Chmod 777 Command In Linux For Directory

Linux Command Chmod 777 Linux Command Long Sleeve T Shirt Teepublic

Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions
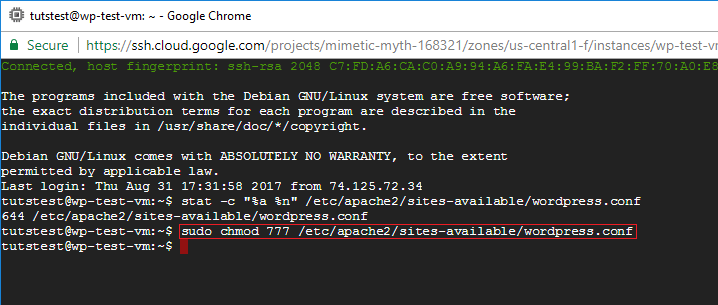
How To Fix Ftp Permission Errors On Google Cloud One Page Zen
What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux Tech Ninja Pro

How Can I Recursively Change The Permissions Of Files And Directories Ask Ubuntu
Why Would Using Chmod 777 Recursively From The Root Cause A Linux Box To Not Boot I Could Understand This If I Were Limiting Permissions But Why Would Adding Permissions Cause This
If you use chmod 777 that means you assigned all the permissions i.e.
Chmod 777 command in linux for directory. If you specify both the -h flag and the -R flag, the chmod command descends the specified directories recursively, and when a symbolic link is encountered, the mode of the file or directory pointed to by the link is not changed. I fixed most of the things by re-restricting some rights and applying the correct rights. Chmod command is used to change access permission of files and directories in Linux operating systems.chmod stands for change mode.Access permissions specify whether a user account or group can read, write, or execute a given file and directory.
In such cases, the chmod recursive option (-R or --recursive) sets the permission for a directory (and the files it contains). Chmod 775 /path/to/file chmod command uses & Explanation. The chmod command has also been ported to the IBM i operating system.
After that no one could run any command and could not login. Give read, write and execute to everybody (user, group, and others) read, write and execute = 4 + 2 + 1 = 7. How to change file and directory permissions in linux using chmod command.
Give execute privilege to user. Group members and other users can read and execute, but cannot write. By issuing these commands, you can change groups of files and directories in Linux.
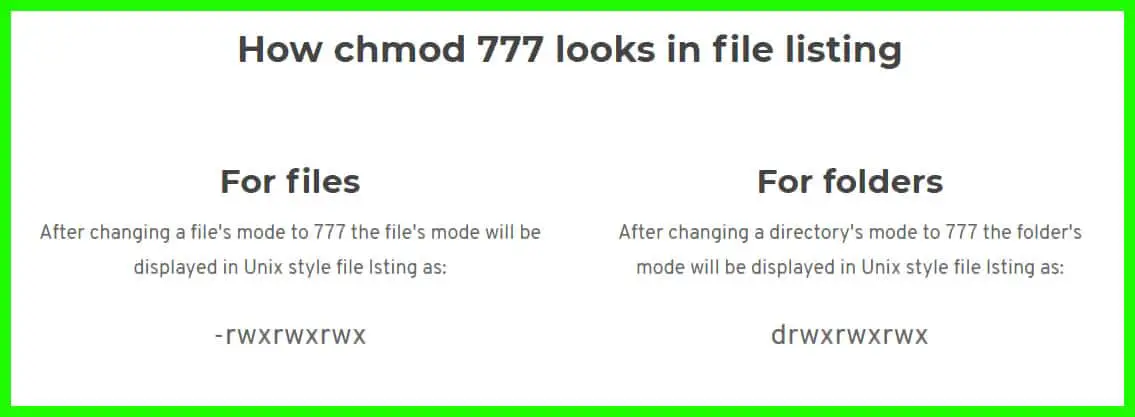
Chmod is the command used to change the permissions of an object, and is short for “CHange MODe”. After changing a directory's mode to 770 the folder's mode will be displayed in Unix style file lsting as:. As you might remember, the default file permission value is 0644, and the default directory’s is 0755.
Simply run the below command:. If you want to change the mode to 777, you can use the command like this:. It is common to use the basic chmod command to change the permission of a single file.
You should totally avoid it. But I want only that user to have R+W rights to that directory, and therefor I can't do chmod 777 to that directory, 'cause there are other users that needs to have only read access to that directory. (G)roup can read, can write and can execute.
It stands for change mode. (O)thers can read, can write and can execute. Permit read, write and execute for members of the file's group.
You can use the find command. Chmod ugo+rwx foldername to give read, write, and execute to everyone. $ chmod OPTIONS MODE filename Only the root user or a regular user with sudo privileges can change file or directory permissions.
The first 7 sets the permissions for the user, the second 7 sets the permissions for the group, and the third 7 sets the permissions for everybody else. Possession is Nine-Tenths of the Law. In Linux operating system everything is a file.
Leave other privileges untouched. The command CHMOD stands for change mode, and this is used to change the permission of a File or Directory.The Command CHOWN stands for Change Owner and this is used to change the ownership of a File or Directory. More of a permission mechanism though.
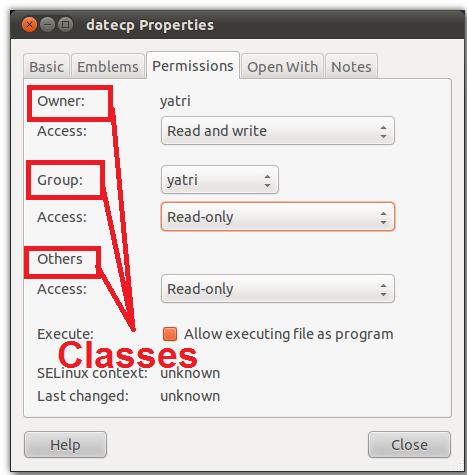
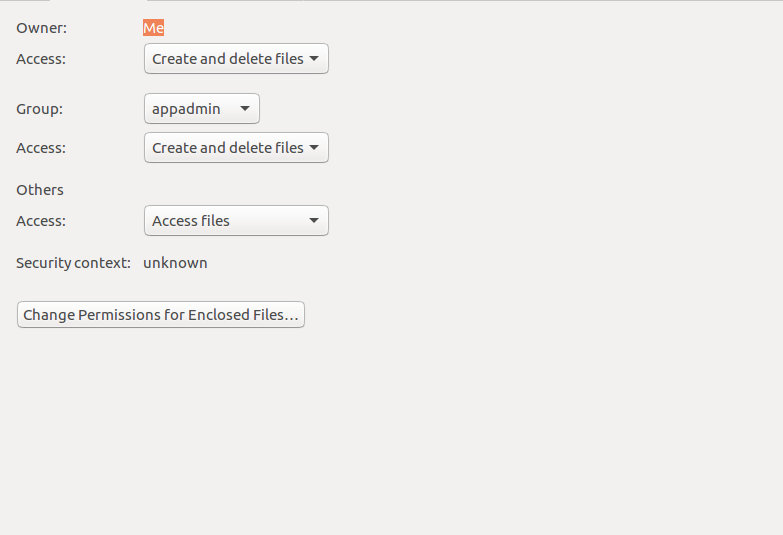
To see what permissions have been set on a file or directory, we can use ls. 777 ) or symbolic notation (e.g. Permit read, write and execute for the file's owner;.
For a directory, the permissions govern who can cd into the directory and who can create, or modify files within the directory. Chmod stands for “ Change Mode ” and is used to modify the permissions of files and directories in a Linux based system. If you ran just chmod 777 * and not the evil chmod -R 777 *, you haven't really done much bad to your system.
However, you may need to modify the permission recursively for all files within a directory. There will be a Permission tab where you can change the file permissions. 9 Comments Originally posted October 13, 14.
In Linux, you can easily change the file permissions by right-clicking the file or folder and select “Properties”. Chmod Linux Command – chmod ใช้ในการเปลี่ยนสิทธิ์ในการอ่าน, เขียน และ execute file หรือ folder แบ่งเป็นสิทธิ์ของ file owner, group owner, other user ซึ่งคำสั่งจะถูกแปลงจากเลขฐาน 8 ในการระบุ. If it is not a file then it’s a process so everything has default permission assigned.
The command that executes such tasks is the chmod command. Conclusion # The chmod command changes the file’s permissions. How to use Check the desired boxes or directly enter a valid numeric value (e.g.
Recursively (-R) Change the permissions of the directory myfiles, and all folders and files it contains, to mode 755:. As all Linux users, you will at some point need to modify the permission settings of a file/directory. Discover chmod and chown for configuring this.
Let us understand CHMOD and CHOWN commands in detail. User can read, write, and execute;. Chmod permission file_name There are two ways to define permission:.
How to Change Groups of Files and Directories in Linux. Chmod -R 755 myfiles. You can set the umask values in /etc/profile or in ~/.bashrc.
Chmod is a command to change permission of a file. Examples chmod 644 file.htm. File permission defines which file has read,write,execute permission and for which user group.
Chmod is a great Linux command for manipulating file and directory permissions. Or so they say. Bash, Shell, Terminal, Command Line cheat sheets linux Ubuntu.
Fortunately, this is a relatively simple operation. But in Linux, ownership is a massive part of file security, with file permissions providing the remainder of it. D rwxrwx--- Popular CHMOD Commands (TOP ) chmod 777.
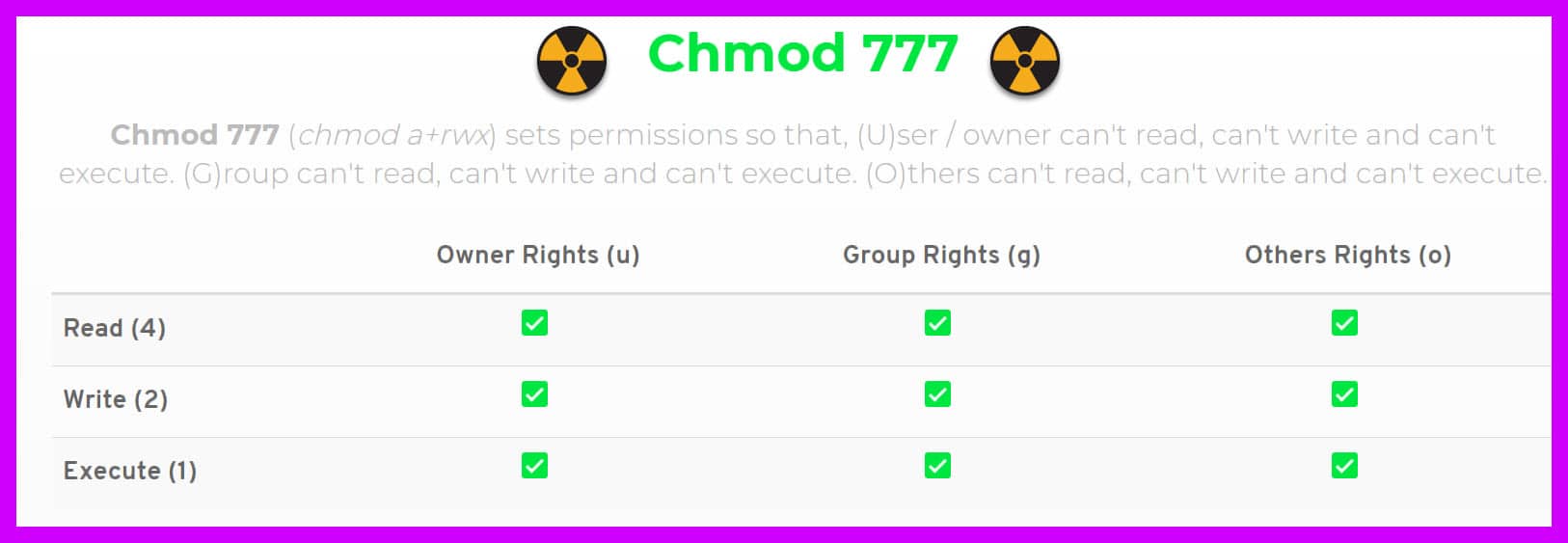
Chmod Calculator is a free utility to calculate the numeric (octal) or symbolic value for a set of file or folder permissions in Linux servers. To make file readable, writable and executable by everyone. Chmod 777 Chmod 777 (chmod a+rwx) sets permissions so that, (U)ser / owner can read, can write and can execute.
In my previous blog post I discussed how Linux file permissions work, and now I am going to discuss how to change permissions using chmod. Set the permissions for a file or directory by using the chmod command. Go into a folder, and run the ls -al command.
Linux file permissions are determined by who owns the file and the visibility of that file to various users. One of our admins here accidently ran chmod -R 777 in the /usr folder on a V440 running Solaris 9. File access permissions can be modified via the chmod command.
Which will chmod all the directories under all the directories under /home/domains/domains1-100 - if you get what I mean. If you specify the -h flag, the chmod command prevents this mode change. This command will set the user and the group ownership to mary.
If you wanted to add or remove permissions to the user, use the command “chmod” with a “+” or “–“, along with the r (read), w (write), x (execute) attribute followed by the name of the directory or file. To change the permissions of the file participants so that everybody has full access to it, enter:. In short, “chmod 777” means making the file readable, writable and executable by everyone.
By using this command, we can set the read, write, and execute permissions for all three of the permission groups (Owner, Group and Other) in Linux. The version of chmod bundled in GNU coreutils was written by David MacKenzie and Jim Meyering. To change permission using the Linux chmod command we have to follow some syntax and rules.
Using symbols (alphanumerical characters) using the octal notation method. Notably, however, every top-level file and directory will need to be restored to their original permissions. The name chmod is short for “change mode”.
In Linux, you will often need to make use of the chmod command. Chmod 755 -R /opt/lampp/htdocs will recursively set the permissions. Chmod 777 a directory only for a user not for all I want to let user x to have all rights (delete, create, append, etc) on a directory / folder.
Now there is a problem with the "su" command. Chmod – adds and removes permissions. Where on a directory, it grants permission to enter it.
Chmod -R 777 / If you ever find yourself thinking of recursively applying mode 777 to any directory, please stop and take a moment to make absolutely sure that's what you want to do.777 is shorthand for:. A chmod command first appeared in AT&T Unix version 1. Every file in the Linux / macOS Operating Systems (and UNIX systems in general) has 3 permissions:.
Setting File Permissions in Command Line. Never Use chmod 777 # Setting 777 permissions to a file or directory means that it will be readable, writable and executable by all users and may pose a huge security risk. Others can read only".
To change all the directories to 755 (drwxr-xr-x):. Sudo chown 1001:1001 at.c. Chmod 777 is one of those file control mechanisms.
The basic syntax is:. Chmod -R 755 will set this as permissions to all files and folders in the tree. In the terminal, the command to use to change file permission is chmod.
The chmod also called change mode that is used to change permissions of a given file according to a certain mode. The syntax for changing the file permission recursively is:. As systems grew in number and types of users, access control lists were added to many file systems in addition to these most basic modes to increase flexibility.
$ chmod 777 file.txt (or) $ chmod ugo+rwx file.txt. The find command will search for files and directories under /var/www/my_website and pass each found file and directory to the chmod command to set the permissions. Chmod a=r foldername to give only read permission for everyone.
The permissions can be set using either the symbolic or numeric mode. The following screenshot shows the execution of the command on a Linux Environment. The Linux command to change permissions on a file or directory is chmod, which we like to read as change file mode.
Chmod has two operating modes:. Use the chown and chmod commands to secure file access on your system. The command executed here is chmod 777 -R home and it gives 777 permission to the folder home itself, also to all of the files and sub-directories inside this folder.
Each row has 2 examples, one for setting that permission for a file, and one for a directory named ‘dir’. Set the permissions of file.htm to "owner can read and write;. The chmod and chown commands are powerful and most popular command line tool that can be used to control access to files in Linux-based operating systems.
The weird strings you see on each file line, like drwxr-xr-x, define the permissions of the file or folder. The other way is terminal , where you can change the permission via Chmod. Chmod is a command used to change those file permissions and controls in terminals.
The chmod command can be used with octals (as. Group can read only;. You use the chmod command to set each of these permissions.
The format of the command is chmod XXX -R directory-location. Linux Tutorial for Beginners && Git Tutorial for Beginners. There's no way to set the permissions for files automatically in only this directory that are created after you set the permissions, but you could change your system-wide default file permissions with by setting umask 022.
Chmod 777 filename chmod 777 is considered potentially dangerous because you are giving read, write and execute permission on a file/directory to everyone (who is on your system). If there are no other directories, other than the ones you wish to operate the chmod command on, in /home/domains you can issue this command:. The chown command stands for “change owner” is used to change the owner.
Rwxrwxrwx ) to see its value in other formats. It takes the following syntax:. Understanding the Linux systems helps make your system secure by restricting access to your files.
Basically, it allows or disallows modifications of the file. Only the object owner, superuser or root account can change the permissions of a file/folder.

What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux Tech Ninja Pro

How To Set 777 Permissions In Windows 7 Youtube
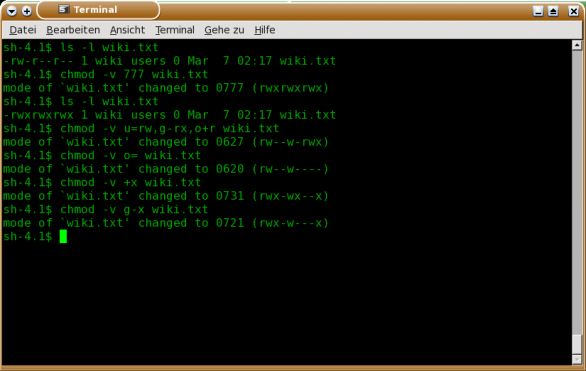
Chmod Shortcuts For Linux

Linux Chmod Example Linux Hint

Recover From Chmod 777 Permission On A Root Filesystem

Permissions Dear Devs Chmod R 777 Is Not The Right Way To Fix Your Application Permissions Issues Yours Truly Sys Ad Devrant

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
Linux Chmod Tips

Understanding File Permissions What Does Chmod 777 Means Linux Technology Theory Report

Xampp Htdocs Permission Issue And Fix In Ubuntu
/GettyImages-1021092796-ea8c63ee76f84bd5bf98c4222337fbb4.jpg)
How To Use The Chmod Command In Linux

Chmod How To Set File And Directory Permission In Linux Using Chmod Youtube
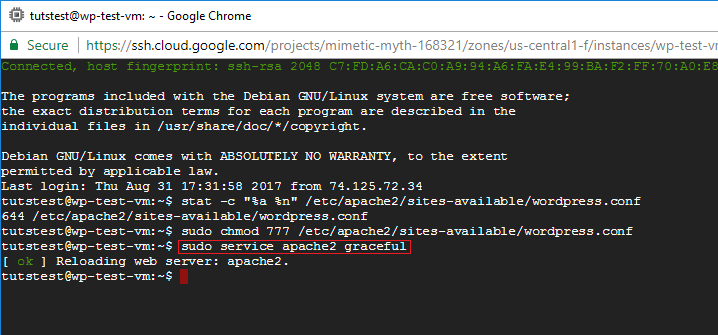
How To Fix Ftp Permission Errors On Google Cloud One Page Zen
How To Share A Directory On A Linux Host On A Private Network With Another Linux Host On The Same Network Stfc Cloud Docs 1 0 Documentation

Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier

Chmod 777 To A Folder And All Contents By Michelle Stanley Medium

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier

How To Give Read Write Permissions To A Folder In Ubuntu Code Example

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials

Course 102 Lecture 14 Users And Permissions

What Does Chmod 777 Mean Linuxize

What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux Tech Ninja Pro

Linux Commands 5 File Permission Chmod Youtube

16 04 How Do I Use Chmod To Make Sh Files Executable Ask Ubuntu

Chmod 0400 Means
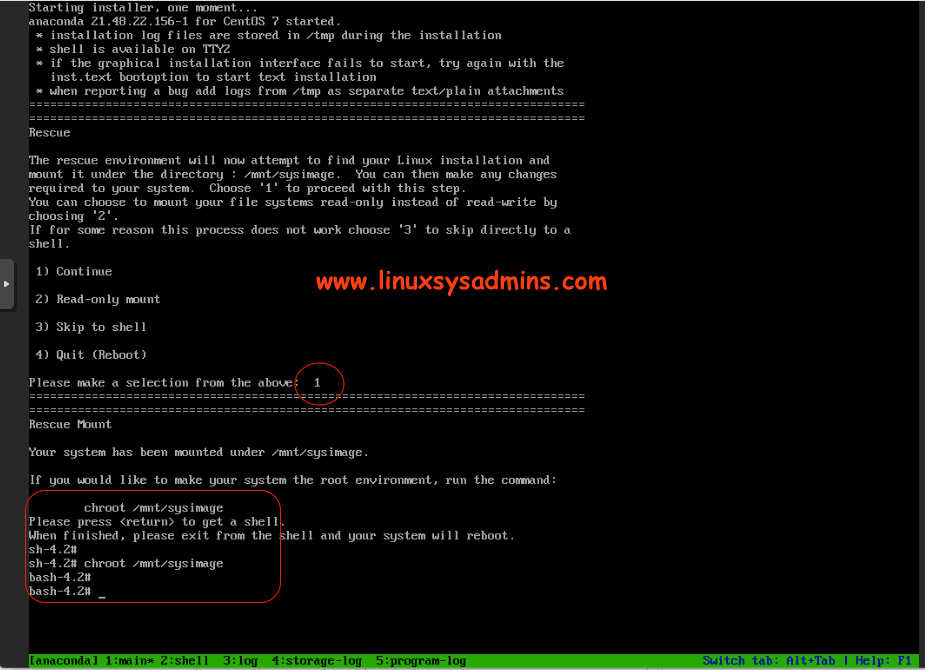
Recover From Chmod 777 Permission On A Root Filesystem

Executable How To Execute A Sh File Ask Ubuntu
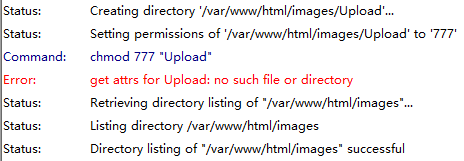
Chmod Problem In Filezilla 3 46 2 Filezilla Forums
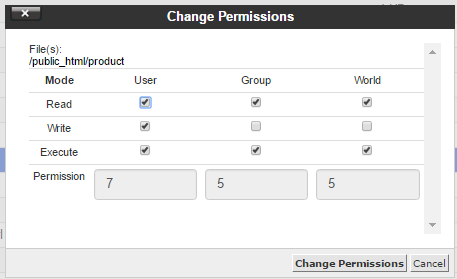
What Is Chmod 777
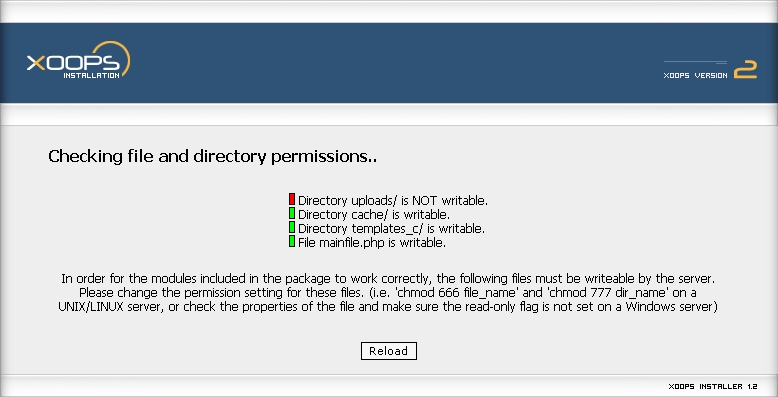
Chapter 3 Folder Permissions

Changing File Permissions Wordpress Org

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
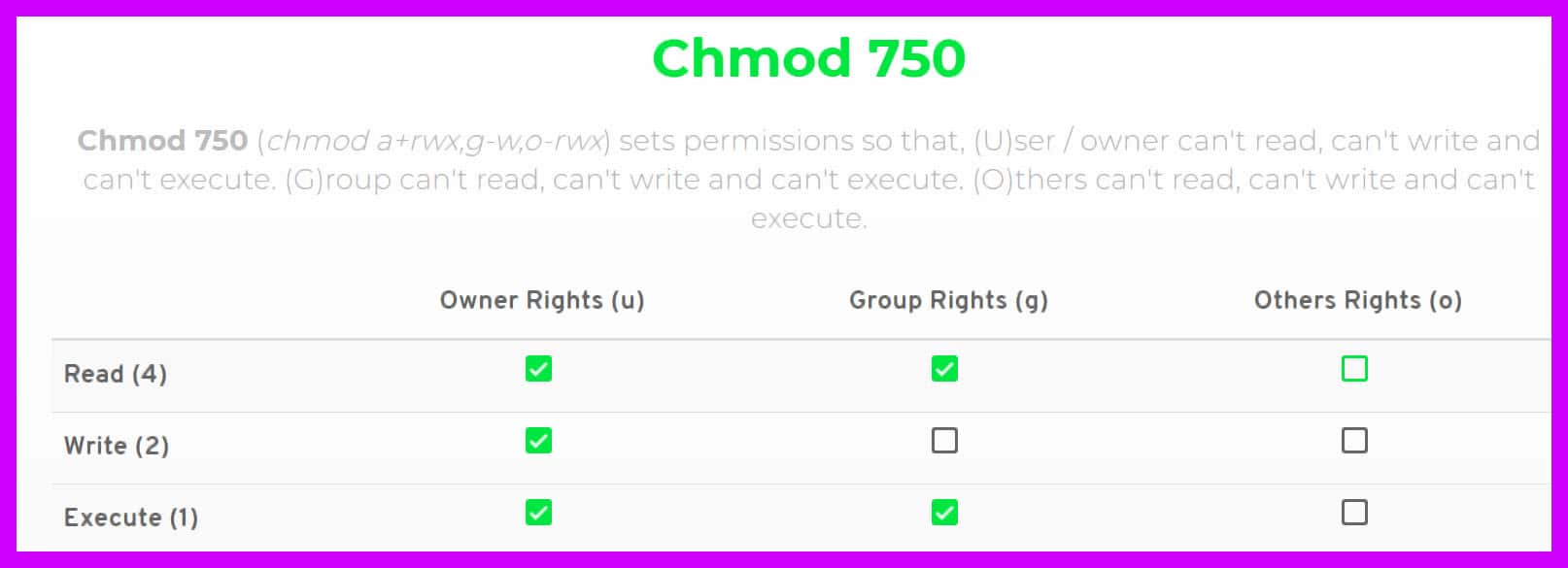
Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions
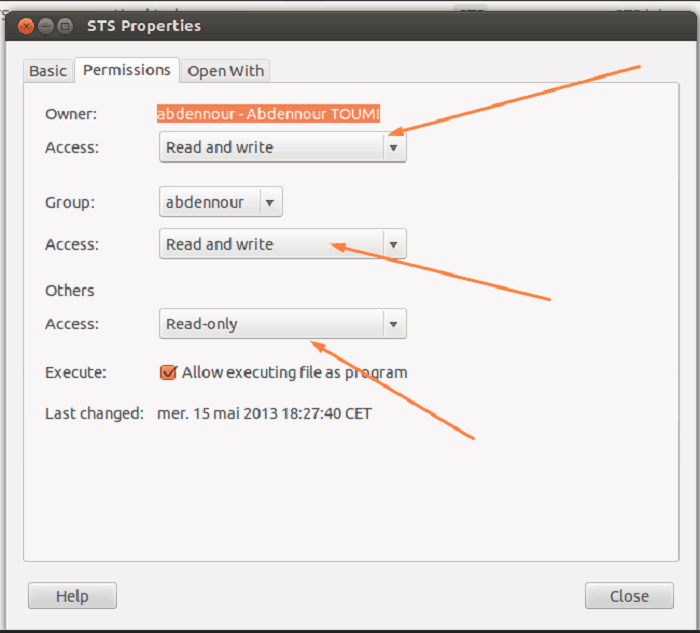
What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux Tech Ninja Pro

Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs Trmaopb41lzfo2wl Mi6olorurkywaddbudhnw Ne1mor3ct Usqp Cau
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs J72hjomdluhqe6xjivy M6yrjmkqx9x3z3ps Rpnb8by3w7z Usqp Cau
Q Tbn 3aand9gct I9jvgnhaxowmpzpaajfkfizchmnvqt Bi Nz3ljrxwqpkb8l Usqp Cau

Fix Ls Colors For Directories With 777 Permission Unix Linux Stack Exchange

Devrant A Fun Community For Developers To Connect Over Code Tech Life As A Programmer

Linux Terminal File Permissions Chmod Chown And Chgrp Youtube

Bash Sudo Abc Sh Command Not Found Ask Ubuntu

Chmod 777 Tutorial The Electric Toolbox Blog

Ubuntu How Can I Chmod 777 All Subfolders Of Var Www Youtube
Cifs And Chmod 777 Ixsystems Community

What Is Chmod 777
Recover From Chmod 777 Permission On A Root Filesystem

What Did We Do When We Were Chmod 777 Develop Paper

14 04 Chmod Not Working In A Non Super User Ask Ubuntu

Linux Chmod 777 Archives Ms Tv Life Com

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials

Chmod And Chown For Wordpress

Linux Command Chmod 777 Linux Command Pin Teepublic

Friendly Arm Mini2440 Setting Up A Nfs Server Alselectro

Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

Linux Command Chmod 777 Linux Command Phone Case Teepublic

Linux Chapter 3 Permission Management Commands Change File Permissions Chmod 777 Root A Programmer Sought

Project Ii Six Task Management System Linux File Permissions Programmer Sought

Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode

Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions
What Is Chmod 777

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

Comandos Terminal Chmod 777 775 600 Youtube
Chmod 777 What Does This Mean Learn Linux Permissions Easy Way

How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux

Linux Command Line Basics Part 4 I Have A Pc I Have A Pc

Linux Command Chmod 777 Linux Command Sticker Teepublic

Chmod Cheatsheet Linux
Chmod Chown Wsl Improvements Windows Command Line
Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions
/i7guGwCYcn-34e068e148ae4e918b29c86cd2d5740e.png)
Configuring Unix Linux File And Directory Access Rights

Lock Your Private Folder In Ubuntu The Digi Life
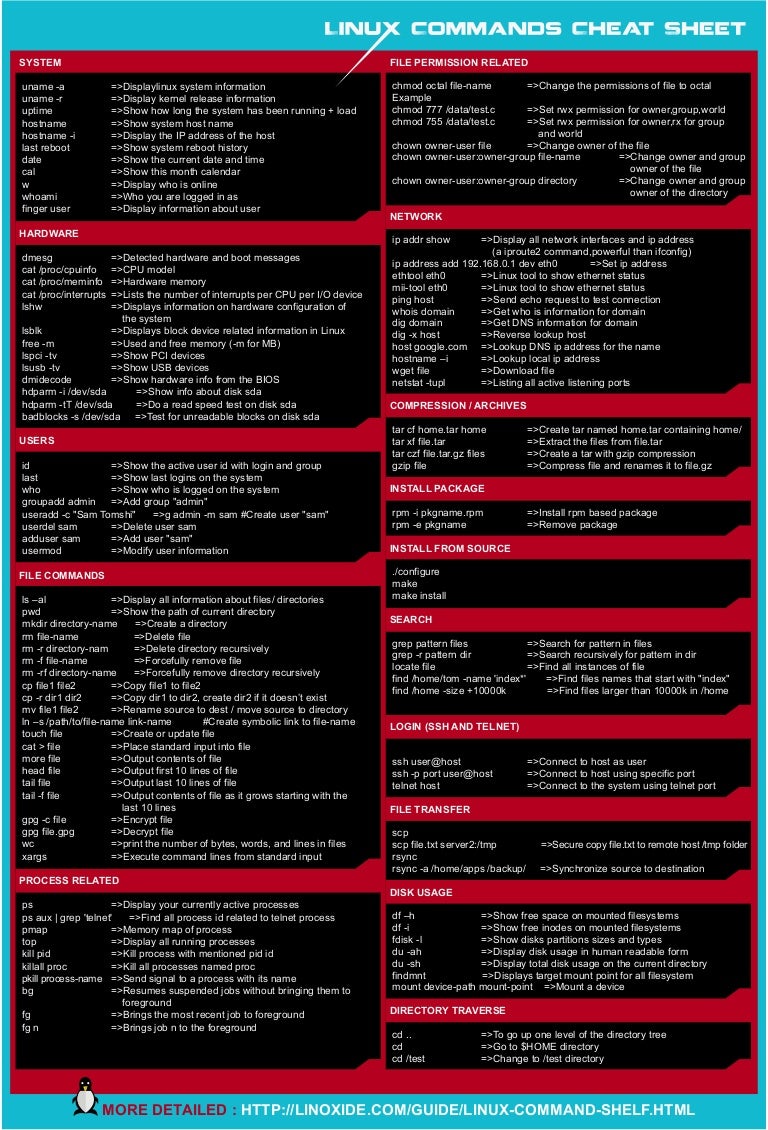
Linux Cheat Sheet

