Chmod Command In Linux To Change Permissions

How To Change Permissions Folder And All Its Subfolders And Files In Linux

Linux File Permission Javatpoint
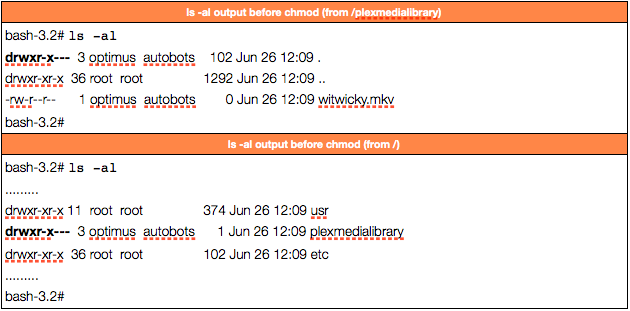
Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

Chmod Command In Linux Operators Used In Chmod Command

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod
1
Discover chmod and chown for configuring this.

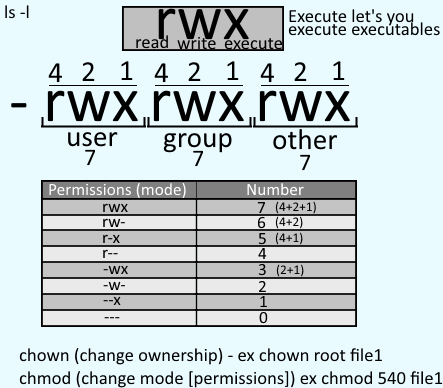
Chmod command in linux to change permissions. As Linux administrator, we always use chmod command to change file permissions in Linux. Access permissions specify whether a user account or group can read, write, or execute a given file and directory. Permissions used to be called mode of access and hence chmod was the short form of change the mode of access.
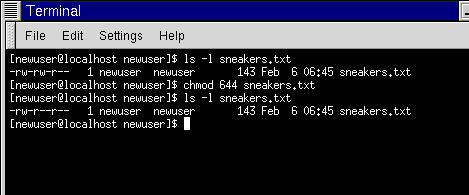
It allows the permissions to be changed in either Symbolic form or in numerical form. The second string shows the number of links that exist to the file. To change permission of only files under a specified directory.
This Linux option allows you to change permissions or owners of all files and subdirectories inside a specific directory. To change the mode of a file, use the chmod command. We can use two ways of calling chmod, symbolic or octal notation.
File access permissions can be modified via the chmod command. Owner, group, and everyone. Chmod command is used to change access permission of files and directories in Linux operating systems.
In this tutorial, we will discuss how to change file permissions in Linux using chmod command. The overall syntax to recursively change the file’s permissions is as follows:. Linux grants three different types of permissions — read, write, and execute — for three different scopes:.
The chmod command in Linux/Unix is abbreviated as CHange MODe. There will be a Permission tab where you can change the file permissions. Actually, chmod Command in Linux plays a greater role to keep all the files and directories of the system safe and secure so that no unauthorized person can change, modify or delete content of any files or directories.
The first digit contains the permissions for file owner, 7 is the octal code in which the permissions are set for the owner:. Chmod is a command in Linux and other Unix-like operating systems that allows to change the permissions (or access mode) of a file or directory. $ chmod 0 sample.txt Write by anyone $ chmod 002 sample.txt Execute by owner only $ chmod 100 sample.txt Execute by group only $ chmod 010 sample.txt Execute by anyone $ chmod 001 sample.txt Allow read permission to owner and group and anyone.
Chmod Recursive # The chmod command means that you can change the permissions of recordsdata utilizing symbolic or numeric mode. To change the permissions of a file, one uses the chmod command, with the following syntax:. A command line / terminal window ( Ctrl + Alt + T or Ctrl + Alt+F2) A user account with sudo privileges (optional) A Linux system.
Permissions (access modes) can be changed with the chmod command by using some operators (-, + or =) to assign permissions (r, w or x) to a specific user (u, g, o or a). In my previous blog post I discussed how Linux file permissions work, and now I am going to discuss how to change permissions using chmod. Characters 8-10 for all others.
The chmod command allows you to change the permissions of files using symbolic or numeric mode. These flags are called file permissions or modes, as in "mode of access." The command name chmod stands for "change mode." It restricts the way a file can be accessed. $ chmod 777 -R /path/to/Dir To assign reasonably secure permissions to files and folders/directories, it's common to give files a permission of 644 , and directories a 755 permission, using the find command and a pipe we can target just files.
