Chmod Octal Chart

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks
Linux Reference Guide To Commands Professional Computer Etsy

List Of All Unix Linux Commands
An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World
Read Just Enough Linux Leanpub

1 Introduction Gmt 6 0 0 R460 Documentation
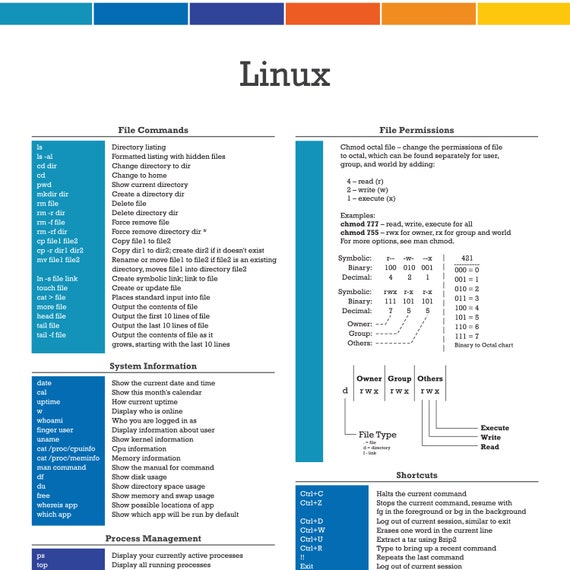
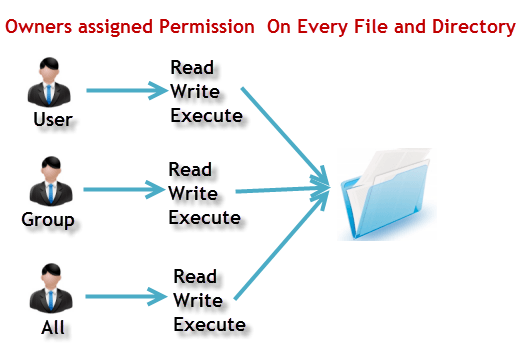
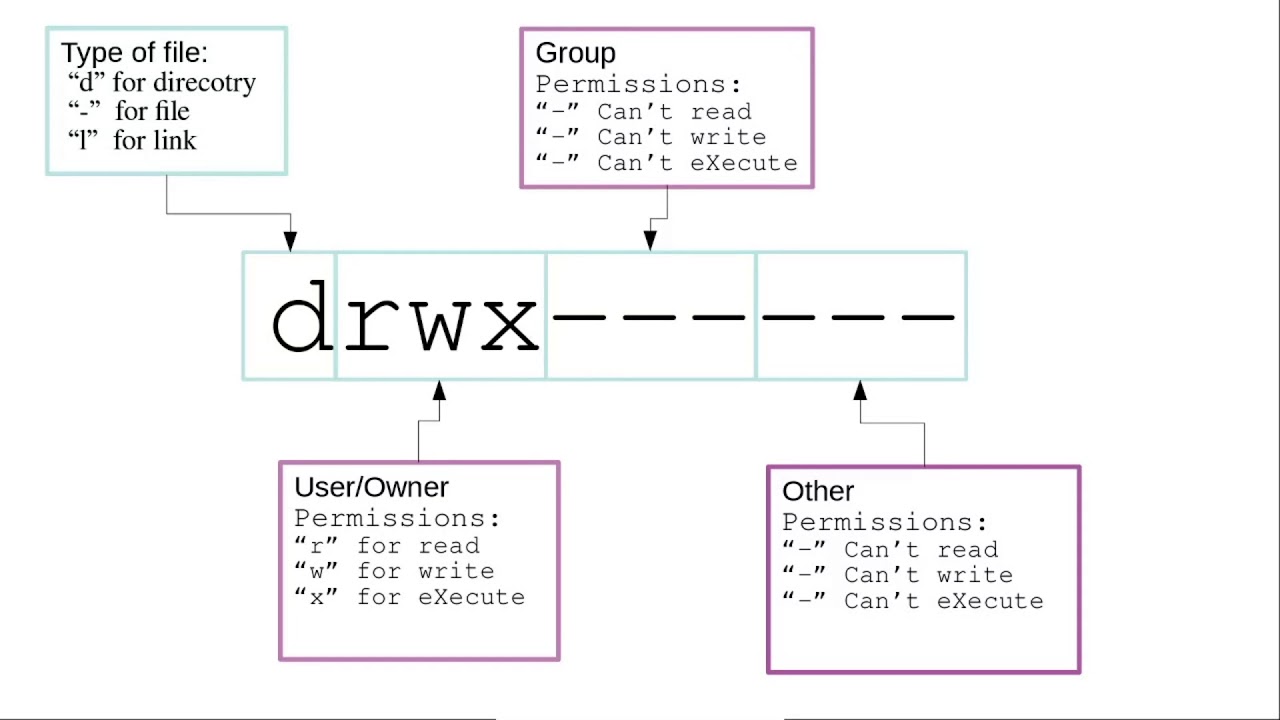
PERMISSION COMMAND U G W rwx rwx rwx chmod 777 filename rwx rwx r-x chmod 775 filename rwx r-x r-x chmod 755 filename rw- rw- r-- chmod 664 filename rw- r-- r-- chmod 644 filename U = User G = Group W = World r = Readable w.