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux
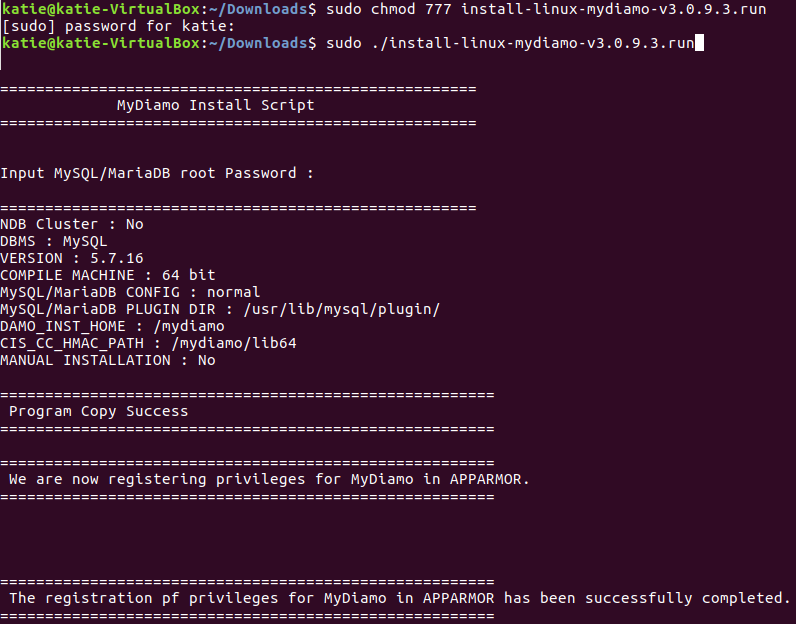
Mydiamo Guide Installation On Linux

How To Use Linux Find Command To Locate Files Computingforgeeks

How To Set File Permissions In Mac Os X Macinstruct

How Did The Number 777 In Chmod 777 Come Out Under Linux Laptrinhx
How To Easily Back Up And Restore Linux File Permissions Linux Com

Linux Command Line Basics Part 4 I Have A Pc I Have A Pc

Chmod Calculator Chmod Generator Chmod Command

Ownership And Permissions

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials
Q Tbn 3aand9gcqylo Axq4l Wudkigbim4eyyuri1sgeprxwkotr9pe74bpl6ic Usqp Cau

Chmod Wikipedia
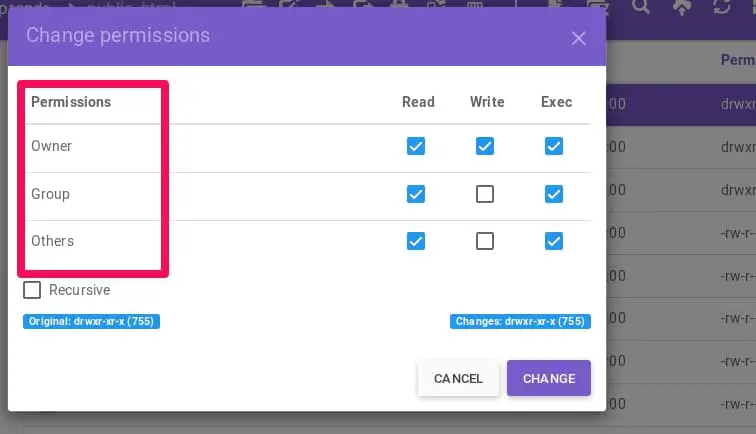
Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions
Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials

Change File And Folder Permission On Ubuntu Chmod Chown Command In Linux Youtube

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier

How To Give 777 Permission In All Subfolders In Htdocs Or Any Folder Ubuntu Youtube

What Does Chmod 777 Mean Ms Tv Life Com

Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu

Linux File Permissions Know The Reason Behind That Chmod 777 By Abhishek Chandra Medium

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command In Linux

How To Set A File To This Drwxrwsrwx Permission On Ubuntu Stack Overflow

Bif703 File Permissions Ppt Download