What is Linux chmod Command?. I have already tried the below command but it works only for the mentioned folder:. The command can accept one or more files and/or directories separated by space as arguments.
One set for the owner of the file, another set for the members of the file’s group, and a final set for everyone else. The third string identifies the owner of the file and the fourth string tells what group the owner of the file is in. 1) Change permissions using Numeric (octal) method.
Chmod stands for change mode. We will explain the modes in more detail later in this article. The command that executes such tasks is the chmod command.
One of the most popular options that you can combine with chmod and chown is -R (Recursive). You can change the permissions on a file with the chmod command. Characters 5-7 similarly show the permissions for the group;.
To recursively function on all recordsdata and directories below a given listing, use the chmod command with the -R, (–recursive) choice. $ chmod 444 sample.txt Allow everyone to read, write, and execute file. Chmod u=r assgn1_client.c AFTER:.
The MKS version of chmod tries to handle options in a way that parallels the POSIX approach. Change file permissions in Linux. Both forms can be interchangeably used.
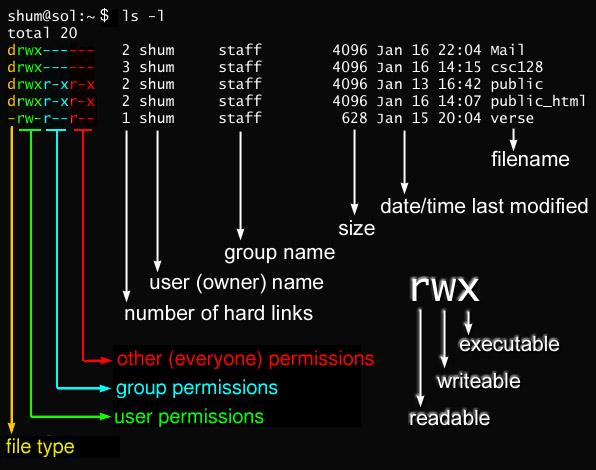
-r--rw-r-- mik mik assgn1_client.c Before :. We explained the chown and chmod command for Linux and Unix users. In Unix and Unix-like operating systems, chmod is the command and system call which is used to change the access permissions of file system objects (files and directories).It is also used to change special mode flags.
More Information on. The references are shorthand (u, g, or o) for each class. Conclusion # You successfully learned how to use chmod command to set or change the file and directories permissions using either the symbolic or numeric mode.
$ chmod 777 sample.txt. To change file access permissions you need to use the chmod command. This can be achieved by changing file permissions.
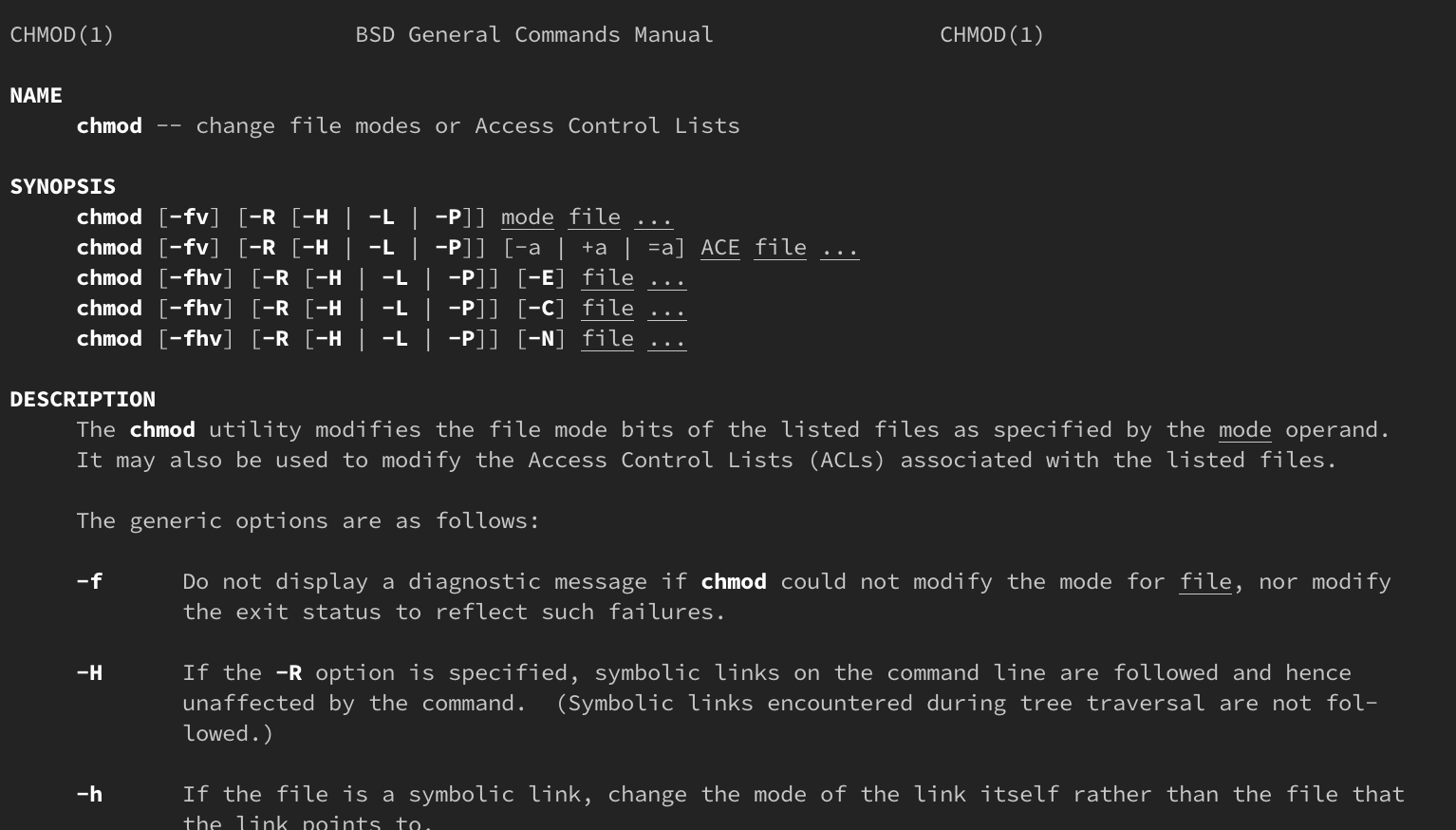
Only the object owner, superuser or root account can change the permissions of a file/folder. Chmod 0000 chmod o=s chmod 00 chmod g=s chmod =s chmod 4000 chmod u=s chmod =h chmod 6000 chmod a=s chmod ug=s chmod =hs Note:. The chmod command stands for “change mode”, and allows changing permissions of files and folders, also known as “modes” in UNIX.
In Linux, who can do what to a file or directory is controlled through sets of permissions. In the terminal, the command to use to change file permission is chmod. The general syntax to recursively change the file’s permissions is as follows:.
It could be a single file or multiple files. If it’s in the same directory, you may need to use chmod command with file name and new file permission to be applied. Below is the command's general structure:.
Chmod 775 /opt/lampp/htdocs Is there a way to set chmod 755 for /opt/lampp/htdocs and all of its content including subfolders and files?. Read, write, execute 0:. This type of restriction is useful for effective file/folder management, securing system and providing a level ….
To change the permissions — or access mode — of a file, use the chmod command in a terminal. To assign reasonably secure permissions to files and folders/directories, it's common to give files a permission of 644, and directories a 755 permission, since chmod -R assigns to both. In short, “chmod 777” means making.
Option is an additional command to change the output of a command. Changing file/directory permissions with 'chmod' command. Use sudo, the find command, and a pipemill to chmod as in the following examples.
How to Change Groups of Files and Directories in Linux. The Linux command to change permissions on a file or directory is chmod, which we like to read as change file mode. Chmod ugo+rwx foldername to give read, write, and execute to everyone.
Linux file permissions are determined by who owns the file and the visibility of that file to various users. The chmod command can be used with octals (as. Chmod command allows you to alter / Change access rights to files and directories.
Chmod a=r foldername to give only read permission for everyone. The chmod command allows you to change the permissions on a file using either a symbolic or numeric mode or a reference file. It may happens many times in a day, it depends on your environment size and team size.
Chmod command is used to change the permissions of files and directories in Linux. In this article, I will take you through 11 Popular Unix/Linux chmod command examples to Change File Permissions. It has -R or –recursive option that change files and directories recursively.
Setting File Permissions in Command Line. This command is used to view your files with what permission they are. (See p 759 in the book, A Practical Guide to Linux, for more information on this command.) It is important that in most cases, it makes no sense to set permissions on yourself more restrictive than group or other, therefore:.
Chmod 707 myfile chmod – is the command to change permissions 7:. How to Use the chmod Command in Linux Command Syntax. File/Directory permission is either Read or Write or executable for either user or group or others.
The chmod command in Linux is used to change file and directory permissions using either text (symbolic) or numeric (octal) notation. How To Change File Permissions In Linux Using ‘chmod’ Command The highly productive Linux system offers various levels of permission to ensure that the user has enough ways to interact with files and directories. I would like to change permissions of a folder and all its sub folders and files in one step (command) in Linux.
The request is filtered by the umask.The name is an abbreviation of change mode. Users can simply modify file permissions using the chmod (change mode) command. You can use chmod in the command line to change file or directory permissions on unix or unix-like systems such as linux or BSD.
The chmod command allows you to change the permissions on a file using either a symbolic or numeric mode or a reference file. The chmod command lets you change the permissions for a Linux file. File Permission is given for users,group and others as, SYNTAX :.
Chmod command is useful to change permission for Files and folders in Linux/Unix. Change permission on all the files in a directory recursively. Chmod 466 filename does not make sense (see below).
It takes the following syntax:. We will explain the modes in more detail later in this article. The chown command can be used to change user and group permission.
To recursively operate on all files and directories under a given directory, use the chmod command with the -R, (--recursive) option. -rw-rw-r-- mik mik assgn1_client.c COMMAND:. Before explaining the syntax of the chmod command, you need to look at the cryptic way Linux reports file permissions.
The operator determines whether to add (+), remove (-) or explicitly set (=) the particular permissions. I strongly suggest that you read man pages by typing the following man. The exact command is.
To change permission using the Linux chmod command we have to follow some syntax and rules. Chmod Modifies File Permissions. In the following list, each line shows a group of calls that are equivalent.
Below is a list of numerical permissions that can be set for the user, group, and everyone else on the. You might have heard of chmod 777. The name chmod is short for “change mode”.
The chown command stands for “change owner”, and allows changing the owner of a given file or folder, which can be a user and a group. $ chmod ug=rw /var/www/html/data.php See “how to use change user rights using chomod command” for more information. Using the command, we can set permissions (read, write, execute) on a file/directory for the owner, group and.
On Unix-like operating systems, a set of flags associated with each file determines who can access that file, and how they can access it. The second digit contains the permissions for group members, 0 is the octal code that is set is to no permissions amongst the members. Using Chmod Command to Change File Permissions As all Linux users, you will at some point need to modify the permission settings of a file/directory.
Chmod is the command used to change the permissions of an object, and is short for “CHange MODe”. In Linux, you can easily change the file permissions by right-clicking the file or folder and select “Properties”. Let’s change the assgn1_client.c permission so that the owner cannot write(w) in the file but can only read it.
Chmod means ‘change mode’ and it changes file or directory mode bits (the way a file can be accessed). The permissions control the actions that can be performed on the file or directory. The first 7 sets the permissions for the user, the second 7 sets the permissions for the group, and.
To change directory permissions for everyone, use “u” for users, “g” for group, “o” for others, and “ugo” or “a” (for all). We can use the 'chmod' command which stands for 'change mode'. The letter or letters representing the owner (u), group (g), other (o) or all (a) followed by a + for adding permissions or a – for taking away permissions and then the letter for the permission (r for read, w for write and x for execute).In the above example, I added the execute permission for all users.
The basic syntax is:. To make a file readable and writable by the group and others. The syntax is as follows:.
Chmod -R MODE DIRECTORY. Following color coding is used to describe the content better in applying chmod command in Linux. You can use chmod command for changing the permissions on a file in Linux.
Chmod -R 755 directory chmod 777:. In this file example, sets read and write permissions for user and group:. Say you do not want your colleague to see your personal images.
$ chmod OPTIONS MODE filename Only the root user or a regular user with sudo privileges can change file or directory permissions. There are two ways to use the chmod command:. The third digit contains the.
The command can accept one or more files and/or directories separated by space as arguments. Chmod A quick guide to the `chmod` command, used to change the file mode Published Sep 23, Every file in the Linux / macOS Operating Systems (and UNIX systems in general) have 3 permissions. Chmod has two operating modes:.
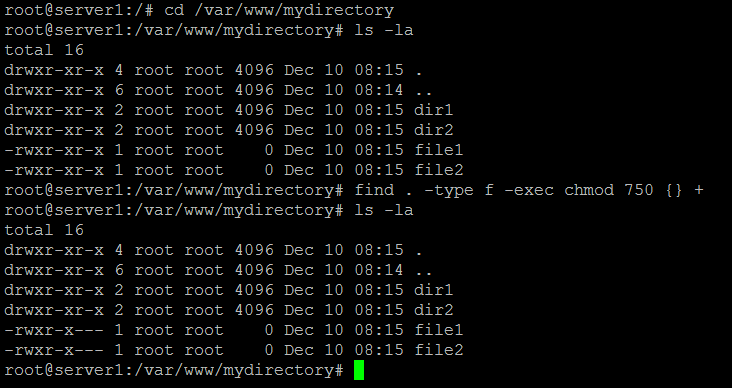
Chmod -R will change all the permissions of each file and folder under a specified directory at once. Donotprint /donotprintThe find command can be used to find files and directories.