Chmod octal chart. How to get octal file permissions on Linux/Unix command line. The symbolic notation consists of three components:. Chmod changes the permissions of each given file according to mode, which can be either an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new permissions or a symbolic representation of changes to make, (+-= rwxXstugoa).
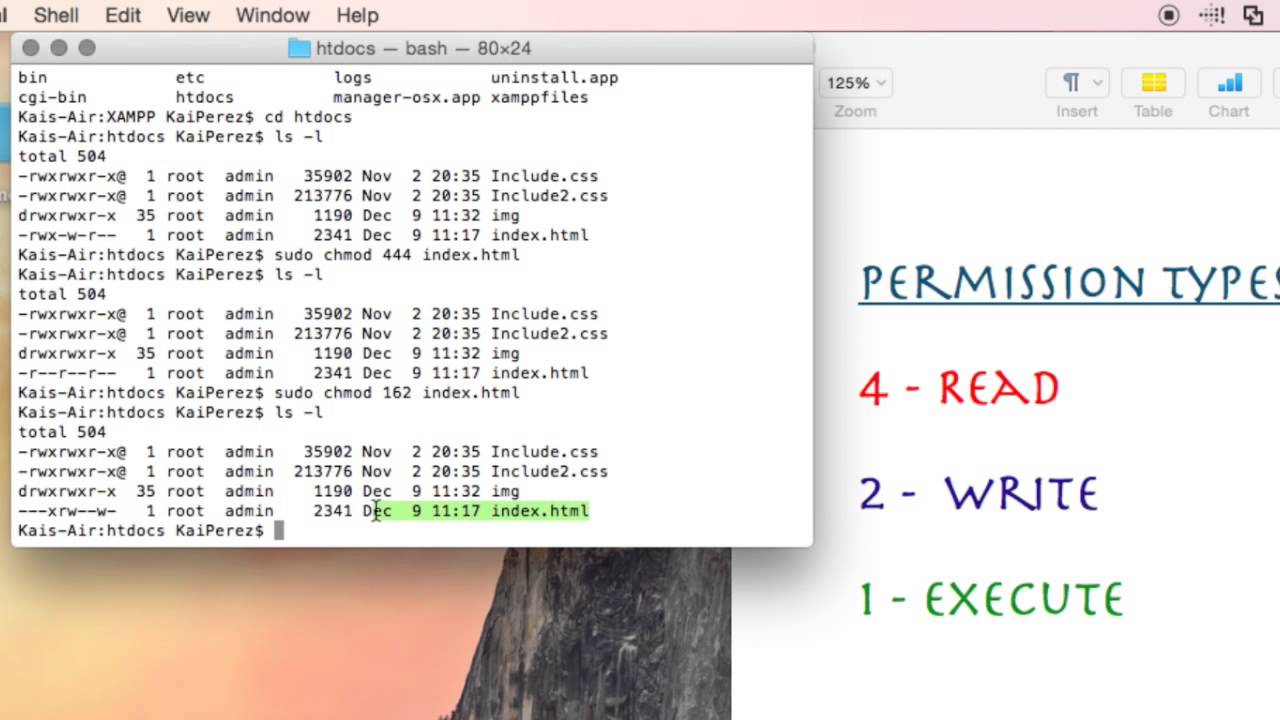
Similarly, the “Octal number system” uses only 8 numbers to represent the numbers, so it has the name “Octal”. Chmod all directories with directory listing (.htaccess Options +Indexes) to 755;. Here's a summary that I have gathered.
The octal representative of the read, write and execute bits, "rwx" are Read 4 Write 2 Execute 1 Octal representation is pure geek talk, and was the only form that worked in the early versions of Unix. Chmod all files to 644;. Here are a few more examples of chmod statements in this form:.
This chmod calculator has two functionalities - you can use it to:. For a new directory - 0777 (octal). There are three different possible user levels, each with three different possible settings.
You can use the chmod command to set permissions in either of two modes:. In the hexa decimal number system, we represent the binary digits as a set of 4 digits (2 4 = 16), in octal numbering system we represent the binary numbers as a set of 3 digits (2 3 = 8. To change file permissions of a file use the syntax below.
Rwx = 4+2+1 = 7 r-x = 4+2+0 = 6 r-- = 4+2+0 = 6 Ultimately, this would give us 766 as the corresponding octal notation to rwx-rw-rw-. Find the command to set the permissions for your files and directories, understand what the octal modes mean - e.g., chmod 777, chmod 400, chmod 4664. Chmod octal file – change the permissions of file to octal, which can be found separately for user, group, and world by adding:.
User/owner (u), group (g), and everyone else/others (o).Permissions can be presented either in numeric (octal) or symbolic notations. Both Octal and symbolic modes. Permissions may be changed later by users and programs using chmod command.
Unix Permissions / chmod Calculator. A numeric file mode is a octal digit from 0 to 7, or a three-bit number, one bit for each of read, write, and execute. Chmod octal value.
View (u)ser, (g)roup and (o)thers permissions for chmod 000 (chmod a-rwx) or use free online chmod calculator to modify permissions easily. Charts and charts have always been very helpful for virtually any kind of project, since they help us imagine the last results and data that we would like to present. Here is the equivalent command using octal permissions notation:.
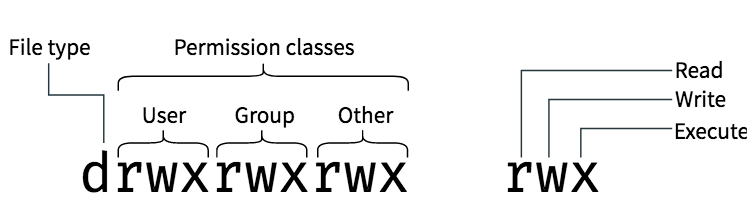
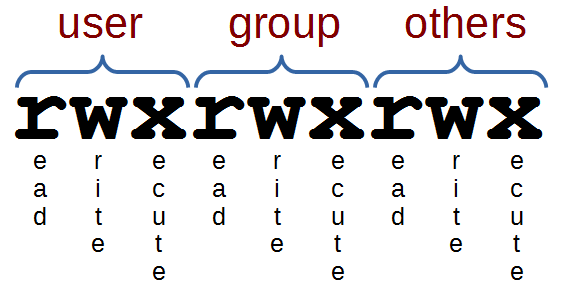
Instead of “u=rwx,go=rx”, you would have “755”. For hexadecimal numbers, values for 10 to 15 are represented by the characters A to F respectively. There are three specific UNIX/Linux file system permissions - read (r), write (w), and execute (x).Permissions are grouped into three sets or triads, each defining access for different scope or class:.
An easier way to specify these 9 bits is with 3 octal digits instead of 9 characters. Chmod¶ The chmod ("change mode") command is used to change the permission flags on existing files. The chmod command is used to alter the permissions of a file.
The owner of the file/directory can read and. The optional leading digit, when 4 digits are given, specifies the special setuid, setgid, and sticky flags. To view these online, enter.
The mode parameter consists of three octal number components specifying access restrictions for the owner, the user group in which the owner is in, and to everybody else in this order. You must be superuser or the owner of a file or directory to change its permissions. The chmod numerical format accepts up to four octal digits.
We will explain the modes in more detail later in this article. The octal notation would be calculated as follows:. The options are set in two file mode bits:.
Chmod special modes Setuid and setgid. Binary executables with the setgid bit (chmod g+s path) can be executed with the privileges of the file's group. Will add execute rights for Owner and Group, but will not modify other existing permissions on the file;.
What is the chmod command?. One component can be computed by adding up the needed permissions for that target user base. So that’s how permissions are displayed in Linux using symbols.
The chmod symbolic notation is more fine-grained compared to the octal notation, allowing the modification of specific mode bits while leaving other mode bits untouched. Set-user-ID (S_ISUID) with the setuid option. Each file on a system has a set of permissions associated with it, users and the related type of access.
4 stands for "read",. Checking the effect of running chmod -R ugo=rwx /local/project-a chmod -R 777 /local/project-a — The result is the same. Chmod calculator is a utility to calculate the numeric (octal) or symbolic value for a set of file or folder permissions in Unix or Unix-like operating systems such as Linux.
When we use the chmod command later on, you’ll see that you can change the permissions using either symbols or octal numbers. Using the chmod command Usage. Chmod all directories to 711;.
Chmod referencesoperatormodes file The references consists of a combination of the letters ugoa, which specify which user's access to the file will be modified:. Octal is a base-8 number system commonly used to represent binary numbers and other numbers in a shorter form. In addition to u, g, and o,.
Or, to add read and write permissions for the group that owns the file, you would run:. The command can accept one or more files and/or directories separated by space as arguments. Man chmod man ls A variable called `umask' is used as a permission mask for all newly created files and directories.
Simply add the values in each section to find the. CHMOD is used to change permissions of a file. For more information, including octal specification of permissions, refer to the Unix User's Manual pages for chmod(1) and ls(1).
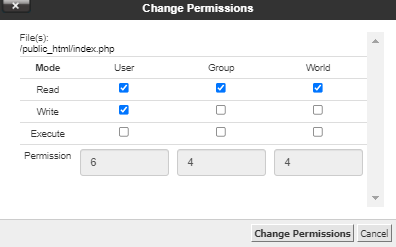
The chart in Table 1 presents numeric values and the associated result for user owner, group owner, and others. The chmod command can be used with either a text-based argument or 3 octal digits (see note 1) to change the permissions on a file.An example of the text-based command to add "read" permission for group members and others to a file named foo is:. Owner (you) Group (a group of other users that you set up) World (anyone else browsing around on the file system) Each digit of this code sets permissions for one of these groups as follows.
Chmod 777 – read, write, execute for all chmod 755 – rwx for owner, rx for group and world For more options, see man chmod. Changing file permissions with chmod command using octal notation. So if you take the octal digit that expresses the permissions in each category, and you line them up in order, you get a three-digit octal number.
Umask is a 3 digit octal number. Use the common Octal notation or UGO notation to quickly assign permissions in a single command. The three digits of the chmod code set permissions for these groups in this order:.
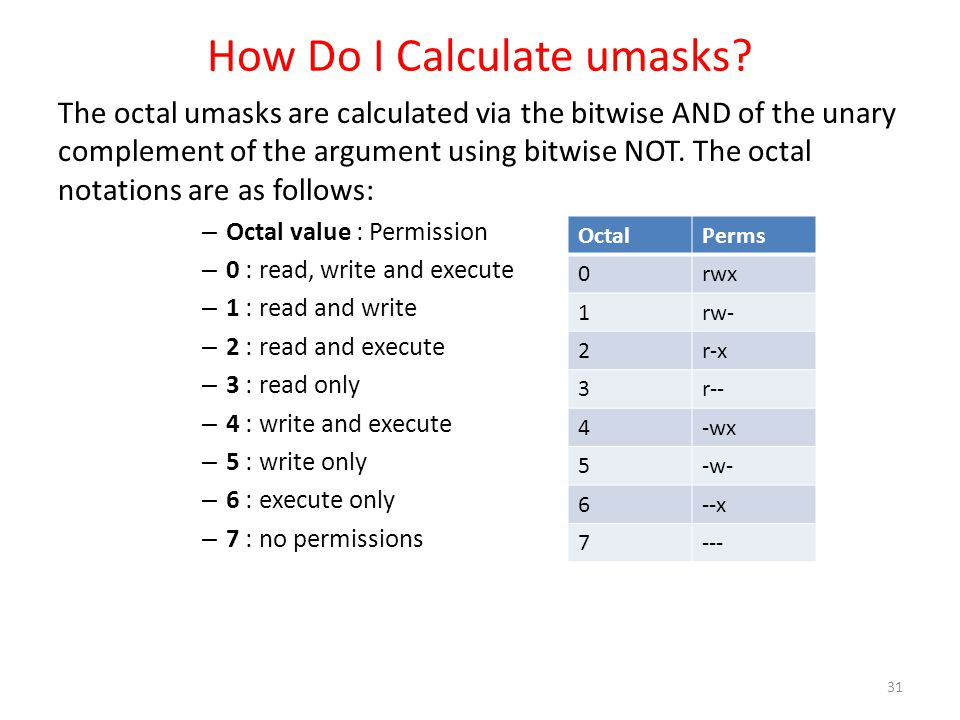
And there you have it:. Remember, there is 4 digits, which correspond to something like "0, user, group, public":. 4 – read (r) 2 – write (w) 1 – execute (x) Examples:.
I propose here an easy manner to "build" this number. Symbolic to Octal Notation Perl Script" was posted on 17/08/07 at 11:58 am and is tagged with Chmod, Code, Linux, Perl Watch this discussion :. /home/user> ls -l foo-rwx--x--- 1 user user 78 Aug 14 13:08 foo /home/user> chmod go+r foo /home/user> ls -l foo-rwxr-xr-- 1.
This quick tutorial shows how to use the stat command to view octal file permissions. Foods high in lectins Source :. It is a confusing topic until you learn it, but it is needed if you plan to work with UNIX or Linux web servers.
Set-group-ID (S_ISGID) with the setgid option. Chmod is a UNIX and Linux command for setting file or directory permissions. To learn more use our calculator and read the references below at the bottom of this page.
A useful property is to set the setgid bit on a directory so that all files and directories newly created within it inherit the group from that directory. Enabling default group write depends on the umask setting). Chmod -R changes filename(s).
It may be used to add or remove permissions symbolically. The mode parameter consists of three octal number components specifying access restrictions for the owner, the user group in which the owner is in, and to everybody else in this order. M) That is, the resulting permission mode (R) is a result of a logical AND operation between the negation of the mask (M), and the requested permission mode (P).
Perfect pushup exercise chart. Rwxrwxrwx) to see its value in other formats. In php, you have to use chmod with octal values, you cannot write something like :.
Chmod all .htaccess files to 644 chmod all robots.txt files to 644;. A superuser or the file owner can use a chmod command or chmod() function to change two options for an executable file. For example, to add execute permissions for the owner of a file you would run:.
To sum up the chart above, all new files created by arnie in /users/project will be owned by the group support when setgid is on (note:. Here the digits 7, 5, and 4 each individually represent the permissions for the user, group, and others, in that order. Chmod all directories that users can upload files to, to 755 (ex:.
The permission in octal form is useful for many commands such as chmod command and other sysadmin tasks. // this is incorrect. The chmod command enables you to change the permissions on a file.
R = P & ( !. The tool will provide you with an octal code that corresponds to these permissions which can then be applied to relevant directories and files with chmod. The chmod command allows you to change the permissions on a file using either a symbolic or numeric mode or a reference file.
Chmod Calculator is a free utility to calculate the numeric (octal) or symbolic value for a set of file or folder permissions in Linux servers. Below is a basic chart of how a binary number is converted to an octal number. In octal, the setgid bit is represented by 00 e.g:.
It can be invoked with either octal values representing the permission flags, or with symbolic representations of the flags. The chmod command uses a three-digit code as an argument. The octal values have the following meaning:.
The first functionality was explained above (in the chmod example paragraph), so let's focus on the other mode. CHMOD Cheat Sheet Dan Flood December 16, 13 Tech Stuff , Unix and Linux Leave a Comment I find myself having to pause and remember exactly what Unix permissions translate to in functionality so posted this handy chart to use. Check the desired boxes to see its value.
$ chmod u+x file_name. Octal (numeric) Permissions Notation. The octal and hexadecimal numbering systems consist of digits ranging from 0 to 7 and ranging from 0 to F respectively.
Number 1 means that you grant execute rights, number 2 means that you make the file writeable, number 4 means that you. Chmod changes the file mode bits of each given file according to mode, which can be either a symbolic representation of changes to make, or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new mode bits. Comments RSS 2.0.
The syntax requires three octal digits, each representing the owner, group, and other permissions, respectively. Select the permissions you require below. CHMOD permissions chart for Linux distros.
The second way to represent the same permissions is by using octal numbers. Absolute Mode - Use numbers to represent file permissions (the method most commonly used to set permissions). From one to four octal digits Any omitted digits are assumed to be leading zeros.
Number 1 means that you grant execute rights, number 2 means that you make the file writeable, number 4 means that you. This video covers the chmod command in depth and everything you want to know about change mode. Using octal syntax for chmod allows setting the absolute permissions for owner, group, and other in one quick command.
There are no relative assignments of permissions using octal. The octal and hexadecimal numbering system are based on sums of the power of 8 and 16 respectively. The three user levels are Owner, Group, and Other.
How to use Check the desired boxes or directly enter a valid numeric value (e.g. Each digit is a combination of the numbers 4, 2, 1, and 0:. Setuid and setgid (short for 'set user ID upon execution' and 'set group ID upon execution', respectively) are Unix access rights flags that allow users to run an executable with the permissions of the executable's owner or group respectively and to change behaviour in directories.
How to set permissions with chmod in octal mode. The resulting permission mode will be:. It can be applied recursively using the "-R" option.
By Vena Treutel Jr. One component can be computed by adding up the needed permissions for that target user base.

Read Write Access Chmod 775

Octal Table 2yamaha Com

Command Line What Is The Difference Between Chmod X And Chmod 755 Ask Ubuntu
How To Change Permissions Chmod Of A File Hostgator Support

A Unix And Linux Permissions Primer Daniel Miessler

Octal Table 2yamaha Com
Buildbot 0 8 10 Documentation
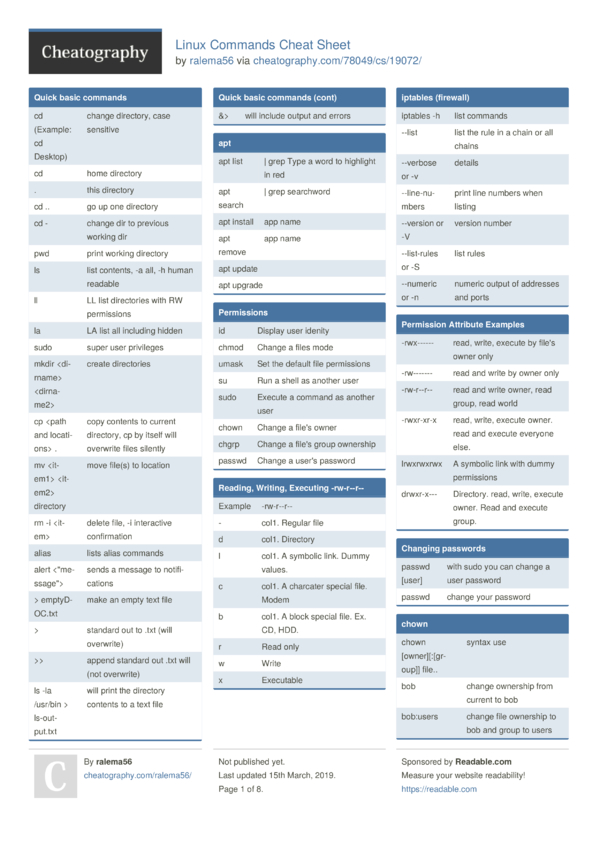
Linux Commands Cheat Sheet By Ralema56 Download Free From Cheatography Cheatography Com Cheat Sheets For Every Occasion

Chmod Calculator App Store Review Aso Revenue Downloads Appfollow

Security Guide Suse Linux Enterprise Server 15 Sp2
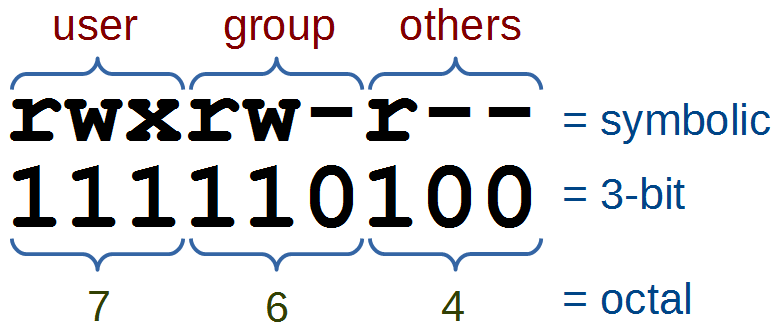
Read Just Enough Linux Leanpub
Buildbot 1 8 1 Documentation
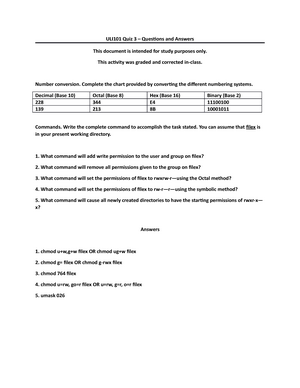
Uli101 Questions And Answers From Quiz 3 Uli 101 Studocu
Omnet Simulation Manual

Catatan Fahmi Lembaran Ilmu Dan Cerita Pengalaman

Two Newly Listed Palm Os Apps
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs J72hjomdluhqe6xjivy M6yrjmkqx9x3z3ps Rpnb8by3w7z Usqp Cau

Security Guide Suse Linux Enterprise Server 15

19b Permissions

Workbook 4 File Ownerships And Permissions Ppt Video Online Download

I M On Pset8 Testing Search Php But This Is The Result To Every Url Cs50 Stack Exchange

40 Best Tutorial For Pisi Linux Images Linux Computer Network Tutorial

Give Write Access Chmod 755

The Unix File System
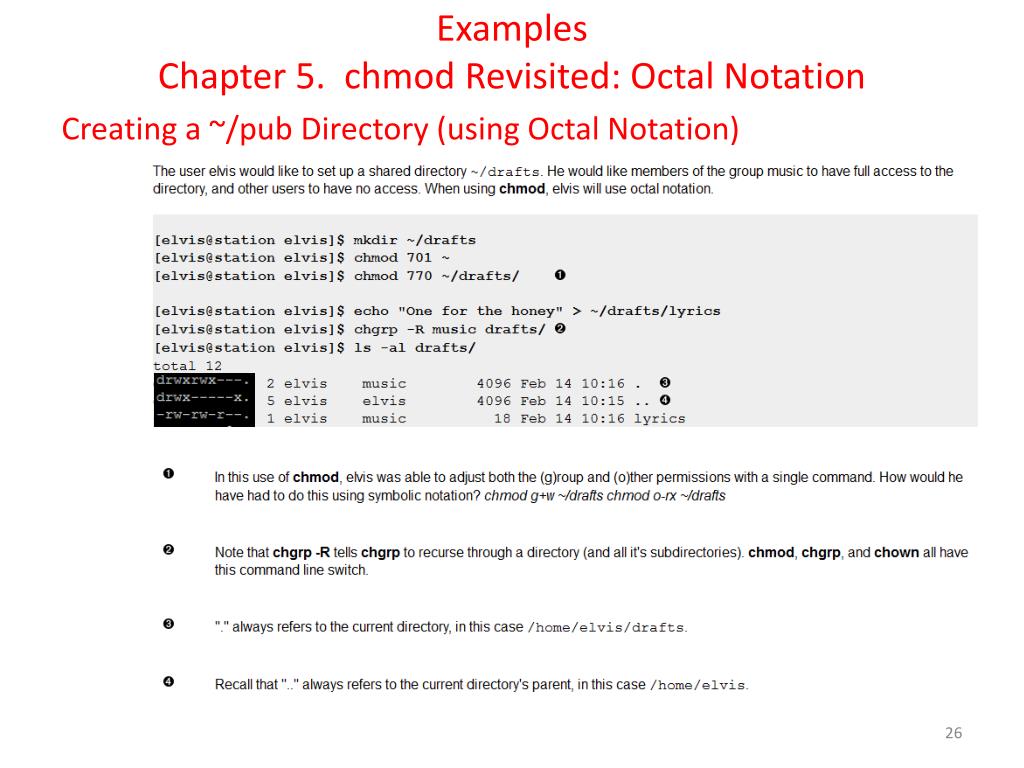
Ppt Workbook 4 File Ownerships And Permissions Powerpoint Presentation Id

19b Permissions

Linuxtutorial Instagram Posts Photos And Videos Picuki Com
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example

An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

Tutorial4 Data Representation Numbering Conversion File Permissions Cdot Wiki

Chmod 600

Thefrugalcomputerguy Youtube
Security Guide Opensuse Leap 15 0
Tip Etf Chart Lcm Ua Org
2

1 Introduction Gmt 6 0 0 R460 Documentation
Security Guide Opensuse Leap 15 1
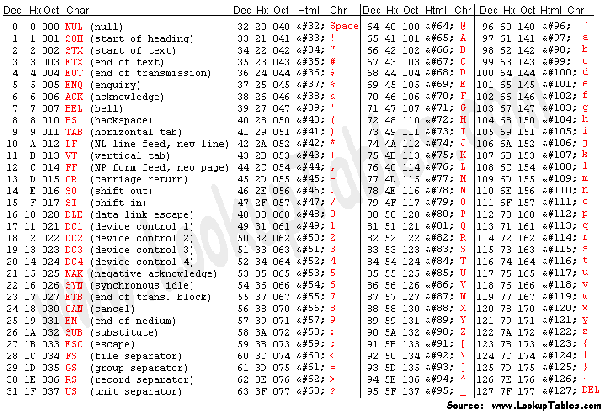
Decimal Hex Octal Binary Chart Skychatz Network Inc
Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

User And Group Permissions With Chmod And Apache
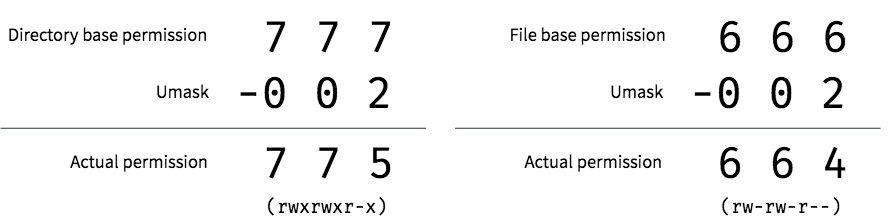
An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

Octal Table 2yamaha Com
1

An Introduction To Linux Permissions Digitalocean
Http Itck Ku Edu Af Linux16 10 file permissions and searching pattern Pdf

10 Linux Unix Command Cheat Sheet 01 Linux Linux Operating System Linux Mint
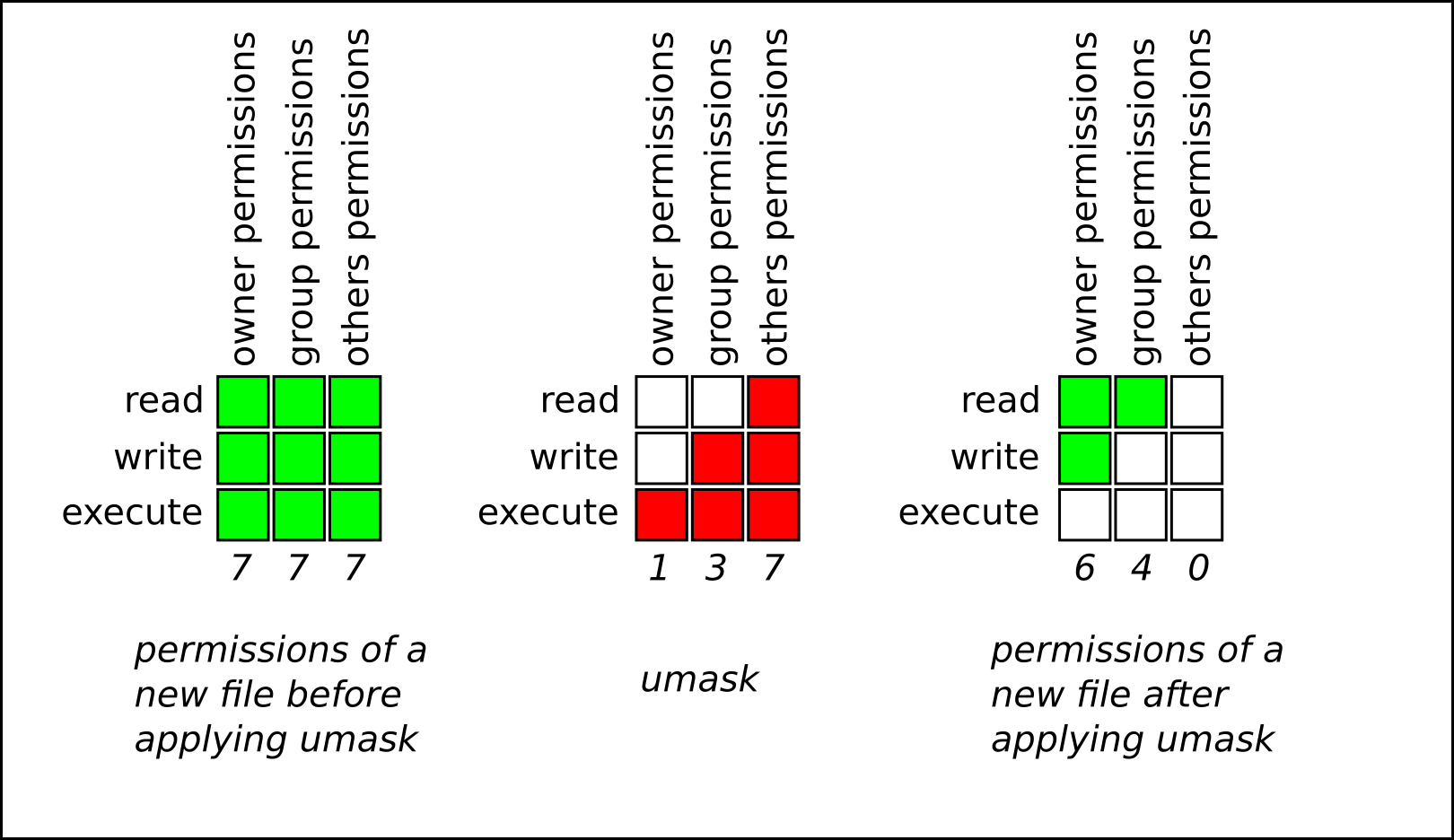
Chapter 5 Managing File Permissions Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 Red Hat Customer Portal

