Chmod Examples Linux

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod
.png)
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders

Basics Of Using Chown And Chmod Commands Anto Online
1

Chmod Umask Stat Fileperms And File Permissions
Chmod stands for “Change Mode” and is used to modify the permissions of files and directories in a Linux based system.

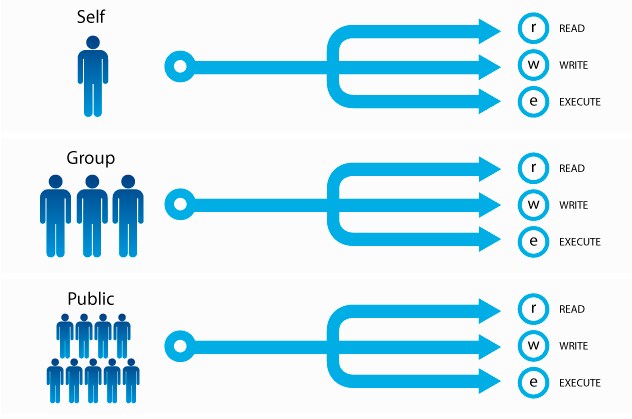
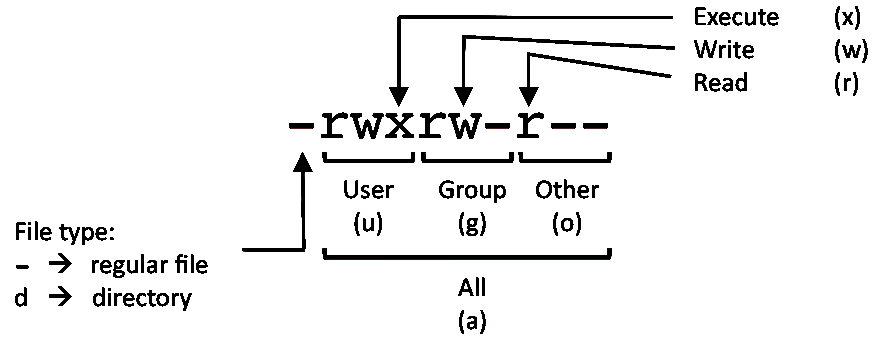
Chmod examples linux. Learn how chmod command is used to manage Linux permission levels (user, group and other) and types (read, write and execute) step by step with practical examples. Changing file permissions with chmod command using octal notation. The letters u, g, and o stand for " user ", " group ", and " other ".
For example, if you want the owner to have all the permissions and no permissions for the group and public, you need to set the permission 700 in absolute mode:. $ sudo chmod OPTIONS numeric_value filename. We've covered almost all its major options/features here.
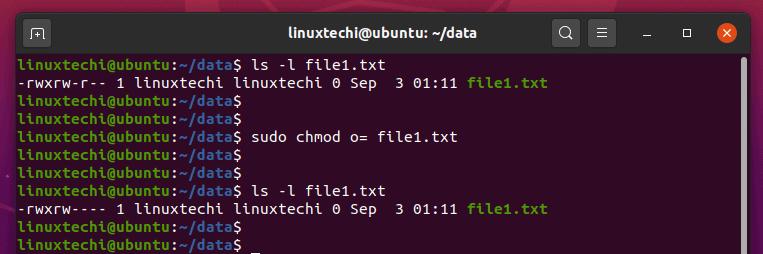
If you want to check chmod command version then you need to use chmod --version command as shown below. For example, to change file permissions of a file file1.txt, to say rw-r--r-- execute:. However, in most cases, 3 numbers are used.
Example chmod 751 tech chmod u=rwx, g=rx, o=x tech chmod =r tech * Please note that there are many flavors of UNIX, so if in doubt, consult your man pages. The symbolic notation using letters and allocation of data rights through digit-based octal codes.As previously mentioned, changes to access rights can only be made by the file owner or root user. We use the chmod command to do this, and eventually to chmod has become an almost acceptable English verb, meaning the changing of the access mode of a file.
Example 1) Assign permissions using numeric notation. Linux ftp linux change file owner linux chmod 777 chmod 755 command change folder owner ubuntu give permission to folder in linux. To have combination of permissions, add required numbers.
$ chmod go+rw sample.txt Make a shell script executable by the user/owner. Chmod -R 755 /var/www/html. This example uses symbolic permissions notation.
For example, for read and execute, it is 4+1=5. The chmod command can be used in a couple of different ways, with permissions (or modes) set by numbers or by letters. Following are the examples of chmod commands in Linux explained in detail.
To change file permissions of a file use the syntax below. The request is filtered by the umask.The name is an abbreviation of change mode. The syntax of chmod command is.
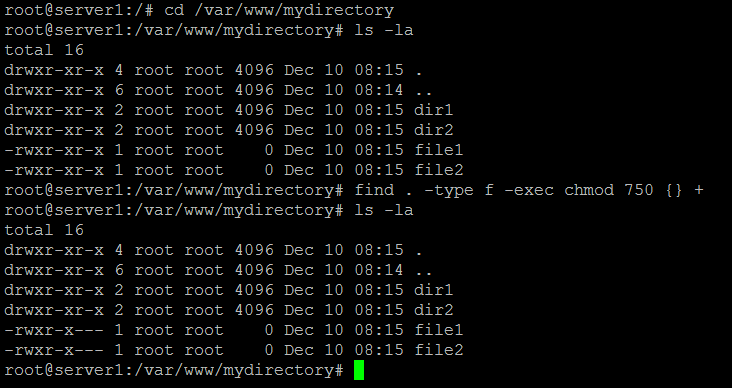
It contains well written, well thought and well explained computer science and programming articles, quizzes and practice/competitive programming/company interview Questions. For example, to change the permissions of all files and subdirectories under the /var/www/html directory to 755 you would use:. Give the members of the group permission to read the file, but not to write and execute it:.
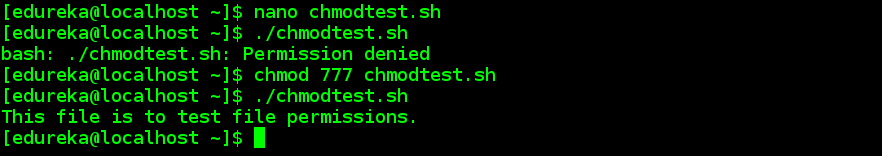
After you have assigned the executable permissions to the script, you can run the script without bash command as shown. We have already described the Linux file permissions. $ chmod a-x sample.txt Allow read permission to everyone.
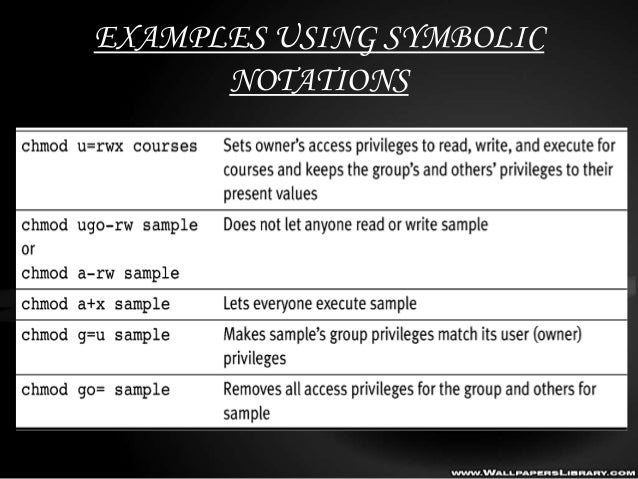
$ chmod a+r sample.txt Make a file readable and writable by the group and others. Chgrp isn't a difficult command to understand and use. The equals sign (" = ") means "set the permissions exactly like this," and the letters " r ", " w ", and " x " stand for "read", "write", and "execute", respectively.