Unix Permissions

How To Change Permissions In Linux

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples
.png)
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq1nsq3kxri7ryrifobs2rfobawbv4hezfw9 Ldf4feblahyn09 Usqp Cau
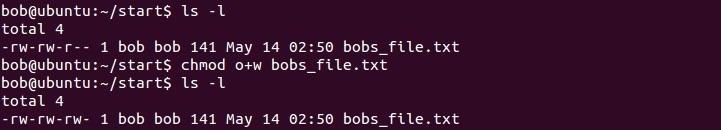
Modify File Permissions Linux

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission

An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight
Q Tbn 3aand9gcr2lfpzbutqythmvbwafnxvyggqfj7hnw6fhh Kcozkk8m5 V7o Usqp Cau

Directory How Can I Change Permissions Of A Folder Including Its Enclosed Files And Subdirectories Ask Ubuntu

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

Linux Users And Groups Linode
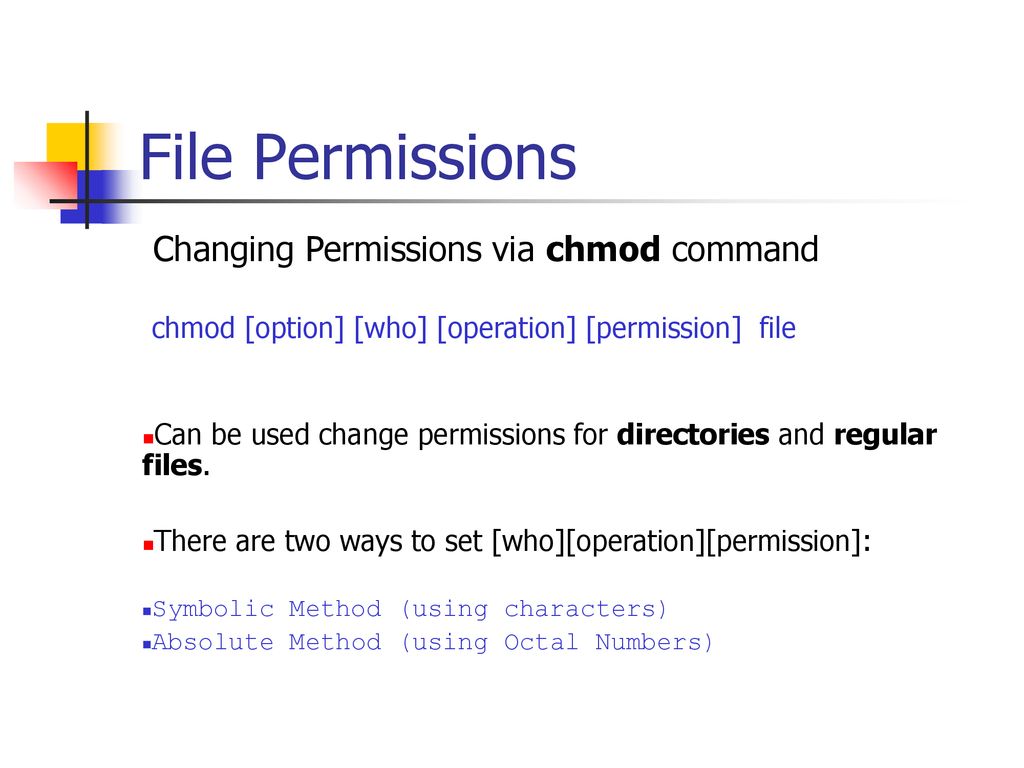
Bif703 File Permissions Ppt Download

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

Change File And Folder Permission On Ubuntu Chmod Chown Command In Linux Youtube

Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu
/GettyImages-1021092796-ea8c63ee76f84bd5bf98c4222337fbb4.jpg)
How To Use The Chmod Command In Linux