Tutorial4 Data Representation Numbering Conversion File Permissions Cdot Wiki

Chapter 2 Exploring The Unix Linux File Systems And File Security
How To Change Permissions Chmod Of A File Hostgator Support

Unix Linux Command Reference Linux Linux Linux Operating System Linux Mint
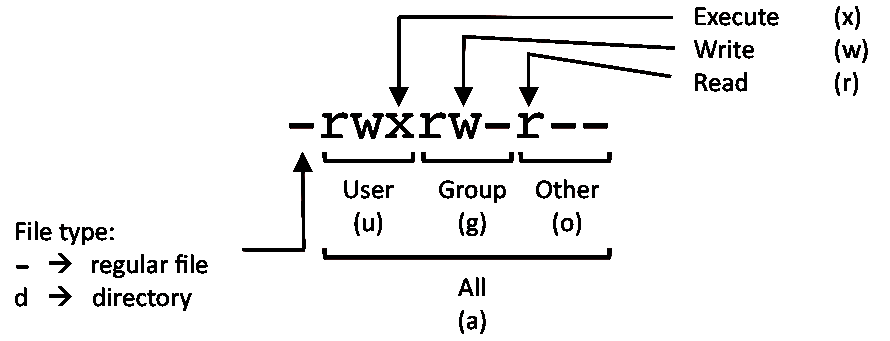
Unix Linux Terminal Javascript Distilled

Octal Table 2yamaha Com
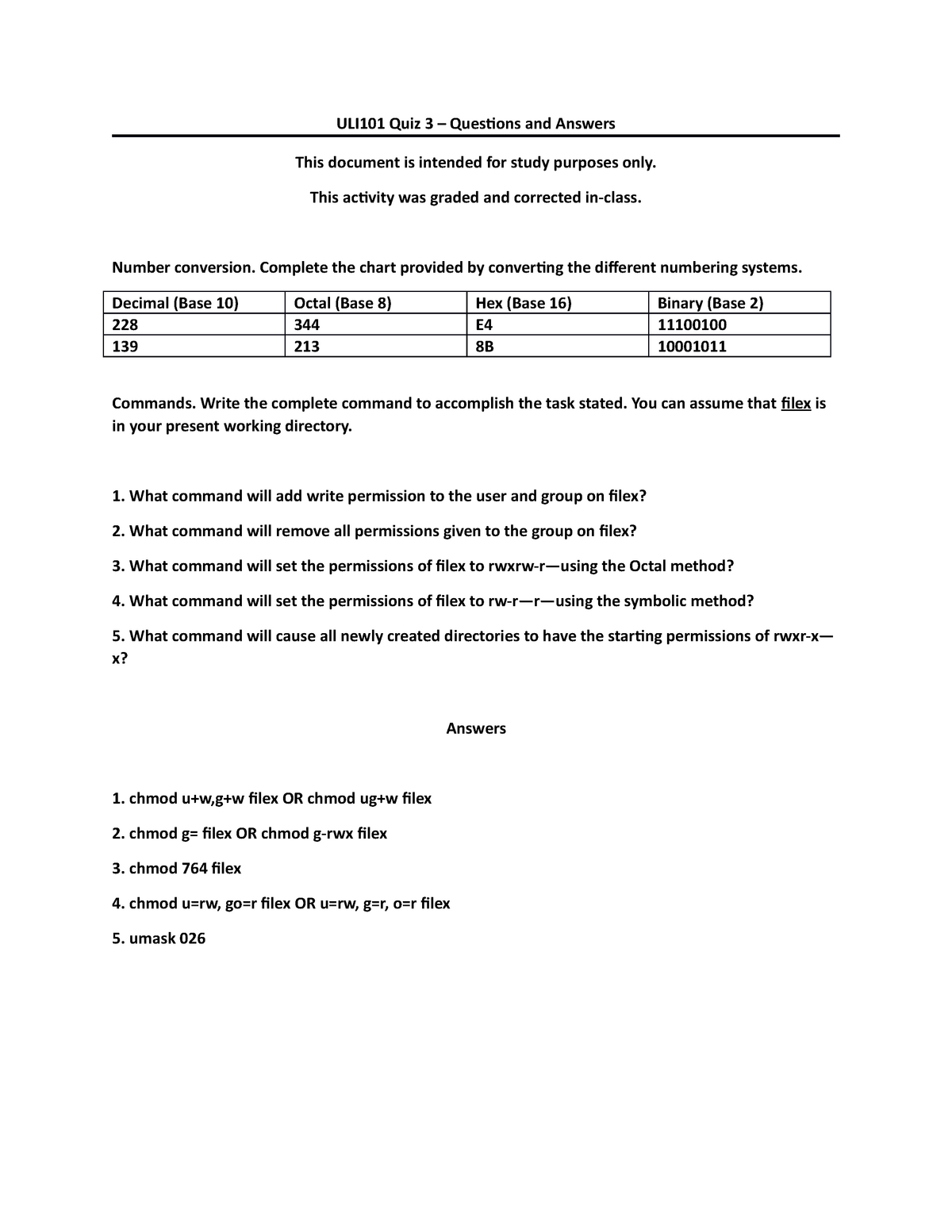
Uli101 Questions And Answers From Quiz 3 Uli 101 Studocu
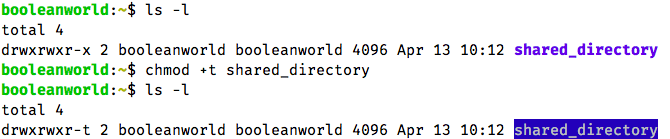
An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

Commandlinefu All Computer File Command Line Interface

An Introduction To Linux Permissions Digitalocean

Chmod Umask Stat Fileperms And File Permissions

Chmod Wikipedia

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

Umask User Mask Or User File Creations Mask In Linux And How To Set Umask Looklinux
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq6mtqrr2tbkvj8mt7j61itbsugnnfl3ltc9cdgqfgdswx0kkor Usqp Cau

Ppt Workbook 4 File Ownerships And Permissions Powerpoint Presentation Id
Thefrugalcomputerguy Youtube
777 Chmod Unix File

Workbook 4 File Ownerships And Permissions Ppt Video Online Download
Workbook 4 File Ownerships And Permissions Ppt Video Online Download
Tip Etf Chart Lcm Ua Org

Slae 5 Reverse Engineering Shellcode For Linux X86 Dmfr Security
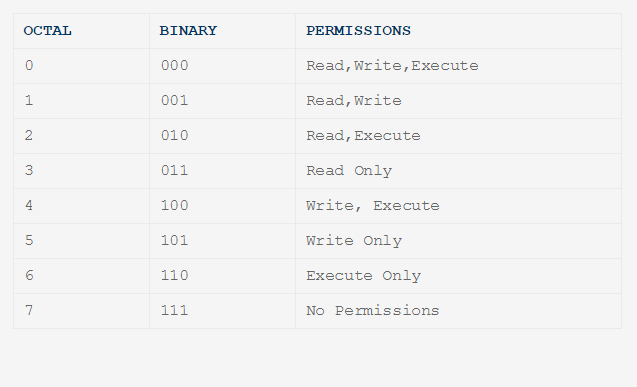
Chmod Directory Read Write And Type
Tip Etf Chart Lcm Ua Org

Tutorial Acrl Techconnect

File Security
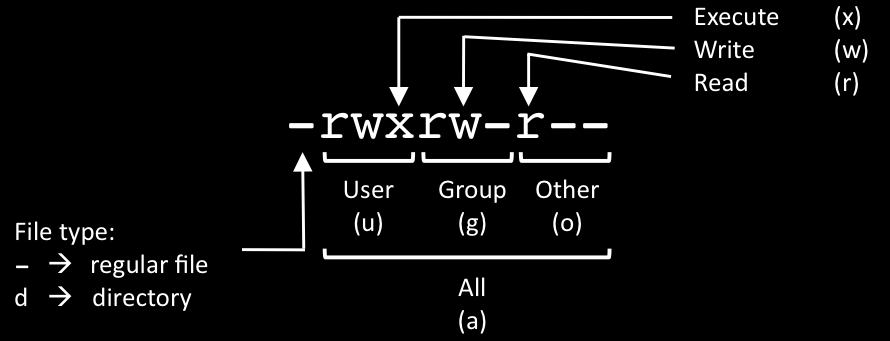
Chmod Cheat Sheet Dan Flood
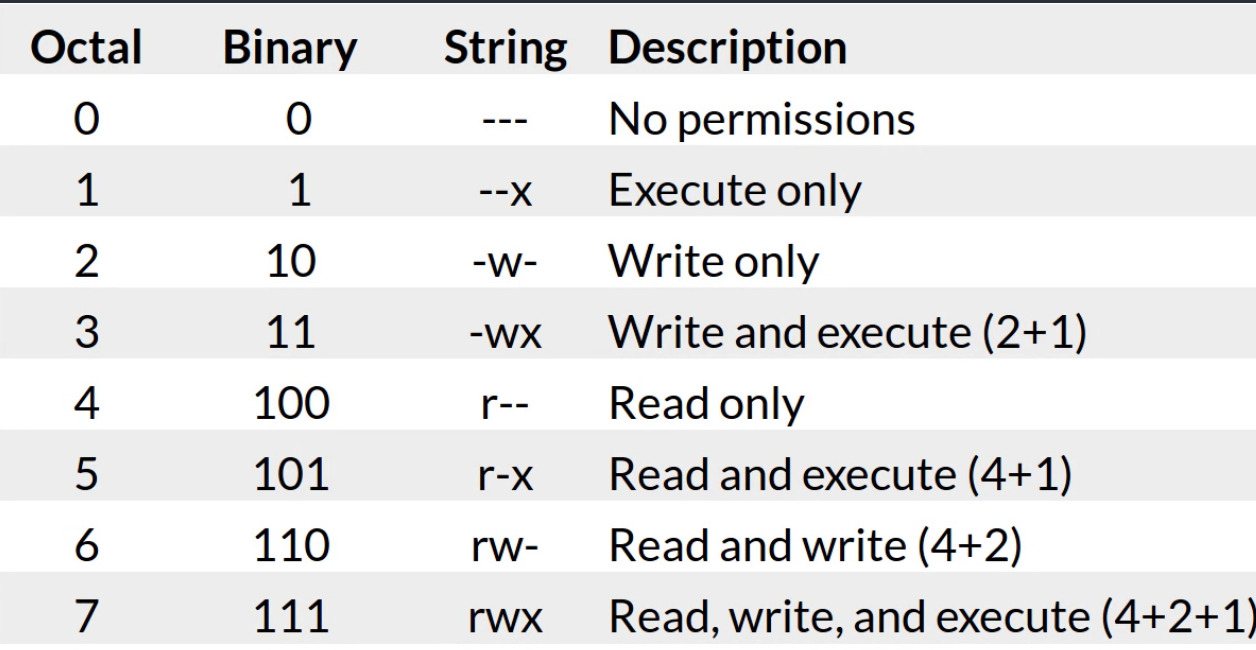
Adrian S Programming Blog

Linux Admin 101 File Permissions With Chmod Chgrp And Chown Trash Computer
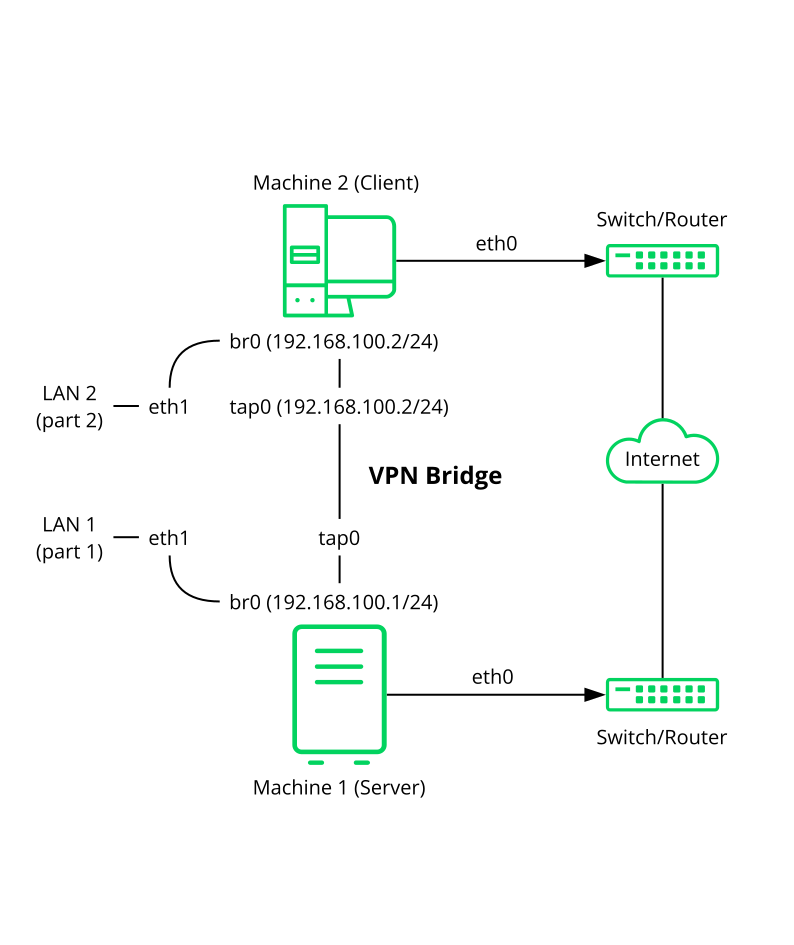
Security Guide Suse Linux Enterprise Server 15 Sp2

Everything About Chmod Command In Linux Hackerearth
Decimal Hex Octal Binary Chart Skychatz Network Inc
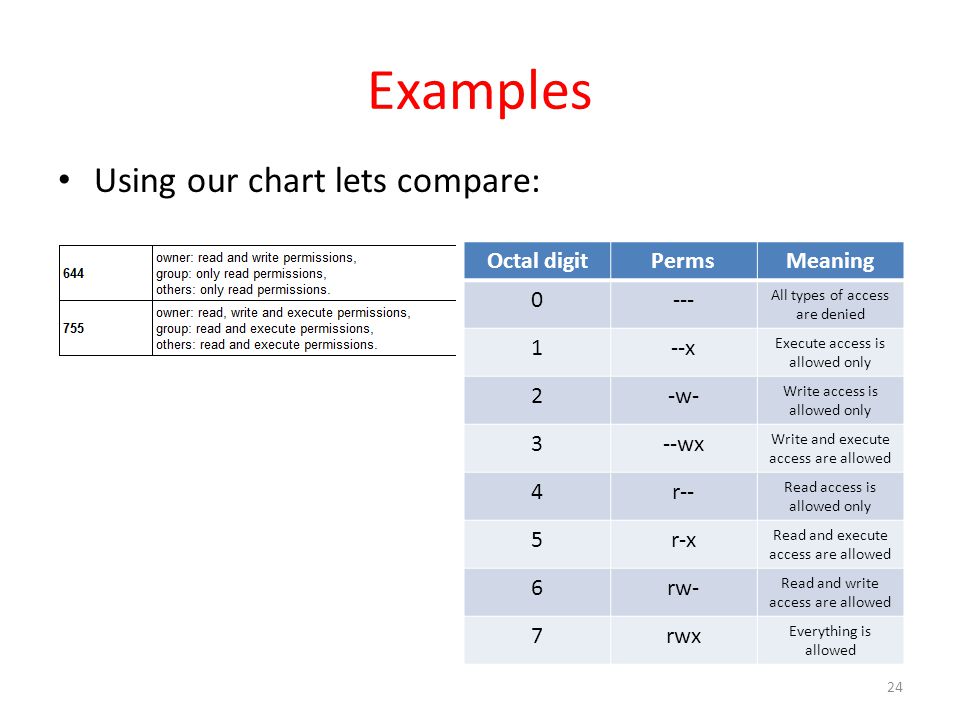
Workbook 4 File Ownerships And Permissions Ppt Video Online Download

Tutorial Acrl Techconnect

Unix Permissions
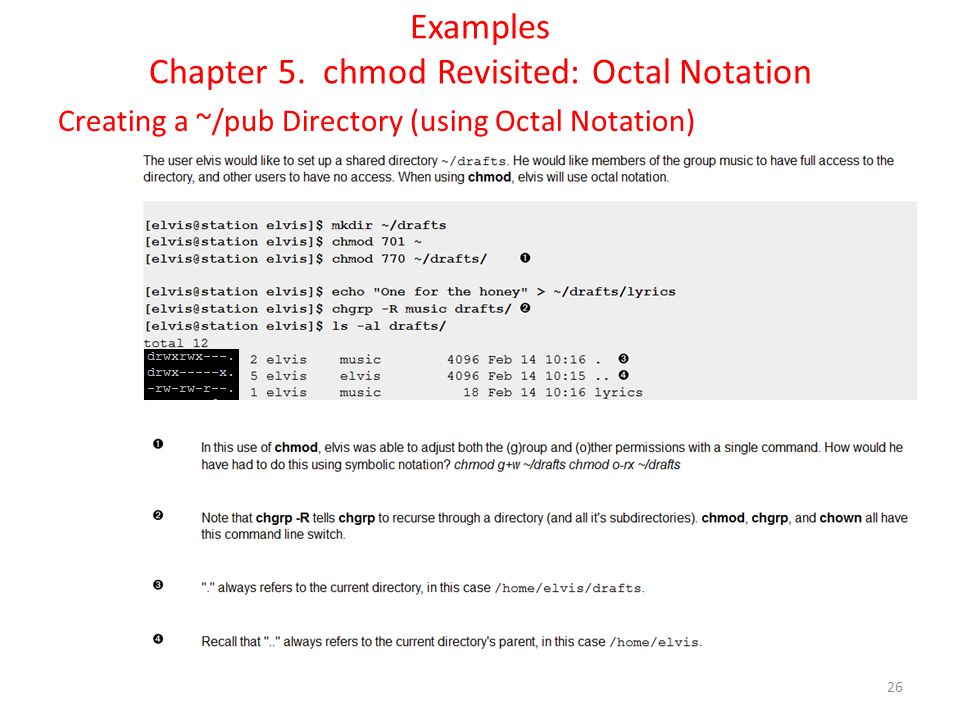
Workbook 4 File Ownerships And Permissions Ppt Video Online Download

Tip Etf Chart Lcm Ua Org

Pin By Dr Stefan Gruenwald On Cheatsheets Computer Science Programming Learn Javascript Linux Operating System

Tutorial4 Data Representation Numbering Conversion File Permissions Cdot Wiki

Linux Gazette July 08 152
Tip Etf Chart Lcm Ua Org

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod
Q Tbn 3aand9gcqzjwejtv9wexgnjg6wrv4scdirjlf8ko Drmhmencfjup H30u Usqp Cau

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

Setting File And Directory Permissions Computational And Information Systems Laboratory

Octal Table 2yamaha Com

Linux Permissions Deep Dive Part 1 By Runcy Oommen Medium

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

Unix Chmod Cheat Sheet Computer Science Programming Learn Javascript Linux Operating System

Linux Command Line Cheat Sheet Kalitut