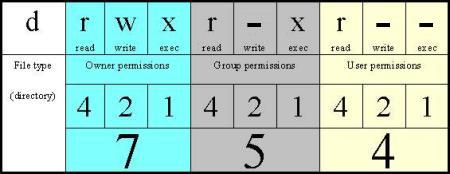
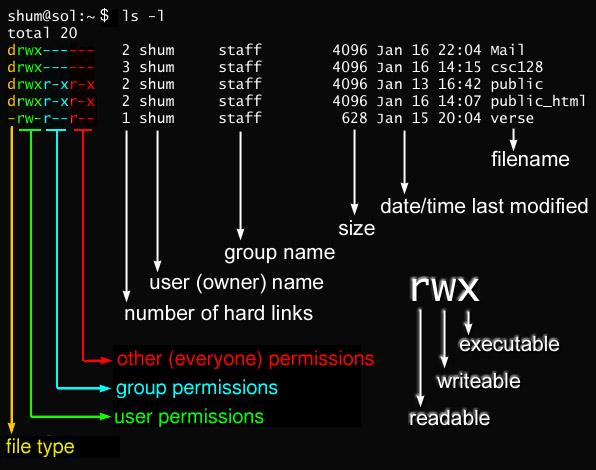
Unix/Linux chmod command examples to Change File Permissions. 3 chmod Examples Give read, write and execute to everybody (user, group, and others) read, write and execute = 4 + 2 + 1 = 7. Last columns of owner, group, others shows individual octal values and actual bit set on file as seen by ls -l.
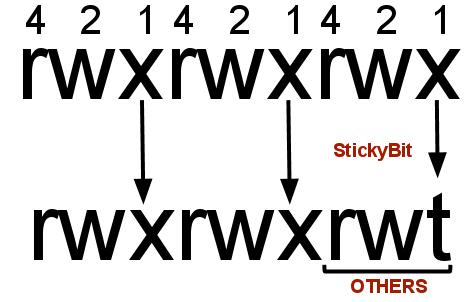
For example, to set the sticky bit, prefix a 1 to the number sequence:. The name is an abbreviation of change mode. Chmod 1755 participants With a sticky bit, only the file owner, the directory owner, or the root superuser can delete the file, regardless of the file's read-and-write group permissions.
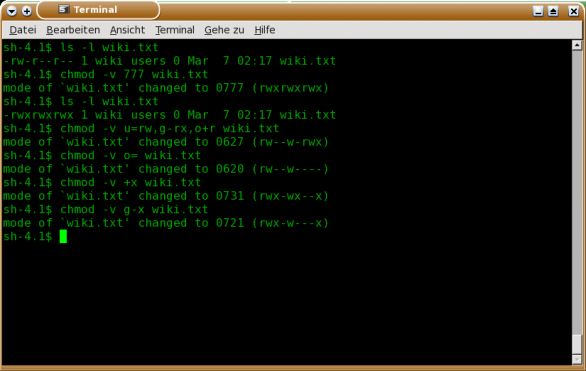
If you look at the permissions on this file now, you’ll see that execute permission has now been added:. 12/08/ 19/06/17 by İsmail Baydan. Add single permission to a file/directory Changing permission to a single set.
Chmod command is used to change access permission of files and directories in Linux operating systems. Remove the execute permission for all users:. Chmod examples using octal mode :.
Chmod a+r file Make a file readable and writable by the group and others:. You can then execute it like this:. $ chmod u+x samplescript.sh.
Using chmod command is very easy if you know what permissions you have to set on a file. 40 Best Examples of Find Command in Linux. Use --no-preserve-root to override this failsafe Linux Permissions Syntax.
Finally, change to create and delete and file acess to read and write and click on button apply. Chmod u=rx file (Give the owner rx permissions, not w) chmod go-rwx file (Deny rwx permission for group, others) chmod g+w file (Give write permission to the group) chmod a+x file1 file2 (Give execute permission to everybody) chmod g+rx,o+x file (OK to combine like this with a comma). Below are some examples of how to run and use the chmod on Ubuntu Linux… If you’re a owner of a file called Confidential and want to change the permisions or modes so that user can read / write and execute, group members can read and execute only and others can only read, you will run the commands below….
Chmod -R permission directory Therefore, to set the 755 permission for all files in the Example directory, you would type:. Examples Using chmod # Below are examples of making changes to permissions:. To use this method you have to remember below Rules and Numbers for proper use.
755 can be separated as. Localhost@user1$ chmod ug+rw,o+r <filename> Example 2:. Like many other Linux commands, chmod has a recursive argument, -R, which allows you to operate on a directory and its contents.
In our previous example, if you want to add execute permission for group owner, you can use chmod command like this:. 4 – To give Read Permission 2 – To give Write Permission 1 – To give Execute Permission. $ chmod u+x hello_script.sh Step 5:.
One example is chmod u=rwx,go=rx,o+t. Examples Deny execute permission to everyone:. Repulsively remove the write permission for other users:.
Go /opt/ then click Properties → Permission. Linux File Permission :. Chmod options mode filename.
To change permission using the Linux chmod command we have to follow some syntax and rules. Deny execute permission to everyone. $ chmod ug=rw /var/www/html/data.php See “how to use change user rights using chomod command” for more information.
Examples of chmod Command in Linux. This type of restriction is useful for effective file/folder management, securing system and providing a level of access to a file/folder for the users who access them. As you can see from below output current chmod version is 8.22.
In this tutorial, we will discuss the basics of this command as well as provide examples explaining how it can be used in various scenarios. To check the options that are available in chmod, we can do by using Linux command:. In this quick tutorial, we will see how we can use chmod command in an Ubuntu machine to find, modify and remove user permissions from specific files which exist on the user’s file system.
By using this command, we can set the read, write, and execute permissions for all three of the permission groups (Owner, Group and Other) in Linux. Make a shell script executable by the user/owner $ chmod u+x myscript.sh. The syntax for changing the file permission recursively is:.
In Terminal go to file manager. File/Directory permission is either Read or Write or executable for either user or group or others. The chmod command in Linux/Unix is abbreviated as CH ange MOD e.
Actually, chmod Command in Linux plays a greater role to keep all the files and directories of the system safe and secure so that no unauthorized person. Read, write, and execute for the user and only read permissions for group and others maps as:. If you are new to Linux, and are looking for a way to change file/directory permissions through the command line, you'll be glad to know there exists a command - dubbed chmod - that lets you easily do this.
Try the examples we've mentioned in this tutorial, and you should be ready to use the command. Chmod u+rw,g+r,o+r Filename Numerical Way :. Linux file permission is a very important aspects in terms of security issues for the system administrator of Linux Operating System.
A Computer Science portal for geeks. Following are some examples:. View (u)ser, (g)roup and (o)thers permissions for chmod 700 (chmod a+rwx,g-rwx,o-rwx) or use free online chmod calculator to modify permissions easily.
Chmod stands for change mode. In general, the system for Unix data rights relies on user classes and individual access rights. We explained the chown and chmod command for Linux and Unix users.
Following are few examples on how to use the symbolic representation on chmod. The numeric value can take 3 or 4 numbers. Below are some examples of how to use the chmod command in symbolic mode:.
This is illustrated in the calculation below. The letter a is a shortcut to assign permissions to all users. Chmod ugo+x myfile - Same as the above command, but specifically specifies user, group and other.
In case of any doubt or query, head to the tool's man page. How to check chmod command version. Chmod command is useful to change permission for Files and folders in Linux/Unix.
When setting permissions using the numeric style/notation, use the syntax shown below:. In such cases, the chmod recursive option (-R or --recursive) sets the permission for a directory (and the files it contains). Chmod +x myfile - Gives everyone execute permission on myfile.
+ symbol means adding permission. Linux Chmod Command Tutorial with Examples To Change Permission of Files and Folders. Sudo chmod -R 755 Example.
Control who can access files, search directories, and run scripts using the Linux’s chmod command. Let’s look at these examples again, but using symbolic representation. 8 Linux chmod command examples to understand it.
Chmod is Linux command used to change file permissions.chmod changes user, group and other read, write and execute permission.chmod 755 is popular use case for chmod .chmod 755 is generally used to make most of the operations without problem because it provides ease for system administrators while running applications. Basic “chmod” Command examples in Linux. Chmod octal value file-name.
$ chmod 777 file.txt (or) $ chmod ugo+rwx file.txt Give execute privilege to user. Permissions can be given to a user who owns the file (u = user), group of said user (g = group), everyone else (o = others) or all users (a). Chmod supports two different systems:.
The command is relatively simple to use and involves using. The mode can also be specified using the symbolic method:. For Example, if you want to give Read & Write permission to User/Owner and Read permission to Group & Others using Alphabetical way then the command would be:.
Chmod u+x myfile - Gives the user execute permission on myfile.;. You can do the same in symbolic mode. Himanshu Arora has been working on Linux since 07.
The chmod command A normal consequence of applying strict file permissions, and sometimes a nuisance, is that access rights will need to be changed for all kinds of reasons. In Unix-like operating systems, the chmod command is used to change the access mode of a file. To make a script executable use +x or u+x, for example :.
This tutorial explains chmod command symbolic notation (r, w, x, a) and octal notation (0, 1, 2, 4) in detail with chmod command arguments and options. # alias chmod='chmod --preserve-root' and also add this to your /etc/bashrc or individual user's .bashrc file for permanent changes. It is dangerous to operate recursively on '/' chmod:.
Let us take an example where a file test_file.txt has full permission to the owner, group and other. This command modifies Linux file permissions, which look complicated at first glance but are actually pretty simple once you know how they work. Chmod has two operating modes:.
Chmod command in Linux with examples Last Updated:. Chmod Command in Linux Linux File Permission Introduction to Linux File Permission. Linux chmod command is used to change access permissions of files and directories.
$ chmod u=rw,g=r,o= birthday.cgi In this file example, sets read and write permissions for user and group:. In Linux, you will often need to make use of the chmod command. Now that you know let’s see how to use chmod command in symbolic mode.
If you want to have a combination of permissions add the required numbers. The Linux command to change permissions on a file or directory is chmod, which we like to read as change file mode. Here in the above, the numbers in the brackets represents the numeric values for the corresponding permissions.
In Unix and Unix-like operating systems, chmod is the command and system call which is used to change the access permissions of file system objects (files and directories).It is also used to change special mode flags. Now if we use chmod, it does not allow to modify root permission # chmod -c --recursive 755 / chmod:. In this article, you will learn how to change permissions of any file or directory with chmod command.
Let’s now delve and see different examples of chmod command. Access permissions specify whether a user account or group can read, write, or execute. Chmod -R o-w dirname.
For example, for read and write permission, it is 4+2 = 6. The command chmod a+rwx is equivalent to chmod ugo+rwx. First column shows the chmod command , second column shows how the value is calculated for the permission.
Several symbolic methods are equivalent;. View (u)ser, (g)roup and (o)thers permissions for chmod 600 (chmod a+rwx,u-x,g-rwx,o-rwx) or use free online chmod calculator to modify permissions easily.

11 Popular Unix Linux Chmod Command Examples To Change File Permissions Cyberithub

Linux Permissions An Introduction To Chmod Enable Sysadmin
Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

Linux Unix Changing Permissions With Chmod Vinish Kapoor S Blog
7 Examples Of Command Chmod On Linux And Explanation
Why Would Using Chmod 777 Recursively From The Root Cause A Linux Box To Not Boot I Could Understand This If I Were Limiting Permissions But Why Would Adding Permissions Cause This

Linux File Permission Change By Chmod Command In Linux Guide For Beginners

9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux

Best Linux Chmod Command With Examples It Smart Tricks

Chmod Cheatsheet Linux

Best Linux Chmod Command With Examples

Chmod Wikipedia

Unix Linux Os X File Permissions

How Did The Number 777 In Chmod 777 Come Out Under Linux Laptrinhx
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq1nsq3kxri7ryrifobs2rfobawbv4hezfw9 Ldf4feblahyn09 Usqp Cau

Linux Chmod Command Help And Examples
Linux File Permissions Octal Mode

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders

How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux
How To Chmod Files Only On Linux

Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected

Linux Chmod Command Tutorial With Examples To Change Permission Of Files And Folders Poftut

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
Filepermissions In Linux
9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

Explained How To Use Chmod Command Complete Guide Youtube

Linux Chmod Command Clearly Explained Codedodle

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

Unix Linux Command Chmod Linux Concept

File Security
What Is A Sticky Bit And How To Set It In Linux The Linux Juggernaut

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

Chmod Command In Unix Learn Unix Online Fresh2refresh Com

Understand Linux File Permissions Using Chmod And Chown Commands Programming Tips For Versatile Coders

Linux And Unix Chmod Command Tutorial And Examples Xsofthost

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices

Solved File Permissions In Linux Can Be Set Using A 3 Dig Chegg Com

Linux Chmod Command Summary With Examples Youtube

Chmod Command Examples In Unix Linux Lpi Central

Linux Chmod Chown Syntax And Chmod Chown Examples
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/i7guGwCYcn-34e068e148ae4e918b29c86cd2d5740e.png)
Configuring Unix Linux File And Directory Access Rights

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials

Unix Permissions
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs9h1s9aymhgxuiwaruv5svj Iw49oju6dx0zyl3syy0y4ft3ya Usqp Cau

What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux Tech Ninja Pro
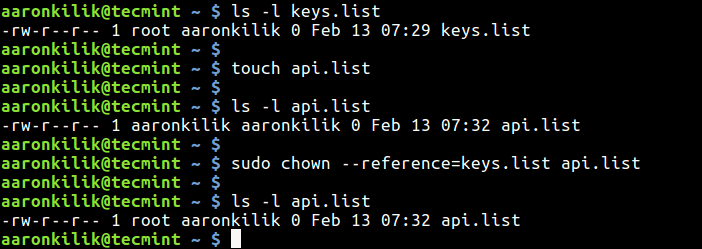
How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux
Linux Chmod Tips

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples
Q Tbn 3aand9gcr2lfpzbutqythmvbwafnxvyggqfj7hnw6fhh Kcozkk8m5 V7o Usqp Cau

Unix Linux Access Permission Bits

Linux Users And Groups Linode

An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

Understanding Basic File Permissions And Ownership In Linux The Geek Diary

Linux Chmod Chown Syntax And Chmod Chown Examples
/GettyImages-1021092796-ea8c63ee76f84bd5bf98c4222337fbb4.jpg)
How To Use The Chmod Command In Linux

8 Linux Chmod Command Examples To Understand It The Linux Juggernaut

Linux Chmod Command Utility Software Computer File

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

Pin By Dr Stefan Gruenwald On Cheatsheets Computer Science Programming Learn Javascript Linux Operating System

How To Use The Chmod Command On Ubuntu 16 04 18 04 With Examples Website For Students

Change File And Folder Permission On Ubuntu Chmod Chown Command In Linux Youtube

Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu

Linux Chmod Example Linux Hint
Linux Commands Most Important Linux Commands Edureka

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

Linux Terminal File Permissions Chmod Chown And Chgrp Youtube

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

Permissions Why Use Chmod Instead Of Chmod U Rw Go R Unix Linux Stack Exchange

Understanding File Permissions What Does Chmod 777 Means Linux Technology Theory Report

Ownership And Permissions

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission
Linux Commands Cheat Sheet Linux Training Academy

Understanding Unix Permissions And File Types Unix Linux Stack Exchange

Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode

A Unix And Linux Permissions Primer Daniel Miessler
Javarevisited 10 Example Of Chmod Command In Unix Linux

Introduction To Linux File Permissions Attributes Chmod Globo Tech

How To Run A Script In Linux Nixcraft

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples
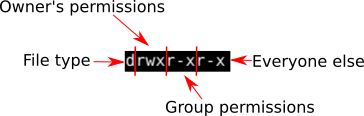
Chmod 777 Or 755 Learn To Use Chmod Command With Examples

Chmod Command In Linux File Permissions Linuxize

Restore Executable Permission To Chmod Command In Linux Ostechnix

How To Chmod Files Only On Linux

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command In Linux
Chmod Shortcuts For Linux

How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials

Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

Chmod Calculator Chmod Generator Chmod Command

Linux File Permission Javatpoint
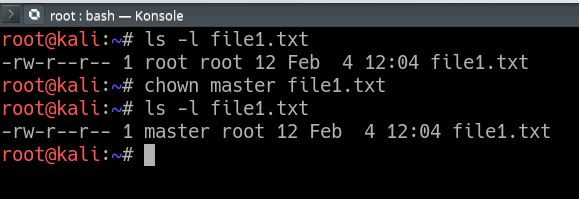
Chown Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

Chmod Options Permissions Files Linux Pocket Guide Book

Linux File Permissions Tutorial For Beginners