Linux Unix Permissions And Attributes Linuxsecrets

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission

How To Set File Permissions In Mac Os X Macinstruct

Changing File Permissions Wordpress Org

Restore Executable Permission To Chmod Command In Linux Ostechnix
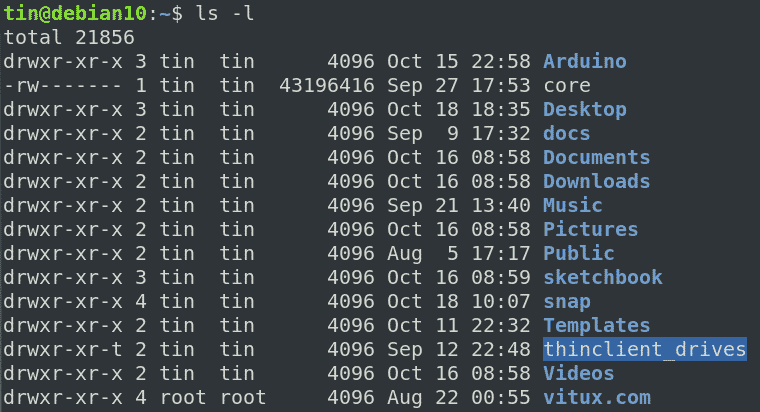
Change File Permissions Recursively Linux Linux Hint

How To Change File Permissions Hostwinds Guides

Chmod Cheatsheet Linux

Some Helpful Linux Commands Recently For A Coding Challenge I Was By Kate Schlunz Medium

Introduction To Linux File Permissions Attributes Chmod Globo Tech
Freekb Linux Commands Chmod Change A File Or Directory Standard Permissions

Linux File Permission Change By Chmod Command In Linux Guide For Beginners

Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux
.png)
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example

Linux File Permissions Tutorial For Beginners

Linux Terminal File Permissions Chmod Chown And Chgrp Youtube

How To Change Permissions In Linux

Linux File System Nevigation Filing System Reading Writing Linux

How Do Linux File Permissions Work
How To Deny File Permissions To Everyone Except Yourself In Linux Linuxhostsupport

How Do Linux File Permissions Work

Setting File And Directory Permissions Computational And Information Systems Laboratory

Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

Changing File Permissions In Linux The Chmod Command By Saswat Subhajyoti Mallick Medium

Linux Commands Chmod

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission

Permissions Why Use Chmod Instead Of Chmod U Rw Go R Unix Linux Stack Exchange

A Unix And Linux Permissions Primer Daniel Miessler

Linux Chmod Example Linux Hint
Javarevisited 10 Example Of Chmod Command In Unix Linux
Q Tbn 3aand9gcr9rnnth31jdnr94db Zmbdt5bh907clokeeor9me5yqbuufaiw Usqp Cau

Linux Chmod Chown Syntax And Chmod Chown Examples

How To Change Permissions And Owners Via Linux Command Line

Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
How To Change Permissions Chmod Of A File Hostgator Support

What Does Chmod 777 Mean Linuxize

11 Popular Unix Linux Chmod Command Examples To Change File Permissions Cyberithub

Understanding Basic File Permissions And Ownership In Linux The Geek Diary

Linux Chmod Command Help And Examples

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command In Linux
How Do Linux Permissions Work

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

Command Line I Can T Change Mode For Some Directories Using Chmod Ask Ubuntu
Fun With Numbers In Chmod

Chmod Permission Denied Unix Linux Stack Exchange

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/i7guGwCYcn-34e068e148ae4e918b29c86cd2d5740e.png)
Configuring Unix Linux File And Directory Access Rights

Unix Linux Access Permission Bits

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

Use Of Chmod Command In Linux Devopsdex
An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

Chmod Calculator Chmod Generator Chmod Command

How To Use The Chmod Command 2 Minute Linux Tips Network World

Change Ownership And Rights To Files And Folders In Linux Smashing Lab

How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux

08 Unix Linux Shell File Directories Permission Chmod Command Youtube

Chown And Chmod Command Usage In Linux System Develop Paper

Linux Chmod Command Tutorial With Examples To Change Permission Of Files And Folders Poftut

8 Linux Chmod Command Examples To Understand It The Linux Juggernaut

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

Chmod Wikipedia

Chmod Command In Linux File Permissions Linuxize

Unix Linux Os X File Permissions

Explained How To Use Chmod Command Complete Guide Youtube

Linux Commands 5 File Permission Chmod Youtube
How To Chmod Files Only On Linux

How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux

Chmod Command In Unix Learn Unix Online Fresh2refresh Com

Ownership And Permissions

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight



