access permissions of files and folders. File permission can be represented in a symbolic or numeric (octal) format.
The chmod system call cannot change their permissions. Add a sticky bit to a given directory:. User/owner, group and others/public.
In linux terminal, to see all the permissions to different files, type ls -l command which lists the files in the working directory in long format. The chmod command uses a three-digit code as an argument. Setting File Permissions in Command Line.
View (u)ser, (g)roup and (o)thers permissions for chmod 766 (chmod a+rwx,g-x,o-x) or use free online chmod calculator to modify permissions easily. The highly productive Linux system offers various levels of permission to ensure that the user has enough ways to interact with files and directories. There are two basic ways of using chmod to change file permissions:.
Chmod -R 777 /www/store. Owner (you) Group (a group of other users that you set up) World (anyone else browsing around on the file system) Each digit of this code sets permissions for. Chown – change ownership.
Viewing and Understanding File Permissions. If you need to list a file's permissions, use the ls command. Changing file permissions is simple with the chmod command:.
Give read, write and execute permission to the file’s owner, read permissions to the file’s group and no permissions to all other users:. If you want an easy way to know the Linux file permission in numeric or symbolic mode, you can use this chmod calculator. Learn how to change these permissions using the chmod command.
In the terminal, the command to use to change file permission is chmod. Add the file’s owner permissions to the permissions that the members of the file’s group have:. Or if you want to make all the files in the current directory have all permissions type:.
How to Set File Permissions Using `chmod' Files. For example, if you can’t open a script file, you can add permission for the owner to execute with:. Chmod never changes the permissions of symbolic links;.
The main difference between access rights for files and directories is that the x permission on a file grants permission to execute it, where on a directory, it grants permission to enter it. Chmod – change permissions. Using letters is easier to understand for most people.
The second way to execute a bash script is by setting up the executable permissions. $ chmod u+x samplescript.sh. Chmod -rwx directoryname to remove permissions.
The first number represents the Owner permission;.
Q Tbn 3aand9gcrjnvlxj0s Bjlyqdmcffgnaicqwuoecwomv8yezuw Usqp Cau

Understanding Basic File Permissions And Ownership In Linux The Geek Diary

Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode

Understanding File Permissions

File Security

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions
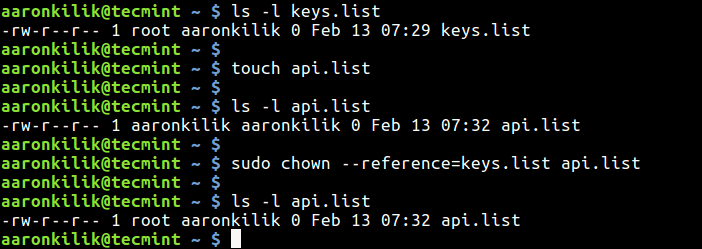
How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux

Linux File Permissions Chmod Umask Tutonics

Linux File Permission Change By Chmod Command In Linux Guide For Beginners

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

Chmod Command In Linux File Permissions Tecnstuff

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices
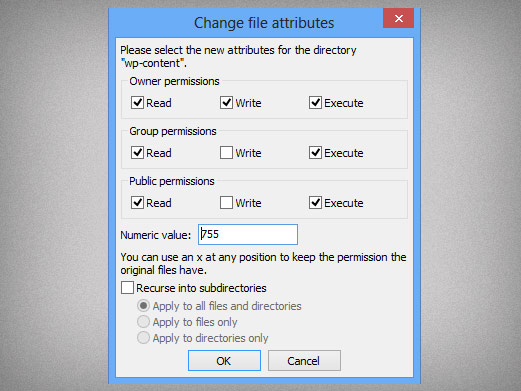
What Is Chmod How To Use Chmod For Wordpress File Permissions

Chmod How To Set File And Directory Permission In Linux Using Chmod Youtube

Directory How Can I Change Permissions Of A Folder Including Its Enclosed Files And Subdirectories Ask Ubuntu

How To Set File Permissions In Mac Os X Macinstruct

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier

How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux

How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux

Unix Linux Os X File Permissions

Linux Concepts File Directory Permissions Hari S Technical Space

Understanding File Permissions 2buntu

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

Chmod Umask Stat Fileperms And File Permissions

Linux Unix Permissions And Attributes Linuxsecrets

Linux Commands 5 File Permission Chmod Youtube

How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux

Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

How Did The Number 777 In Chmod 777 Come Out Under Linux Laptrinhx

Csc128 Permissions And Links Chmod And Ls

Ownership And Permissions

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight
Chmod Archives Yet Another Linux Blog

Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected

Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

Understanding Linux File Permissions With Chmod Umask Chown And Chgrp Liquidon Net
.png)
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example

Changing File Permissions Wordpress Org

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission
Controlling File Permissions With Umask

Pin By Dr Stefan Gruenwald On Cheatsheets Computer Science Programming Learn Javascript Linux Operating System

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight

Explained How To Use Chmod Command Complete Guide Youtube

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux Basic Linux Permission Linux File Permission Wiz Maverick Benisnous
Linux Jessica Peng

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

Solved File Permissions In Linux Can Be Set Using A 3 Dig Chegg Com

How To Get Octal File Permissions On Linux Unix Command Line Nixcraft

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices

Modifying File Permissions With Chmod Command In Gnu Linux Openforums

Linux File Permission Javatpoint

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight

Chmod Cheatsheet Linux

File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example
Video Linux File Permissions Chmod And Chown Linux Org

Introduction To Linux File Permissions Attributes Chmod Globo Tech

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission
An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example

Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

Chmod Options Permissions Files Linux Pocket Guide Book

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

Chmod File Permissions In Linux Unix

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier

8 Linux Chmod Command Examples To Understand It The Linux Juggernaut
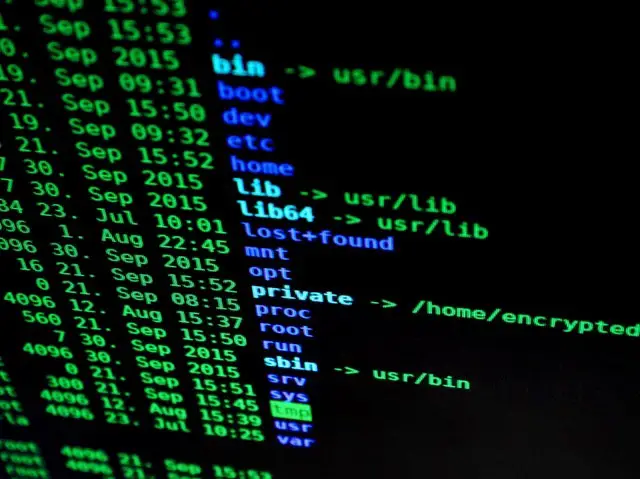
An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World
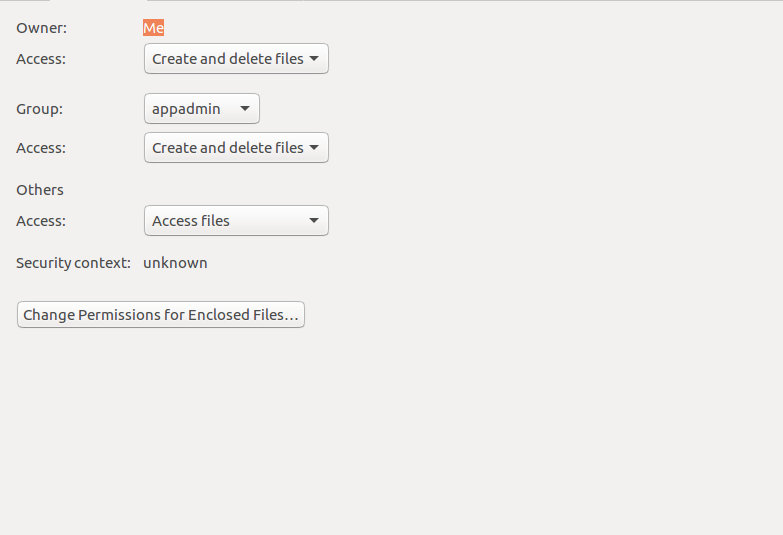
Chmod 777 What Does This Mean Learn Linux Permissions Easy Way

Linux File Permissions Tutorial For Beginners

Linux Terminal File Permissions Chmod Chown And Chgrp Youtube
Q Tbn 3aand9gcslbhvh5emm 4 Trrp3thfcmqosdrfzef Gvyldtqf1wtkgi37f Usqp Cau
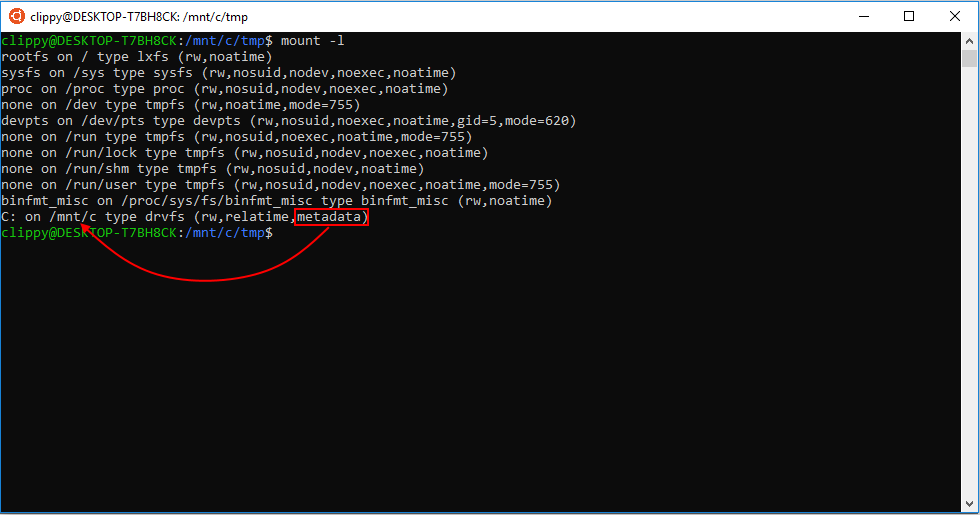
Chmod Chown Wsl Improvements Windows Command Line

Chmod All Directories Permissions Only And Omit Files Recursively On Linux Howto Walking In Light With Christ Faith Computing Diary Walking In Light With Christ Faith Computing Diary

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

Linux Users And Groups Linode

Linux File Permissions Know The Reason Behind That Chmod 777 By Abhishek Chandra Medium
.png)
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example

Linux File Permissions And Chmod Doug Vitale Tech Blog

A Unix And Linux Permissions Primer Daniel Miessler

Understand Linux File Permissions Using Chmod And Chown Commands Programming Tips For Versatile Coders

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission

An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

Linux Permissions An Introduction To Chmod Enable Sysadmin

Chmod Wikipedia

What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux Tech Ninja Pro

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders
Q Tbn 3aand9gcr2lfpzbutqythmvbwafnxvyggqfj7hnw6fhh Kcozkk8m5 V7o Usqp Cau
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq1nsq3kxri7ryrifobs2rfobawbv4hezfw9 Ldf4feblahyn09 Usqp Cau
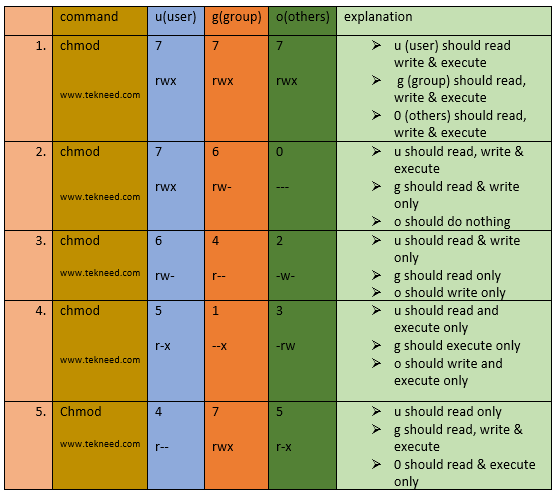
How To Set And Manage File Permission In Linux Part 1

Changing File Permissions In Linux The Chmod Command By Saswat Subhajyoti Mallick Medium



