Chmod Permissions Linux

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
How To Deny File Permissions To Everyone Except Yourself In Linux Linuxhostsupport

How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux

An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission

Linux Commands 5 File Permission Chmod Youtube
The owner of a file can change the permissions for user (u), group (g), or others (o) by adding (+) or subtracting (-) the read, write, and execute permissions.

Chmod permissions linux. In other words, give read permission to user, group and others:. In Linux, who can do what to a file or directory is controlled through sets of. The default Linux security model is a bit inflexible.
By using this command, we can set the read, write, and execute permissions for all three of the permission groups (Owner, Group and Other) in Linux. To assign reasonably secure permissions to files and folders/directories, it's common to give files a permission of 644, and directories a 755 permission, since chmod -R assigns to both. In Linux, we have 3 types of file permissions:.
Chmod -rwx directoryname to remove permissions. In this article, you will learn how to change permissions of any file or directory with chmod command. The command chmod changes the file mode bits of each given file according to mode, which can be either a symbolic representation of changes to make, or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new mode bits.
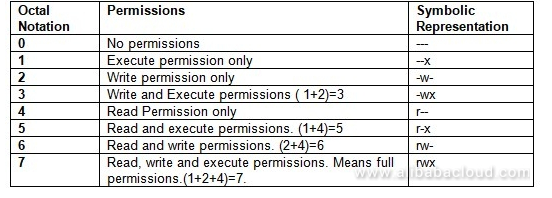
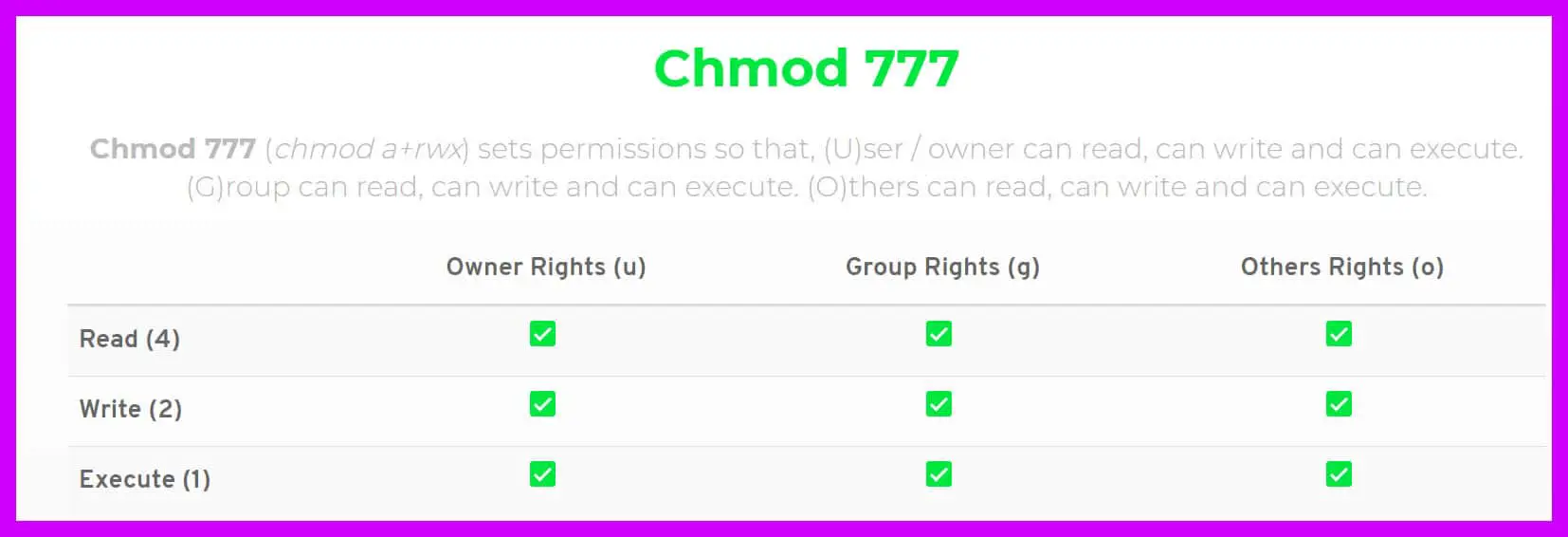
Chmod 775 /opt/lampp/htdocs Is there a way to set chmod 755 for /opt/lampp/htdocs and all of its content including subfolders and files?. Therefore, full permissions for everyone on the system would look like:-rwxrwxrwx. File permission can be represented in a symbolic or numeric (octal) format.
To meet our goal, we will run:. (G)roup can read, can't write and can't execute. We will be using the chmod command to change file and folder permissions in Linux.
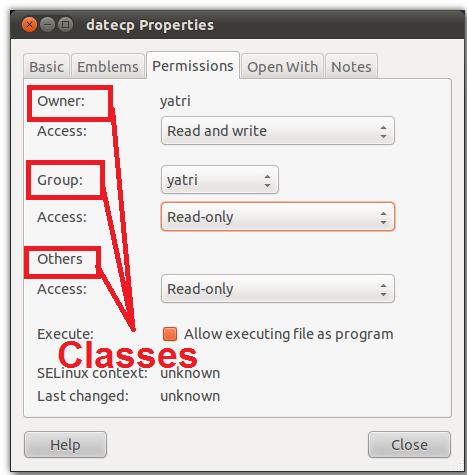
Read (r), write (w) and execute (x) permissions. Checking through the graphical interface or using the command. The highly productive Linux system offers various levels of permission to ensure that the user has enough ways to interact with files and directories.
The first number represents the Owner permission;. (G)roup can read, can write and can't execute. Chmod never changes the permissions of symbolic links;.
The chmod command in Linux/Unix is abbreviated as CHange MODe. This tutorial covers how to use the chmod command to change the access permissions of files and directories. These permissions determine which users can read, write or execute the files.
You can use chmod command for changing the permissions on a file in Linux. Chmod +x filename to allow executable permissions. Group — all users who are members of the same group.
Chmod 775 file_name chmod ug+rwx,o=rx file_name Both the commands give all permissions (code=7) to user and group, read and execute (code=5) for others. File permissions in Linux file system are managed in three distinct user classes:. But this raises security concerns as an unsolicited or malign user can corrupt, change or remove crucial data.
The possible values are:. It’s usually used when installing and configuring various services and features in a Linux system. (O)thers can read, can't write and can't execute.
Mykyta Dolmatov / Getty Images. A sample permission string would be chmod 640 file1, which means that the owner has read and write permissions, the group has read permissions, and all other user have no rights to the file. The syntax is as follows:.
Chmod 755 -R /opt/lampp/htdocs will recursively set the permissions. The second represents the Group permissions;. The main difference between access rights for files and directories is that the x permission on a file grants permission to execute it, where on a directory, it grants permission to enter it.
Check Permissions using GUI Finding the file (directory) permission via the graphical user interface is simple. Users can simply modify file permissions using the chmod (change mode) command. In Linux, you will often need to make use of the chmod command.
It’s important to make sure any web-facing files have their permissions set correctly, so that a compromised process can’t write to places it shouldn’t. But first, you need to be aware that there are three types of users who can interact with a file:. I would like to change permissions of a folder and all its sub folders and files in one step (command) in Linux.
Chmod is a great Linux command for manipulating file and directory permissions. File/Directory permission is either Read or Write or executable for either user or group or others. Chmod command is useful to change permission for Files and folders in Linux/Unix.
In short, “chmod 777” means making. Linux File Permissions #. Multi-user systems, such as Linux, require setting up and managing file permissions that ensure only authorized users have access to files they are supposed to.
Change file permissions in Linux. (O)thers can read, can write and can't execute. To better understand how the chmod command works, it’s prudent that we study the Linux file permissions model.
User/owner, group and others/public. Sets UID, sets read, write, and execute permissions for user, and sets read and execute permissions for Group and Others:. = turns on the specified permissions and turns off all others.
In this article we'll explain how to recursively change permissions of files and directories. Chmod is a command in Linux and other Unix-like operating systems that allows to ch ange the permissions (or access mod e) of a file or directory. The command is relatively simple to use and involves using.
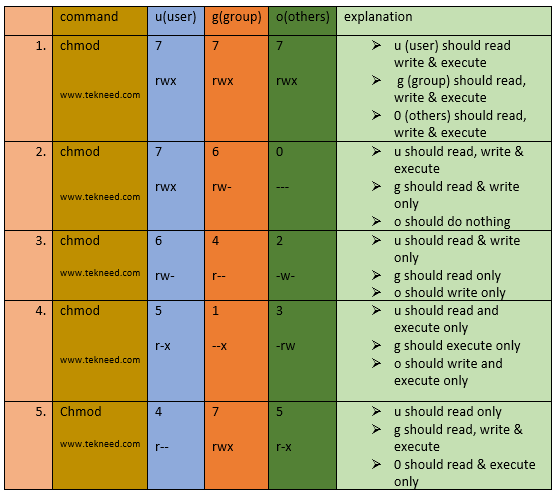
Rwxrwx--- How does 770 correspond to rwxrwx---?. Each of the three digits in our chmod statement — 7, 7, 0 — corresponds to Owner, Group, and Others rights. How To Change File Permissions In Linux Using ‘chmod’ Command.
Running chmod 770 on project-a gives us the permission set we want:. To change directory permissions in Linux, use the following:. The chmod command stands for “change mode”, and allows changing permissions of files and folders, also known as “modes” in UNIX.
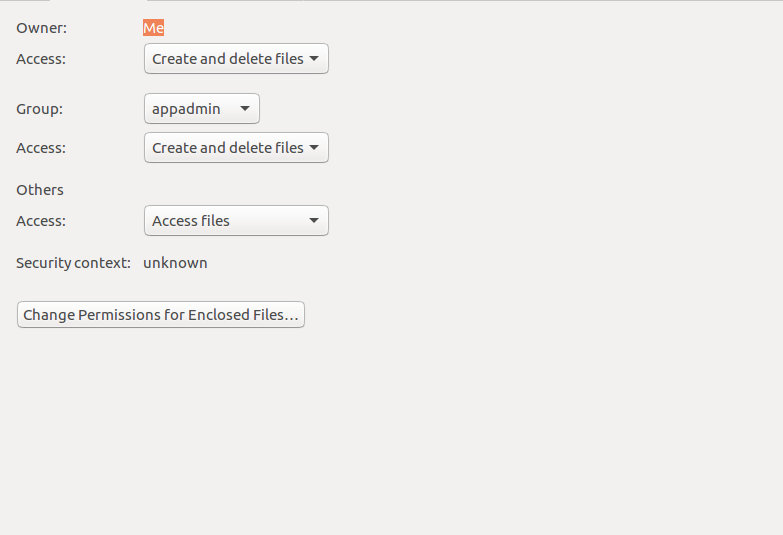
In Linux, file permissions determine the levels of privilege for file owners and everyone else. In the terminal, the command to use to change file permission is chmod. Select the permissions you require below.
To change permission of only files under a specified directory. How to Use the chmod Command on Linux chmod Modifies File Permissions. Use sudo, the find command, and a pipemill to chmod as in the following examples.
Each class can have read, write and execute permissions. There will be a Permission tab where you can change the file permissions. This ensures that only authorized users and processes can access files and directories.
Permissions used to be called mode of access and hence chmod was the short form of change the mode of access. These flags are called file permissions or modes, as in "mode of access." The command name chmod stands for "change mode." It restricts the way a file can be accessed. There are two ways to use the chmod command:.
-turns off a permission. The permission part of a symbolic mode is any combination of the following:. $ chmod a-x myscript.sh Adds read and execute permissions for everyone (a):.
Chmod is used to make changes:. Just select the appropriate permissions and it will tell you the permissions in both absolute and symbolic mode. If you need to list a file's permissions, use the ls command.
Change permission on all the files in a directory recursively. In Linux, files and directories are treated similarly. $ chmod a+r file.pl Delete execute permission for all everyone (a):.
Sets sticky bit, sets read, write, and execute permissions for owner, and sets read and execute permissions for group and others (this suggests that the script be retained in memory) chmod 4755 setCtrls.sh:. The chmod system call cannot change their permissions. Chmod u=rx file (Give the owner rx permissions, not w) chmod go-rwx file (Deny rwx permission for group, others) chmod g+w file (Give write permission to the group) chmod a+x file1 file2 (Give execute permission to everybody) chmod g+rx,o+x file (OK to combine like this with a comma).
Let’s say you are currently in the root directory of your Unix-like system and you want to change the file permissions of a folder and all of the other files and sub-directories present inside that folder. To start with file permissions, you have to find the current Linux permission settings. Linux chmod command is one of the most commonly used commands especially by system administrators when assigning modifying file and folder permissions.
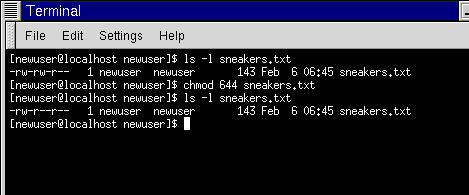
Viewing and Understanding File Permissions. $ chmod 004 sample.txt Write by owner only $ chmod 0 sample.txt Write by group only $ chmod 0 sample.txt Write by anyone $ chmod 002 sample.txt Execute by owner only $ chmod 100 sample.txt Execute by group only $ chmod 010 sample.txt Execute by anyone $ chmod 001 sample.txt Allow read permission to owner and group and anyone. Chmod 644 (chmod a+rwx,u-x,g-wx,o-wx) sets permissions so that, (U)ser / owner can read, can write and can't execute.
Using chmod with Absolute Permissions. If you want an easy way to know the Linux file permission in numeric or symbolic mode, you can use this chmod calculator. Sets read, write, and execute permissions for user, and sets read permission for Group and Others:.
To change file and directory permissions, use the command chmod (change mode). The chmod command, like other commands, can be executed from the command line or through a script file. Following are some examples:.
The name speaks for itself. In Linux, you can easily change the file permissions by right-clicking the file or folder and select “Properties”. The op part of a symbolic mode is an operator that tells chmod to turn the permissions on or off.
Linux is a multi-user system and access to the files is controlled through the file permissions, attributes, and ownership. $ chmod a+rx pager.pl Next, sets read and write permission for user, sets read for group, and remove all access for others:. And the last number represents the permissions for all other.
Chmod 766 (chmod a+rwx,g-x,o-x) sets permissions so that, (U)ser / owner can read, can write and can execute. The chown command stands for “change owner”, and allows changing the owner of a given file or folder, which can be a user and a group. Linux can also be used in mainframes and servers without any modifications.
Chmod +rwx filename to add permissions. The symbolic method and the absolute form. The second way to modify permissions with the chmod command is to use a number to specify each set of permissions for the file.
In Linux, access to the files is managed through the file permissions, attributes, and ownership. Chmod is a very helpful command to change the file permissions of a file or a folder in any UNIX-like operating system. There are two options to choose from, depending on your personal preference:.
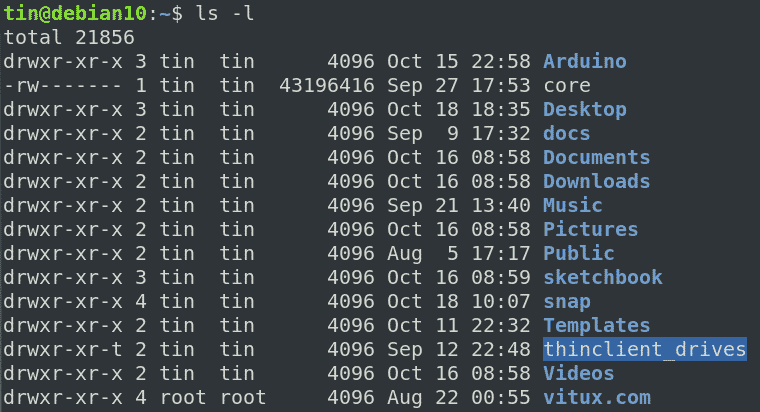
The tool will provide you with an octal code that corresponds to these permissions which can then be applied to relevant directories and files with chmod. There's no way to set the permissions for files automatically in only this directory that are created after you set the permissions, but you could change your system-wide default file permissions with by setting umask 022. We can use the -l (long format) option to have ls list the file permissions.
There are two basic ways of using chmod to change file permissions:. Linux chmod command is used to change access permissions of files and directories. If you need to change a file permission, use the chmod command.
+ turns on a permission. Chmod stands for “Change Mode” and is used to modify the permissions of files and directories in a Linux based system. The exact command is.
On Unix-like operating systems, a set of flags associated with each file determines who can access that file, and how they can access it. This type of restriction is useful for effective file/folder management, securing system and providing a level …. The letter or letters representing the owner (u), group (g), other (o) or all (a) followed by a + for adding permissions or a – for taking away permissions and then the letter for the permission (r for read, w for write and x for execute).In the above example, I added the execute permission for all users.
The chmod command changes the access permissions of files and folders. With the concepts mentioned in this article, you are equipped with sufficient knowledge to handle permissions in Linux-based distros. I have already tried the below command but it works only for the mentioned folder:.
Setting File Permissions in Command Line. We have already described the Linux file permissions.

Csc128 Permissions And Links Chmod And Ls
Linux Chmod Tips

How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux
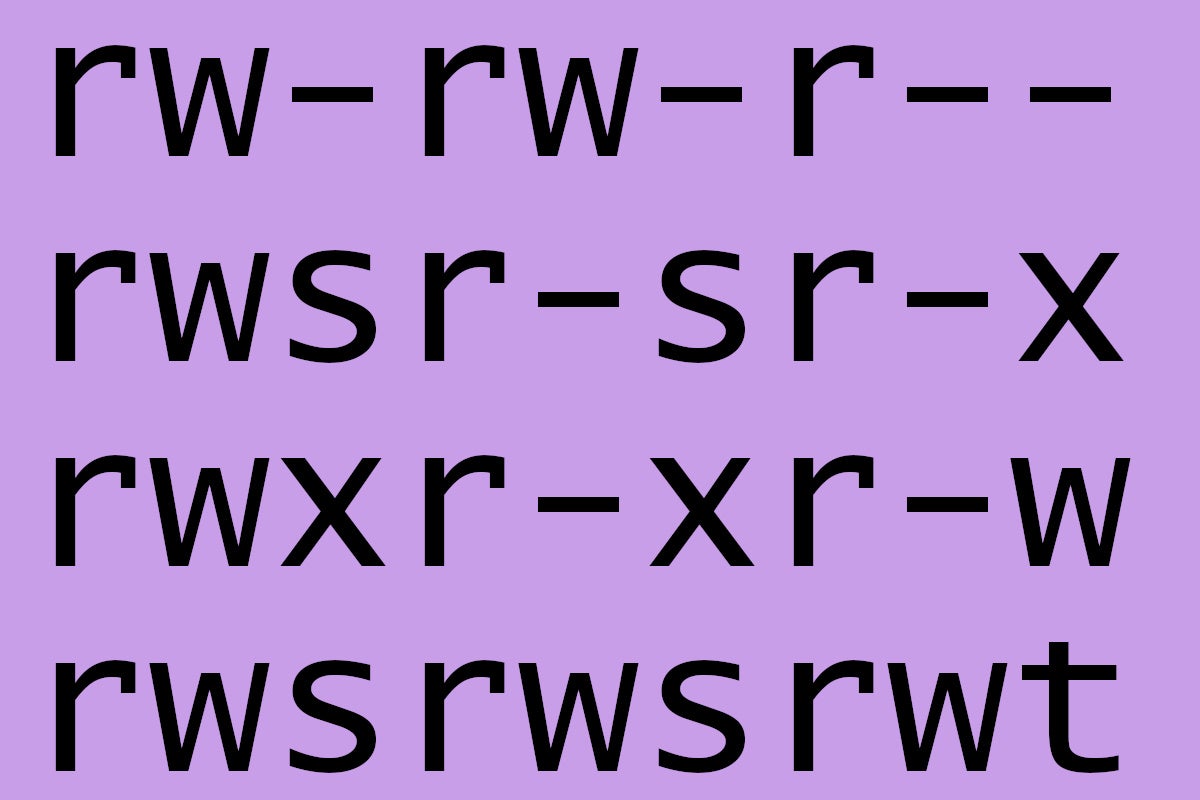
A Deeper Dive Into Linux Permissions Network World

Linux Users And Groups Linode

Unix Permissions The Easy Way Index Of All Chmod Permutations By Semi Koen Sep Towards Data Science

How Did The Number 777 In Chmod 777 Come Out Under Linux Laptrinhx

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

Linux Chmod Chown Syntax And Chmod Chown Examples

Ownership And Permissions

Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier

Restore Executable Permission To Chmod Command In Linux Ostechnix
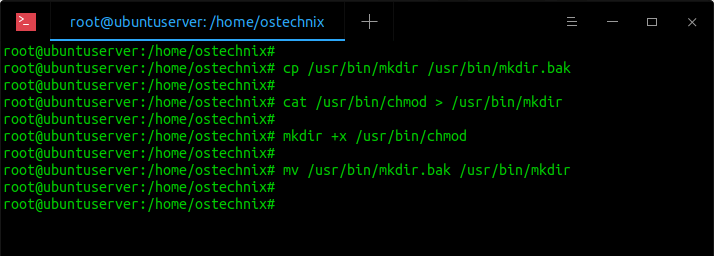
Restore Executable Permission To Chmod Command In Linux Ostechnix
Video Linux File Permissions Chmod And Chown Linux Org
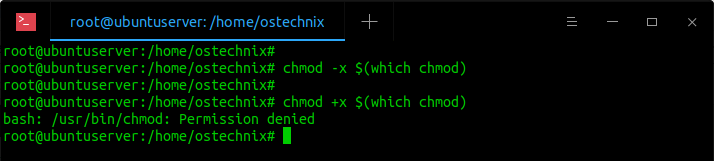
Restore Executable Permission To Chmod Command In Linux Ostechnix

A Unix And Linux Permissions Primer Daniel Miessler

Unix Permissions

Understanding Linux File Permissions With Chmod Umask Chown And Chgrp Liquidon Net

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders

Linux File Permission Change By Chmod Command In Linux Guide For Beginners
Q Tbn 3aand9gcr2lfpzbutqythmvbwafnxvyggqfj7hnw6fhh Kcozkk8m5 V7o Usqp Cau

Execute Vs Read Bit How Do Directory Permissions In Linux Work Unix Linux Stack Exchange

Linux File Permissions Know The Reason Behind That Chmod 777 By Abhishek Chandra Medium
What Is Chmod 777

Linux File Permissions Tutorial For Beginners

8 Linux Chmod Command Examples To Understand It The Linux Juggernaut

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux
How To Use Linux File Permissions And Ownership On Alibaba Cloud Ecs Dzone Open Source
Chmod 777 What Does This Mean Learn Linux Permissions Easy Way

Linux Users And Groups Linode

14 Permission And Modification Times

Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected
How To Set And Manage File Permission In Linux Part 1

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission

Linux File Permission Javatpoint

Chmod File Permissions In Linux Unix

File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example

Linux Unix Permissions And Attributes Linuxsecrets

Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu

An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

Understand Linux File Permissions Using Chmod And Chown Commands Programming Tips For Versatile Coders

Chmod Command In Linux File Permissions Linuxize

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command In Linux

Linux Chmod Example Linux Hint
Change File Permissions Recursively Linux Linux Hint

Linux File Permissions And Chmod Doug Vitale Tech Blog

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu

Unix Linux Os X File Permissions
Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq1nsq3kxri7ryrifobs2rfobawbv4hezfw9 Ldf4feblahyn09 Usqp Cau

What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux Tech Ninja Pro

Linux Terminal File Permissions Chmod Chown And Chgrp Youtube

Linux Permissions An Introduction To Chmod Enable Sysadmin

Explained How To Use Chmod Command Complete Guide Youtube

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials
Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs J72hjomdluhqe6xjivy M6yrjmkqx9x3z3ps Rpnb8by3w7z Usqp Cau

How Do Linux File Permissions Work

Understanding File Permissions
Fun With Numbers In Chmod

Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

File Security

Introduction To Linux File Permissions Attributes Chmod Globo Tech

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected

Chmod Umask Stat Fileperms And File Permissions

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage
.png)
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example

Chmod Wikipedia

Linux Chmod Command Clearly Explained Codedodle

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

Pin By Dr Stefan Gruenwald On Cheatsheets Computer Science Programming Learn Javascript Linux Operating System

How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux

08 Unix Linux Shell File Directories Permission Chmod Command Youtube

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

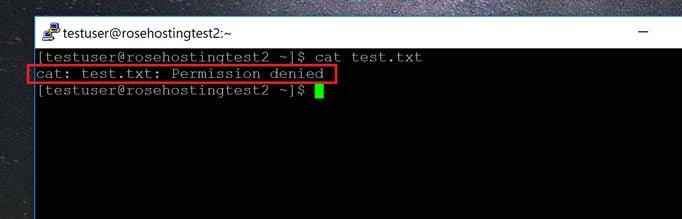
Chmod Permission Denied Unix Linux Stack Exchange

Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

Understanding Unix Permissions And File Types Unix Linux Stack Exchange

Understanding Basic File Permissions And Ownership In Linux The Geek Diary
Q Tbn 3aand9gcrjnvlxj0s Bjlyqdmcffgnaicqwuoecwomv8yezuw Usqp Cau
/GettyImages-1021092796-ea8c63ee76f84bd5bf98c4222337fbb4.jpg)
How To Use The Chmod Command In Linux

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks
Why Would Using Chmod 777 Recursively From The Root Cause A Linux Box To Not Boot I Could Understand This If I Were Limiting Permissions But Why Would Adding Permissions Cause This

Chmod Cheatsheet Linux

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage



