Chmod 777 Command In Linux Syntax
Linux Commands In Structured Order Diaxeirish Linux Server Design Host

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks
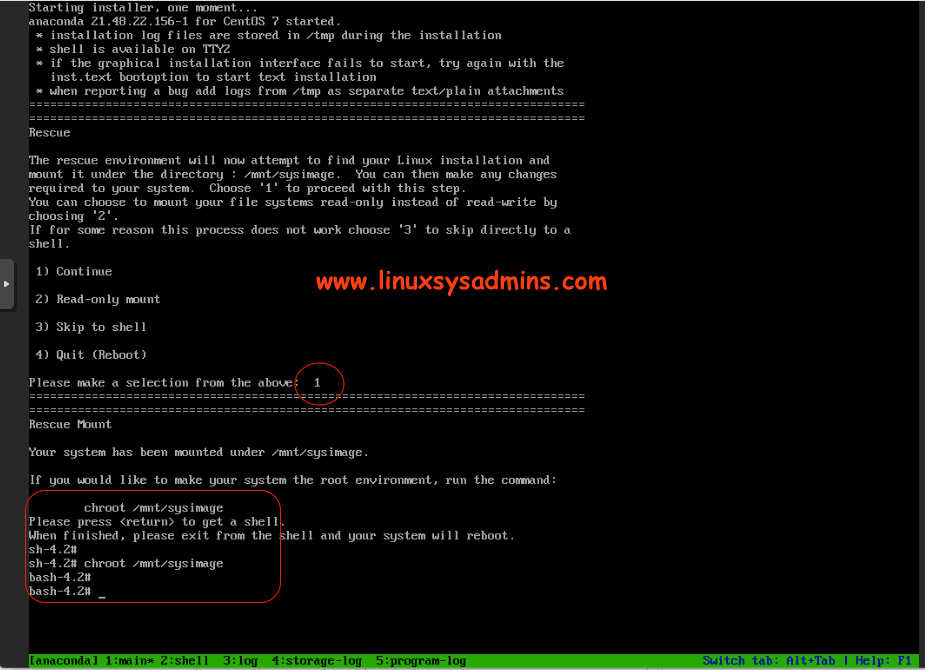
Recover From Chmod 777 Permission On A Root Filesystem

What Does Chmod 777 Mean Linuxize

Linux Chapter 3 Permission Management Commands Change File Permissions Chmod 777 Root A Programmer Sought
Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions
Chmod is a command used to change those file permissions and controls in terminals.

Chmod 777 command in linux syntax. Linux file permission is a very important aspects in terms of security issues for the system administrator of Linux Operating System. The chmod command stands for change mode… and it’s used to limit access to resources…. In my previous blog post I discussed how Linux file permissions work, and now I am going to discuss how to change permissions using chmod.
This command modifies Linux file permissions, which look complicated at first glance but are actually pretty simple once you know how they work. Representations used for File permission. There are three basic modes to files and directories:.
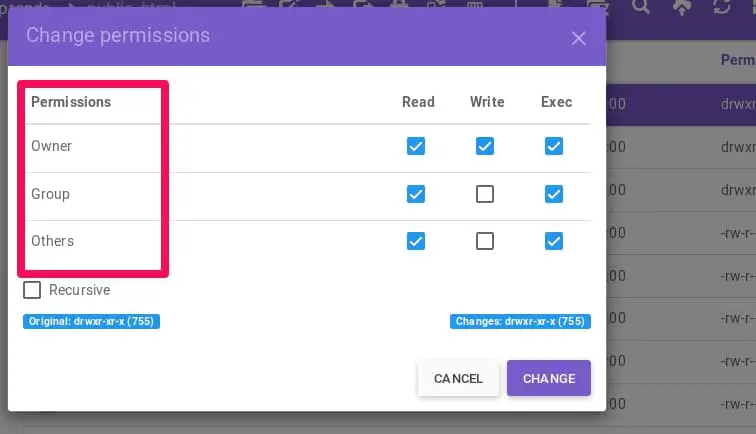
Set the permissions of file.htm to "owner can read and write;. By using this command, we can set the read, write, and execute permissions for all three of the permission groups (Owner, Group and Other) in Linux. The references are used to distinguish the users to whom the permissions apply i.e.
To change the permissions of the file participants so that everybody has full access to it, enter:. Denotes the access given to others other than the user or group. The chmod command has also been ported to the IBM i operating system.
The version of chmod bundled in GNU coreutils was written by David MacKenzie and Jim Meyering. Actually, chmod Command in Linux plays a greater role to keep all the files and directories of the system safe and secure so that no unauthorized person. In short, “chmod 777” means making the file readable, writable and executable by everyone.
Chmod never changes the permissions of symbolic links;. $ chmod u+x file.txt. I used to work with linux command in the University and after a pause of few years… it brought me back to ‘beginers mode’ when I needed to use chmod.
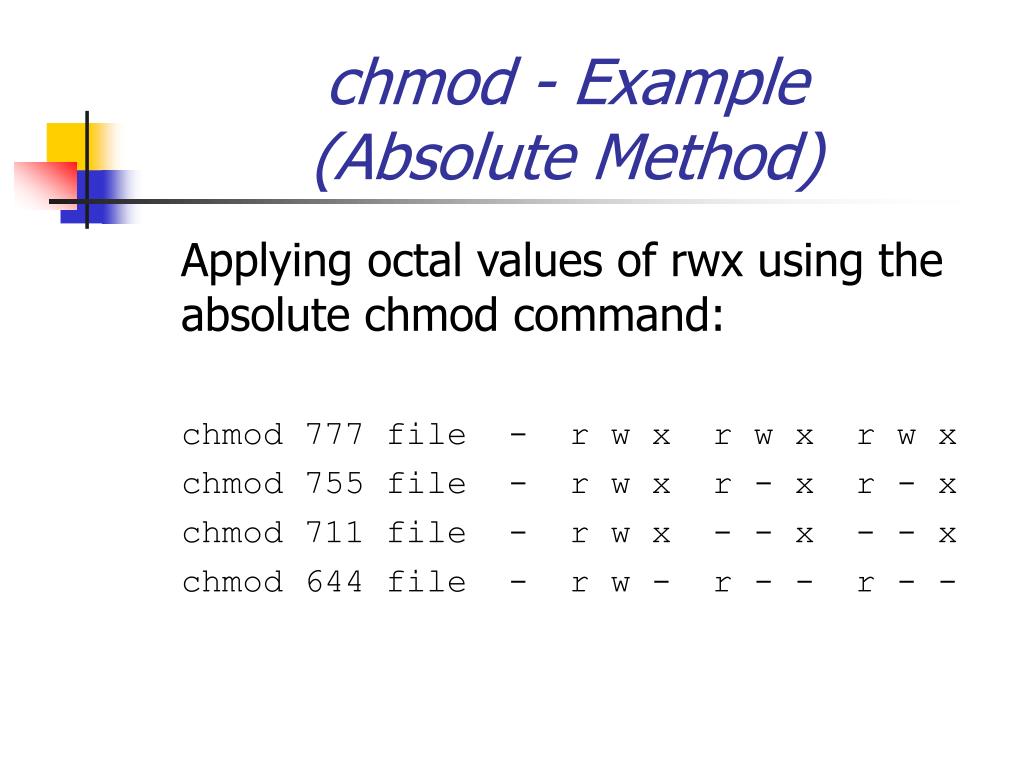
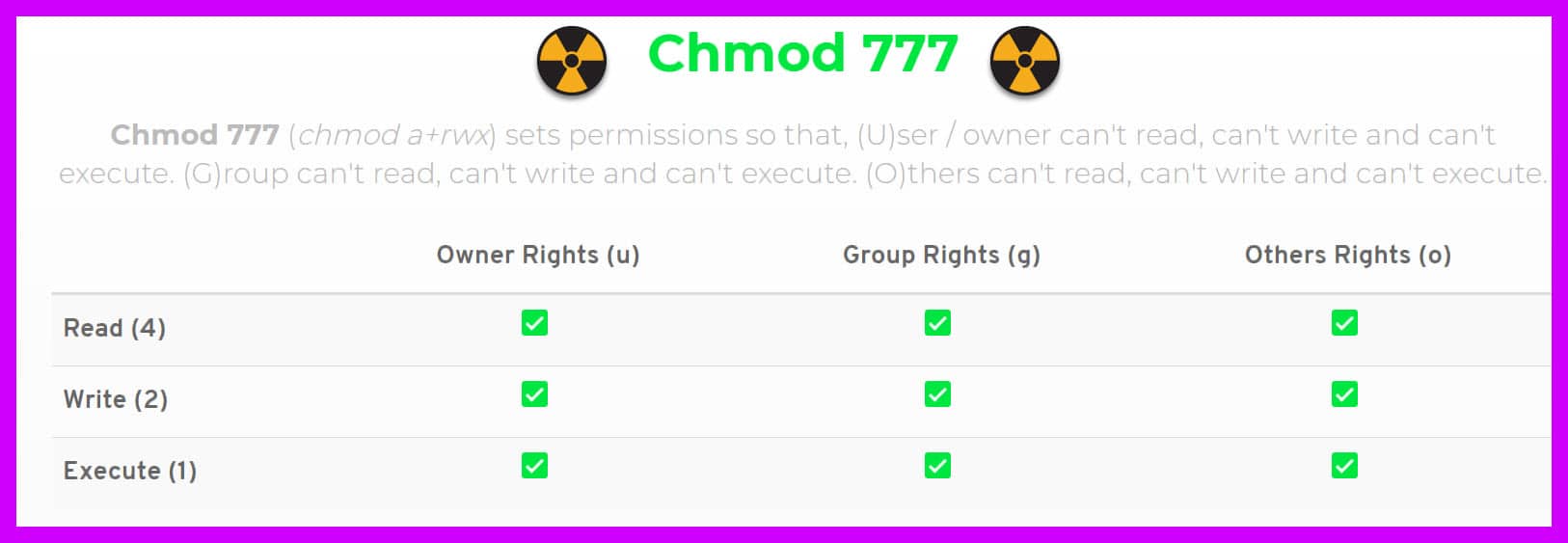
The chmod Linux command is used to change the access mode (aka file system permissions) of one or more files (or directories) only the owner or a privileged user may change the mode. (G)roup can read, can write and can execute. $ chmod 777 file.txt (or) $ chmod ugo+rwx file.txt Give execute privilege to user.
This is not a problem since the permissions of symbolic links are never used. In this quick tutorial, we will see how we can use chmod command in an Ubuntu machine to find, modify and remove user permissions from specific files which exist on the user’s file system. Use the chown and chmod commands to secure file access on your system.
(umask u=rwx,g=rwx,o=rwx && mkdir -p a/b/c) Note that this won't change the permissions if any of a, b and c. Find /opt/lampp/htdocs -type d -exec chmod 755 {} \;. Linux File Permission :.
Others can read only". So, when the whole thing is executed output of pwd will replace its position and serve as the argument to chmod, and the result is that all your present working directory get the permission 777 which I guess should never be used in production environment. Chmod 777 $(pwd) pwd command gives the current working directory.
# chmod -R 777 / Once after running the chmod everything will have rwx. You should totally avoid it. Linux Permissions are a great set of rules which.
To change permission using the Linux chmod command we have to follow some syntax and rules. If you want to just add execute privilege to users and leave all other privileges as it is, do the following. In the previous section, you used the chmod command to change file permissions relative to their current settings.
777 means that anyone can do anything with those files. Root@web04 ~# ls -lthr / total 16K drwxrwxrwx. Mkdir -m 777 -p a/b/c since that will only set permission 777 on the last directory, c;.
Possession is Nine-Tenths of the Law. Chmod Command in Linux Linux File Permission Introduction to Linux File Permission. Additionally, each of these modes can be applied to the user, the group, or others.
You can get output after assigning permission to any files/directories by using Linux chmod command with argument -v. Group members and other users can read and execute, but cannot write. Chown can also change the ownership of a file to match the user/group of an existing reference file.
(O)thers can read, can write and can execute. CHMOD and CHOWN. Leave other privileges untouched.
2 root root 6 Apr 11 18 opt drwxrwxrwx. Unix/Linux chmod command examples to Change File Permissions. Second solution is to generate list of all files with find command and supply this list to the chmod command (as suggested by @lamgesh).
A and b will be created with the default permission from your umask. The chown command stands for “change owner” is used to change the owner. Basically, it allows or disallows modifications of the file.
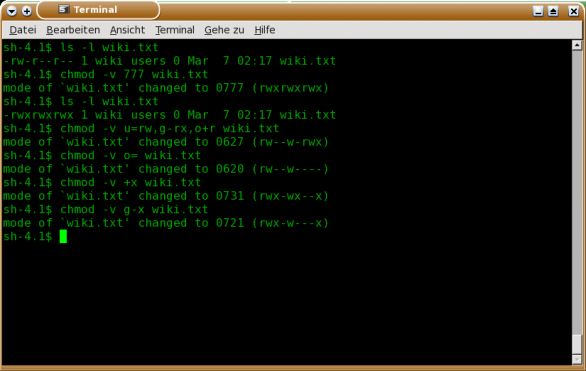
User can read, write, and execute;. Read, write and execute:. $ chmod -v 777 file.txt mode of 'file.txt' changed from 0664 (rw-rw-r--) to 0777 (rwxrwxrwx).
Below, we are talking about the chmod commands in Linux:. $ chmod 777 sample.txt. A Computer Science portal for geeks.
Chmod 777 filename chmod 777 is considered potentially dangerous because you are giving read, write and execute permission on a file/directory to everyone (who is on your system). Chmod -R 755 myfiles. If you need to test this guide run these commands on your own risk in a test server.
Chmod 775 / path / to / file Hopefully, this article can help you understand better about the file permissions in Unix system and the origin of the magical number “777”. The chmod command can be used with octals (as. We will explain the modes in more detail later in this article.
The first digit is for user permissions, second is for group and third is for others permission. R &ndash Read (value is 4). The chmod and chown commands are powerful and most popular command line tool that can be used to control access to files in Linux-based operating systems.
It contains well written, well thought and well explained computer science and programming articles, quizzes and practice/competitive programming/company interview Questions. Denotes the access given to the users. Sudo chown 1001:1001 at.c.
The chmod command works on Linux, macOS, WSL, and anywhere you have a UNIX environment. The syntax for this usage of the chmod command is:. Chmod 755 $(find /path/to/base/dir -type d).
Read, write, and execute. Examples chmod 644 file.htm. The chmod command allows you to change the permissions on a file using either a symbolic or numeric mode or a reference file.
It’s a same as using your mouse to right-click a file or folder and selecting the permission tabs and. Understanding the Linux systems helps make your system secure by restricting access to your files. You should never set 777 (rwxrwxrwx) permissions files and directories permissions.
More of a permission mechanism though. (O)thers can read, can write and can execute. In simple language, you can change the permissions of files and directories in Linux using chmod command.
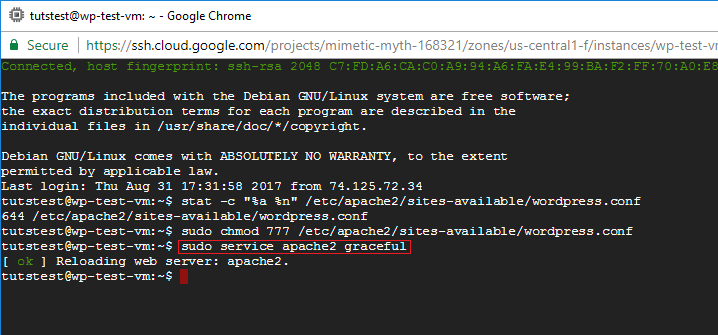
Chmod 777 access to a file Posted 08-02-17 12:15 PM (9361 views) | In reply to Tal The surest way is to set it after the file has been written, either with the x statement, or the filename pipe method. Be extra careful when using chmod, especially when recursively changing the permissions. Only the object owner, superuser or root account can change the permissions of a file/folder.
A chmod command first appeared in AT&T Unix version 1. The syntax for the chmod command is:. Either it is a directory or a file.
Instead to create any new directories with permission 777, run mkdir -p in a subshell where you override the umask:. It works on *.MP3 but it does not work on *.mp3 root@lxp-cheung New Folder chmod command on linux. Chmod Linux Command & Examples.
We use them in pairs of 3, to set the permissions of all the 3 groups altogether:. If you want to change the mode to 777, you can use the command like this:. Conclusion # If you are managing a Linux system, it is crucial to know how the Linux permissions work.
In Linux, you will often need to make use of the chmod command. Chmod The chmod command changes the access mode of one file or multiple files. Command for change the file permission in Linux – Chmod 775 syntax.
Recursively (-R) Change the permissions of the directory myfiles, and all folders and files it contains, to mode 755:. 2 root root 6 Apr 11 18 srv drwxrwxrwx. The first 7 sets the permissions for the user, the second 7 sets the permissions for the group, and the third 7 sets the permissions for everybody else.
This tutorial explains CHMOD and CHOWN commands that are broadly used in Linux. $ chmod 777 sample.sh. Chmod is the command used to change the permissions of an object, and is short for “CHange MODe”.
But in Linux, ownership is a massive part of file security, with file permissions providing the remainder of it. Chmod g-w mydir chmod o-w mydir chmod g+x mydir chmod o+x mydir. Chown - To change owner, change the user and/or group ownership of each given File to a new Owner.
2 root root 6 Apr 11 18 mnt drwxrwxrwx. Linux Tutorial for Beginners && Git Tutorial for Beginners. The name is an abbreviation of change mode.
U - User g - Group o - Others. The command CHMOD stands for change mode, and this is used to change the permission of a File or Directory.The Command CHOWN stands for Change Owner and this is used to change the ownership of a File or Directory. I was looking for some sites where I can find a comprehensive explanation with few examples.
Let’s play through various conditions so that we can master basic chmod commands which can make our everyday life easier with Ubuntu. Chmod go-w+x mydir This denies group members and others the permission to create or delete files in mydir (go-w) and allows group members and others to search mydir or use it in a path name (go+x). Chmod 777 is one of those file control mechanisms.
Group can read only;. -c--changes Verbosely describe the action for each File whose ownership actually changes. First one is find the file and apply chmod as it finds (as suggested by @WombleGoneBad).
40 Best Examples of Find Command in Linux. As systems grew in number and types of users, access control lists were added to many file systems in addition to these most basic modes to increase flexibility. In the above example, you can see that the permissions are specified with a three digit number.
Chmod 4777 Chmod 4777 (chmod a+rwx,ug+s,+t,g-s,-t) sets permissions so that, (U)ser / owner can read, can write and can execute.(G)roup can read, can write and can execute. In Unix-like operating systems, the chmod command is used to change the access mode of a file. However, for each symbolic link listed on the command line, chmod changes the permissions of the pointed-to file.
Denotes the access given to the group. Chmod stands for “ Change Mode ” and is used to modify the permissions of files and directories in a Linux based system. This $() is used for executing a command mostly inside some other command.
Representations used for Ownerships. The chmod command is used to define or change permissioins or modes on files and limit access to only those who are allowed access… It changes the mode of each FILE to MODE…. Or so they say.
$ chmod 444 sample.txt Allow everyone to read, write, and execute file. Hi, I am trying to execute 'chmod 777 *.mp3', but I get an invalid option. Chmod 777 filename chmod 755 filename chmod 644 filename.
You can also set the permissions for a file or directory absolutely by using numeric codes with the chmod command. In this example, numcode is the numeric code and name is the. Hope the article helps you to understand the concept of permissions in a Linux system and the meaning of “777” & “775”.
The chmod also called change mode that is used to change permissions of a given file according to a certain mode. The chmod system call cannot change their permissions. 7 can read, write and execute.
Refer the command below. Chmod option mode files Options. Control who can access files, search directories, and run scripts using the Linux’s chmod command.
This is equivalent to the command sequence:. Chmod 777 Chmod 777 (chmod a+rwx) sets permissions so that, (U)ser / owner can read, can write and can execute. If you want to check chmod command version then you need to use chmod --version command as shown below.
This command will set the user and the group ownership to mary. The command can accept one or more files and/or directories separated by space as arguments. There are two methods by which we can change the permissions:.
Chmod command means change mode. $ chmod 0 sample.txt Write by anyone $ chmod 002 sample.txt Execute by owner only $ chmod 100 sample.txt Execute by group only $ chmod 010 sample.txt Execute by anyone $ chmod 001 sample.txt Allow read permission to owner and group and anyone. They are list of letters that specifies whom to give permissions.

Chmod Calculator Chmod Generator Chmod Command

Basic Linux Commands Gooribi Inc
How To Fix Ftp Permission Errors On Google Cloud One Page Zen

Linux Hacker Chmod 777 Command Active T Shirt By Clubtee Redbubble

How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux

Linux Command Line Basics Part 4 I Have A Pc I Have A Pc
Why Would Using Chmod 777 Recursively From The Root Cause A Linux Box To Not Boot I Could Understand This If I Were Limiting Permissions But Why Would Adding Permissions Cause This

Chmod Ftp File Permissions Stadtaus Com

Ownership And Permissions
Chmod Shortcuts For Linux
Linux Commands Most Important Linux Commands Edureka

14 04 Chmod Not Working In A Non Super User Ask Ubuntu

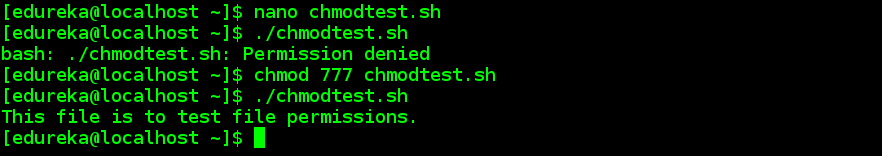
Executable How To Execute A Sh File Ask Ubuntu

Chmod Wikipedia

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks
/GettyImages-1021092796-ea8c63ee76f84bd5bf98c4222337fbb4.jpg)
How To Use The Chmod Command In Linux

Recover From Chmod 777 Permission On A Root Filesystem

777 Chmod Unix File

Linux Common Commands Tutorial And Use Examples Linuxcommands Site
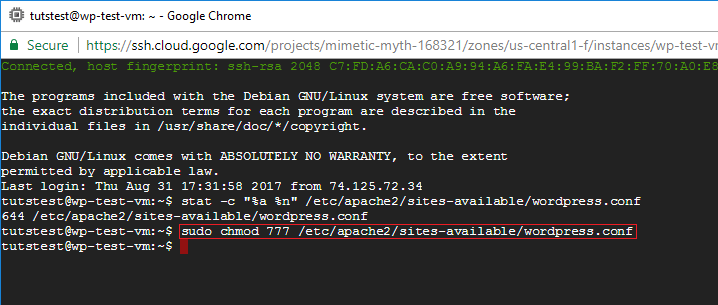
How To Fix Ftp Permission Errors On Google Cloud One Page Zen

Linux Chmod Example Linux Hint

Lock Your Private Folder In Ubuntu The Digi Life

16 04 How Do I Use Chmod To Make Sh Files Executable Ask Ubuntu
1

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials

Basic Linux Commands That Every User Should Know Techbrackets

Basic Linux Commands Linuxmasterrace

The Basics Of The Chmod Command Pi My Life Up

How To Give Read Write Permissions To A Folder In Ubuntu Code Example
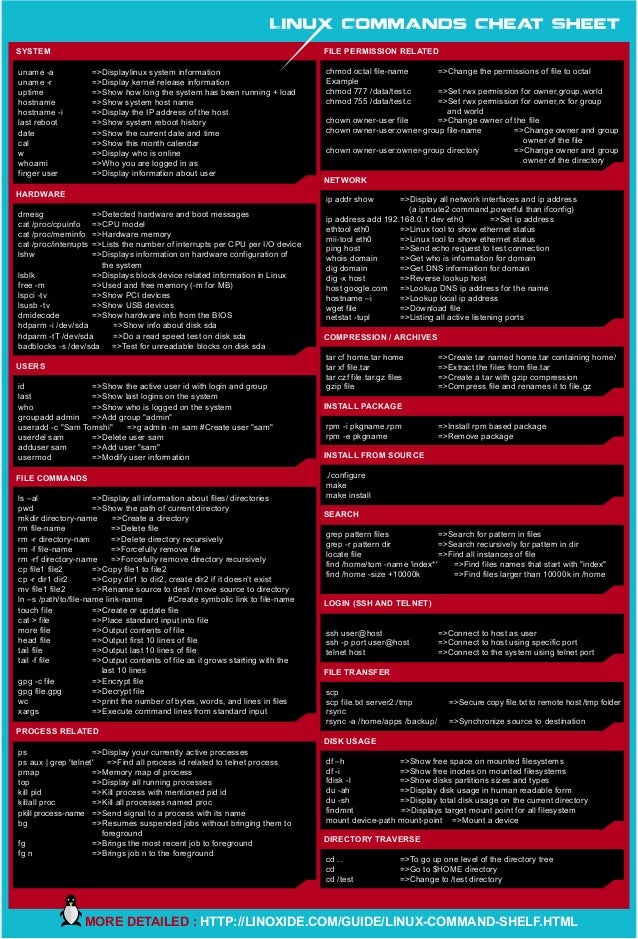
Linux Cheat Sheet

Chmod 777 Comic Dzone Security

How To Use Chmod 777 Command In Linux File Permissions How To Use Chmod Command Hindi Tutorial Youtube
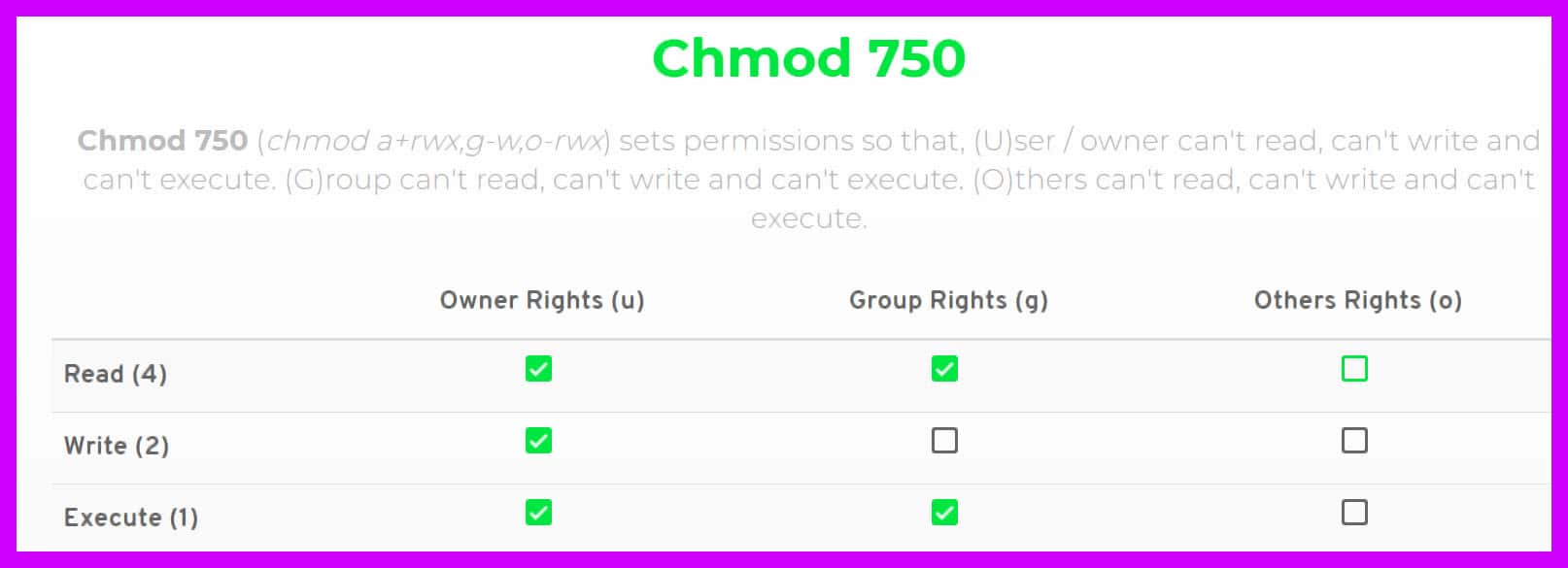
Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions
Chmod 777 Unix Linux Chmod Command Examples 01 12

What Did We Do When We Were Chmod 777 Develop Paper

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials

Linux File Permission Javatpoint

What Does Chmod 777 Mean Ms Tv Life Com

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier
Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions

Chmod 777 Allocating The Least By Amith Jayasekara Medium

Linux Commands 5 File Permission Chmod Youtube
Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions
Recover From Chmod 777 Permission On A Root Filesystem

Linux Command Line Basics Part 4 I Have A Pc I Have A Pc

Chmod Ftp File Permissions Stadtaus Com

Comandos Terminal Chmod 777 775 600 Youtube
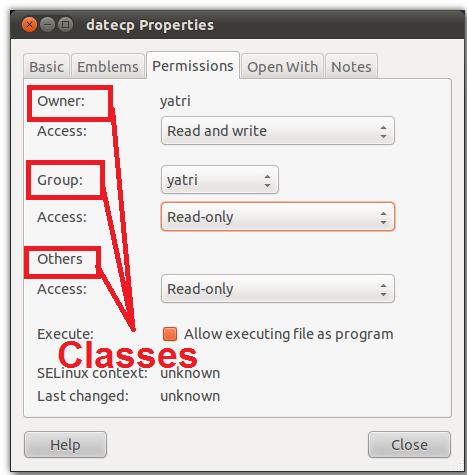
What Is Chmod 777

Chmod 777 Or 755 Learn To Use Chmod Command With Examples

Changing File Permissions Wordpress Org

Linux Chmod Chown Syntax And Chmod Chown Examples

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command In Linux

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials

Chmod 777 Tutorial The Electric Toolbox Blog

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier

Project Ii Six Task Management System Linux File Permissions Programmer Sought
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq1nsq3kxri7ryrifobs2rfobawbv4hezfw9 Ldf4feblahyn09 Usqp Cau

Explained How To Use Chmod Command Complete Guide Youtube

What Is The Difference Between Chmod And Chown Programmer Sought

Chmod Command In Unix Learn Unix Online Fresh2refresh Com

07 Kali Linux Command Line Tutorial File Permission Command Chmod 777 Hindi Urdu Youtube

Bif703 File Permissions Ppt Download
1

Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier

How To Give 777 Permission In All Subfolders In Htdocs Or Any Folder Ubuntu Youtube

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

Ubuntu How Can I Chmod 777 All Subfolders Of Var Www Youtube

Bash Sudo Abc Sh Command Not Found Ask Ubuntu

How Did The Number 777 In Chmod 777 Come Out Under Linux Laptrinhx

Linux Chmod Command Tutorial With Examples To Change Permission Of Files And Folders Poftut

How To Set File Permissions In Mac Os X Macinstruct

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials

How To Set 777 Permissions In Windows 7 Youtube

Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions

What Is Chmod 777

Linux Story Part Ii Prashant

Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected
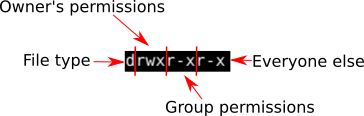
Chmod 777 Or 755 Learn To Use Chmod Command With Examples

Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu

Linux Chmod 777 Archives Ms Tv Life Com

Chmod 777 Shell Scripting Tips

Linux Chmod Chown Syntax And Chmod Chown Examples

Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions
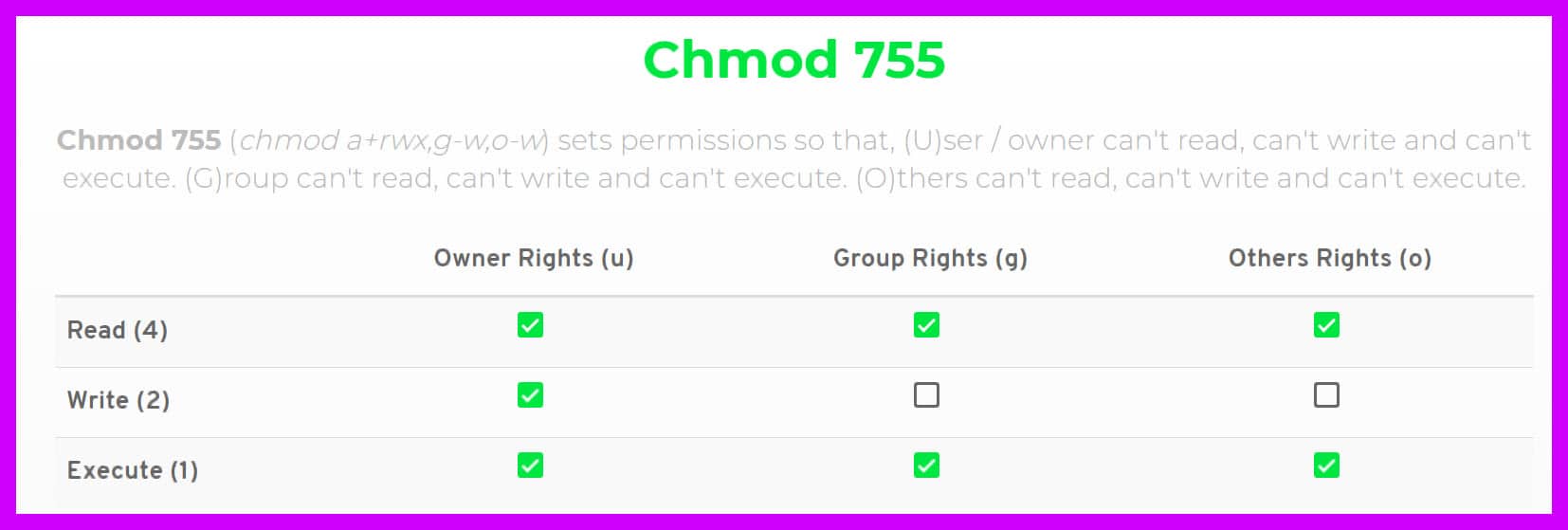
Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions

Devrant A Fun Community For Developers To Connect Over Code Tech Life As A Programmer

Devrant A Fun Community For Developers To Connect Over Code Tech Life As A Programmer

Friendly Arm Mini2440 Setting Up A Nfs Server Alselectro

Sudo Chmod 777 Opt
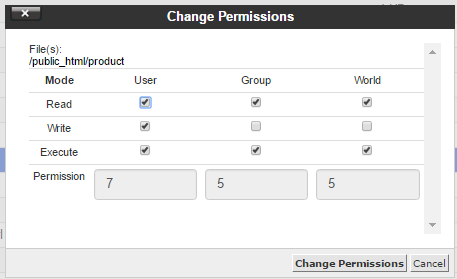
What Is Chmod 777

What Does Chmod 777 Mean In Linux Youtube

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials

Linux File Permissions Know The Reason Behind That Chmod 777 By Abhishek Chandra Medium

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux
Q Tbn 3aand9gcr2lfpzbutqythmvbwafnxvyggqfj7hnw6fhh Kcozkk8m5 V7o Usqp Cau

Linux Hacker Chmod 777 Command Ipad Case Skin By Clubtee Redbubble



